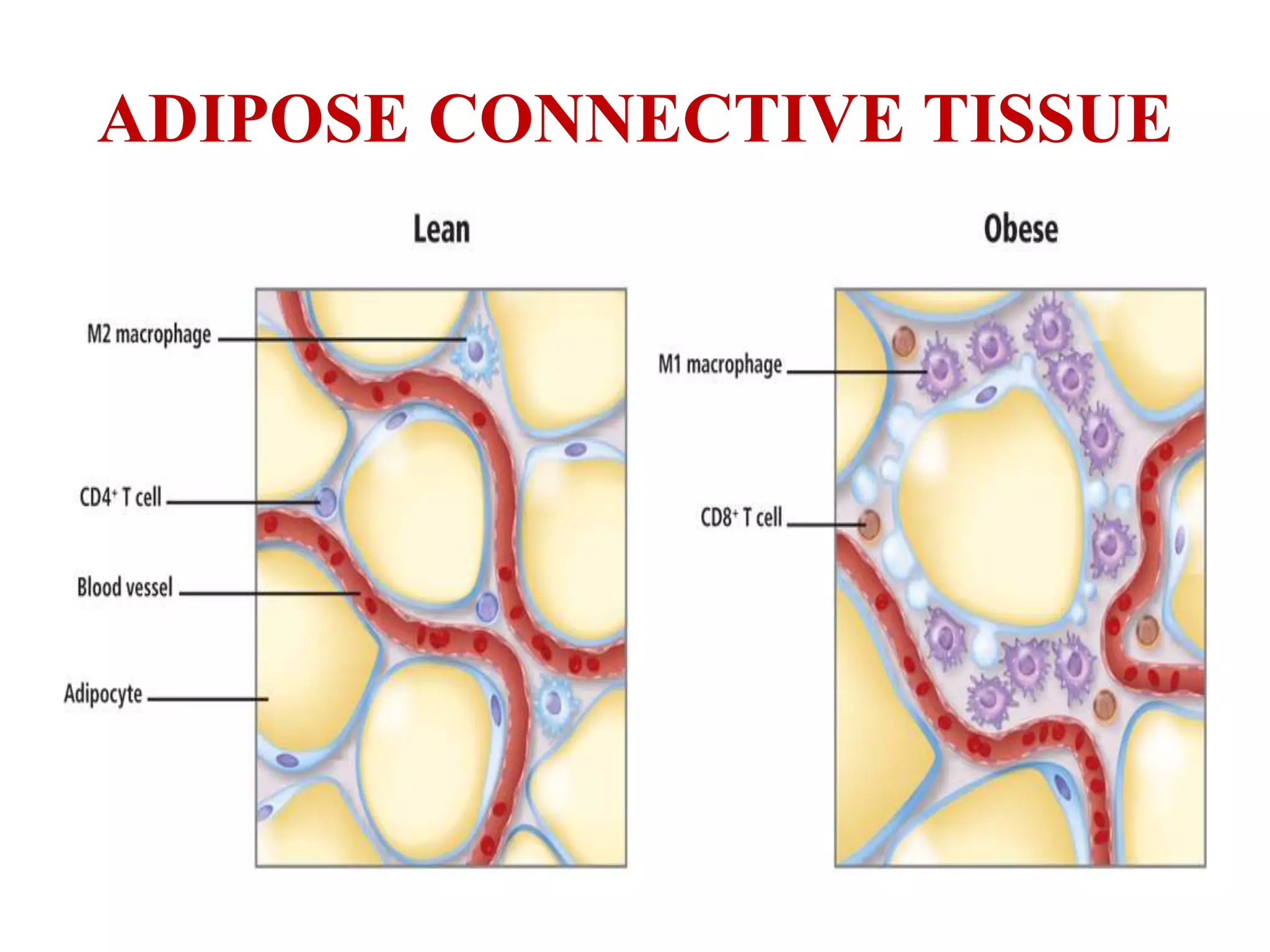
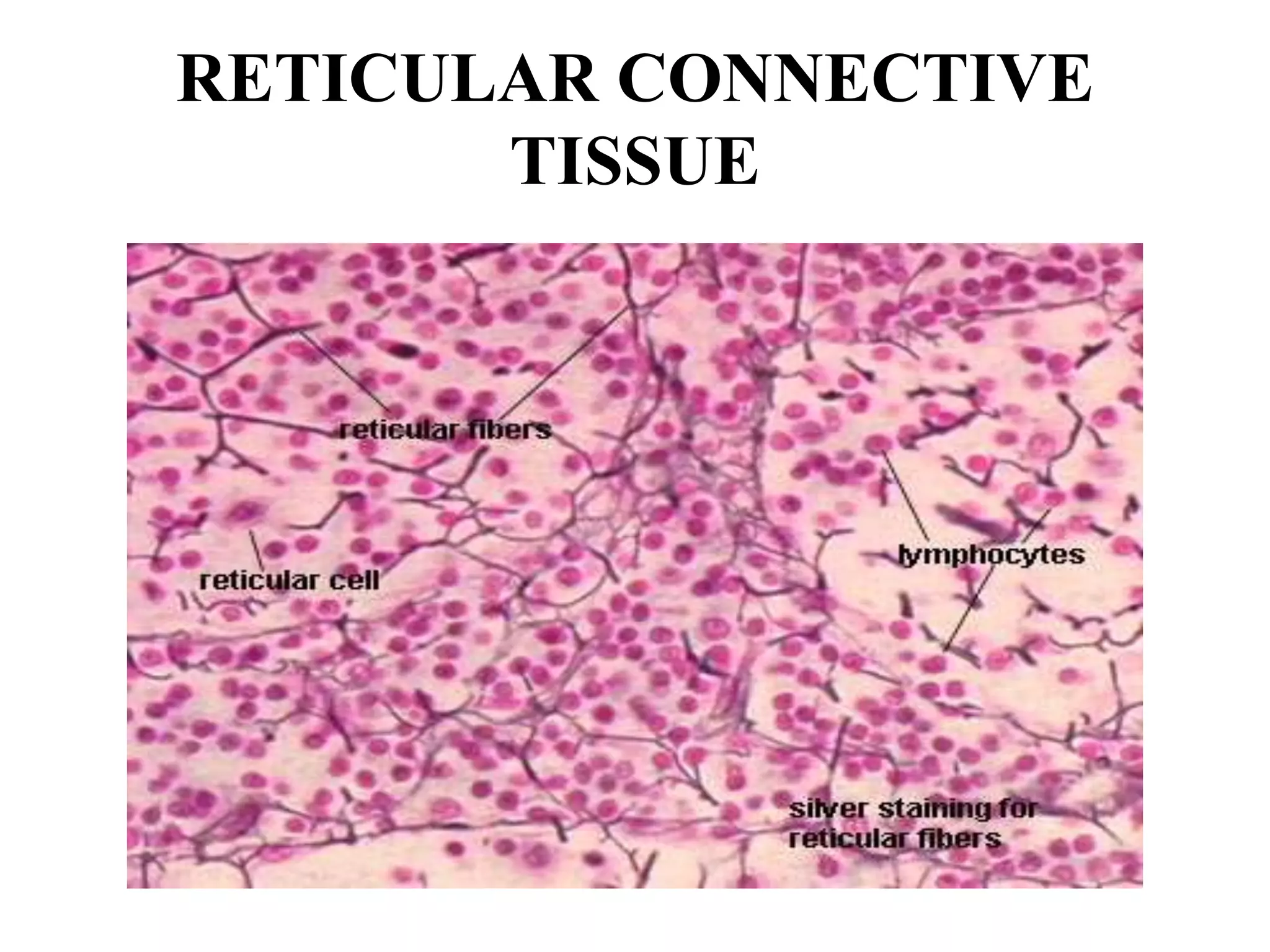
Connective tissue connects and supports other tissues in the body. It has several functions including mechanical support, transport of nutrients and waste, energy storage, and defense. Connective tissue is composed of collagen, elastic, and reticular fibers. It can be classified as loose connective tissue including areolar and adipose tissue, dense connective tissue including regular and irregular tissue, cartilage including hyaline, fibro, and elastic cartilage, bone tissue, and liquid connective tissue including blood and lymph. Loose connective tissue forms a network and fills spaces between organs, dense connective tissue has densely packed fibers, and cartilage and bone provide structure and support.