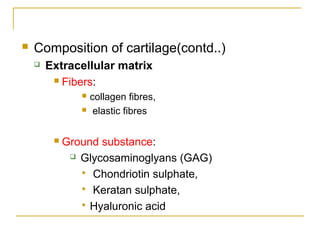
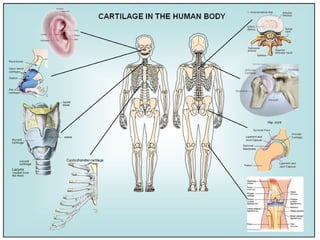
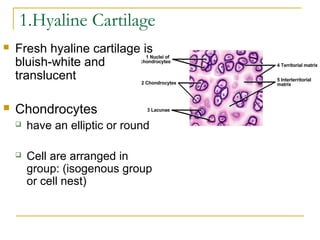
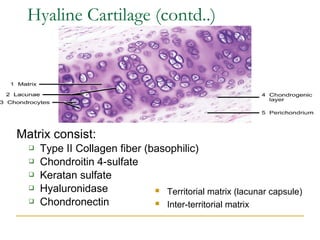
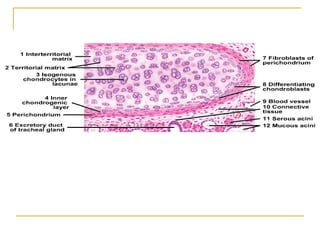
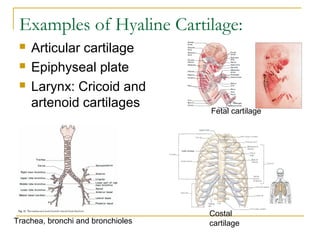
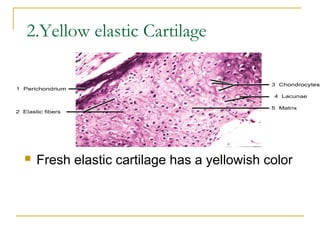
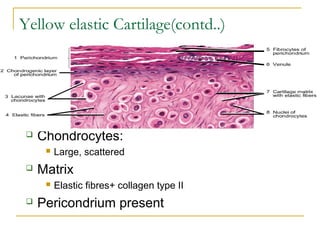
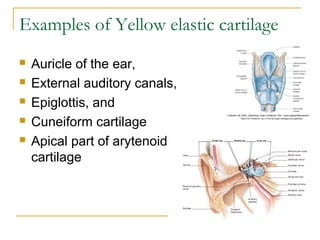
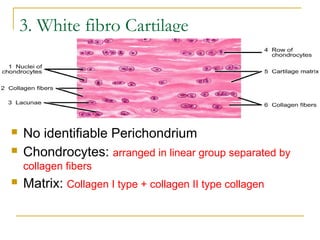
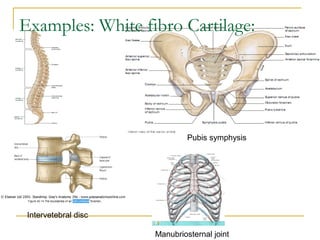
Cartilage is a specialized connective tissue composed of chondrocytes embedded in an extracellular matrix. It is avascular and provides structure, support, and acts as a shock absorber. There are three main types of cartilage - hyaline cartilage found in joints, elastic cartilage in the ear, and fibrocartilage in intervertebral discs. Hyaline cartilage contains collagen type II and glycosaminoglycans that allow it to withstand compression. Elastic cartilage contains elastic fibers that give it flexibility. Fibrocartilage contains collagen types I and II and connects bones together.