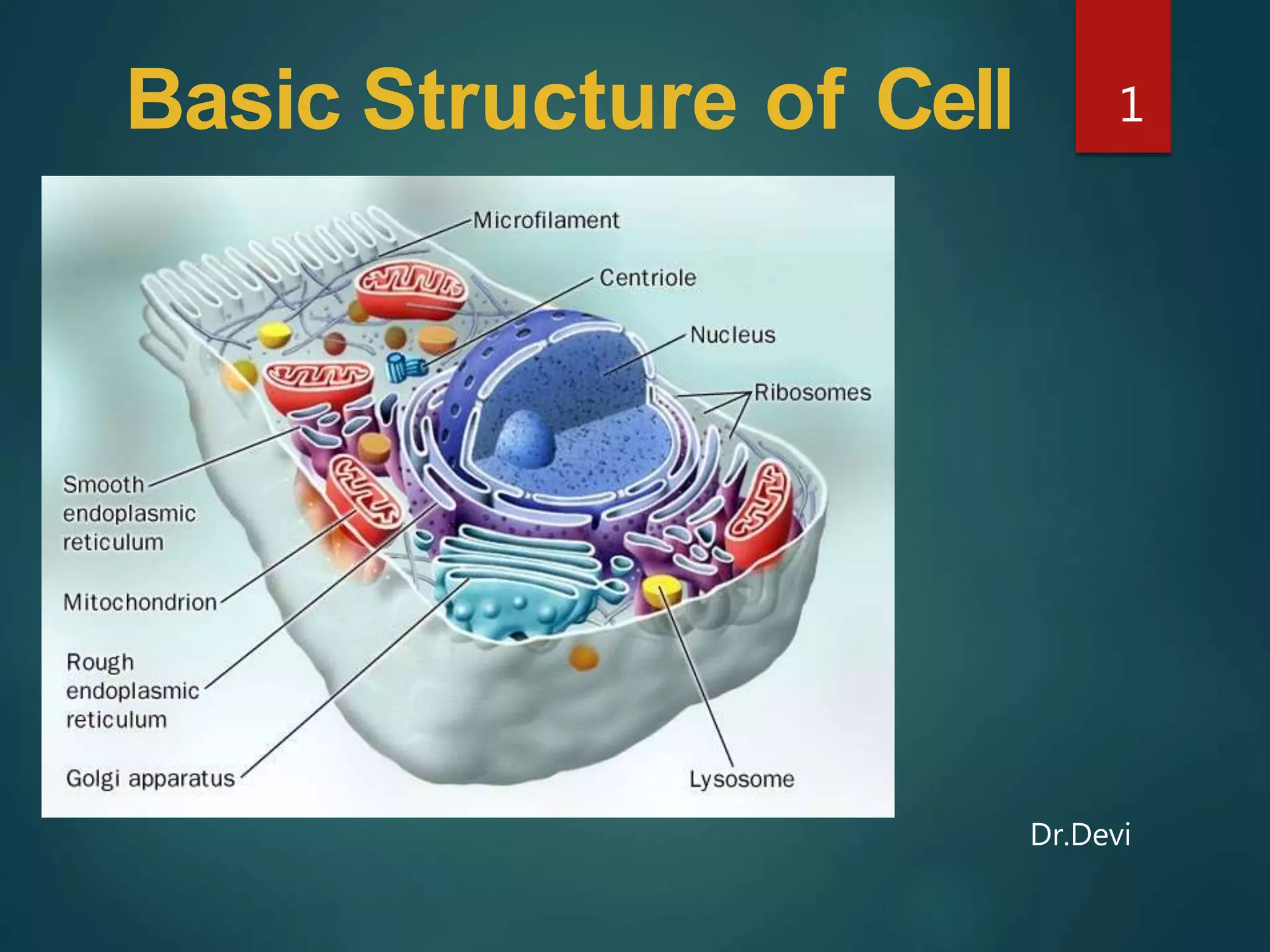
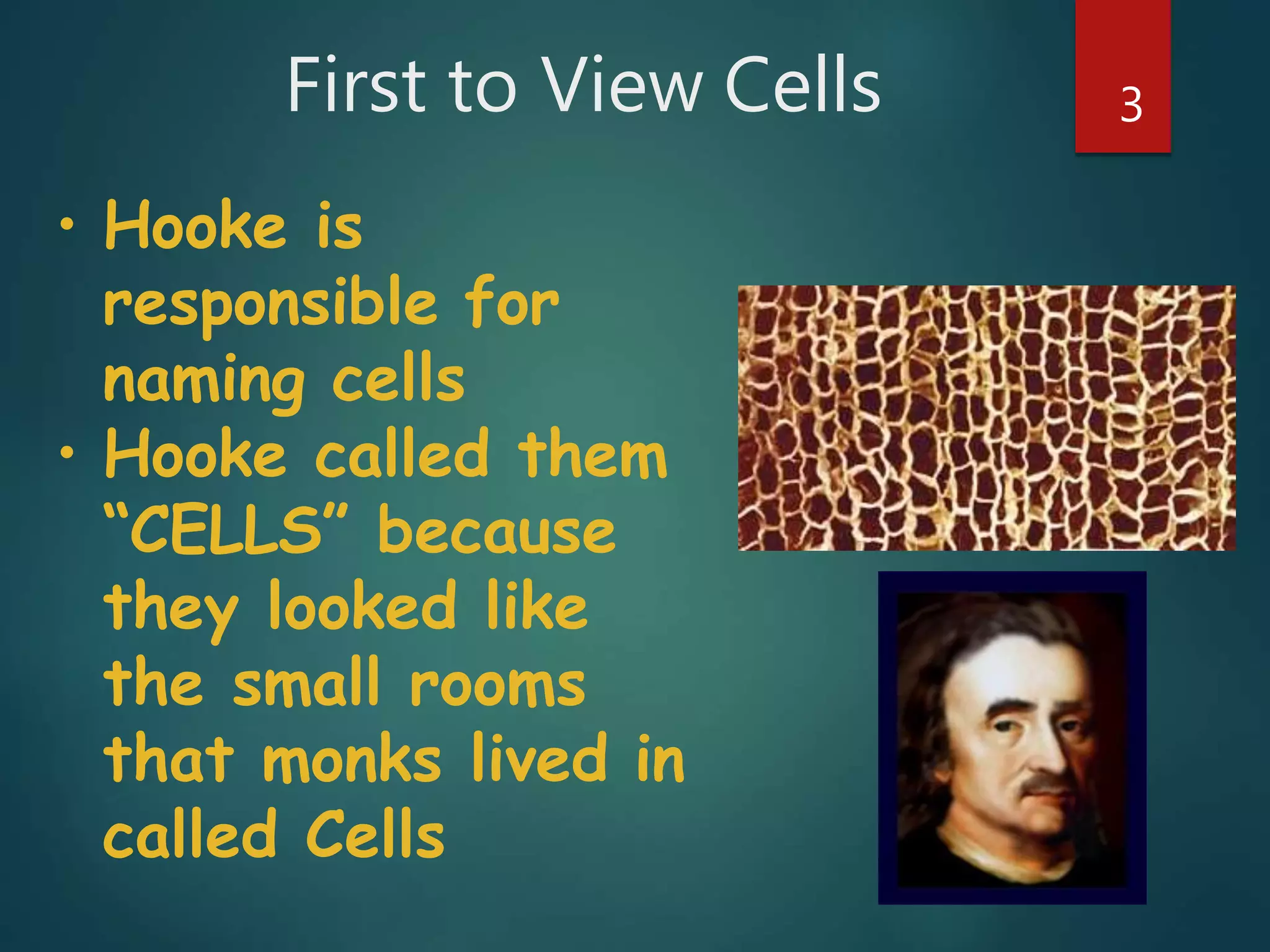
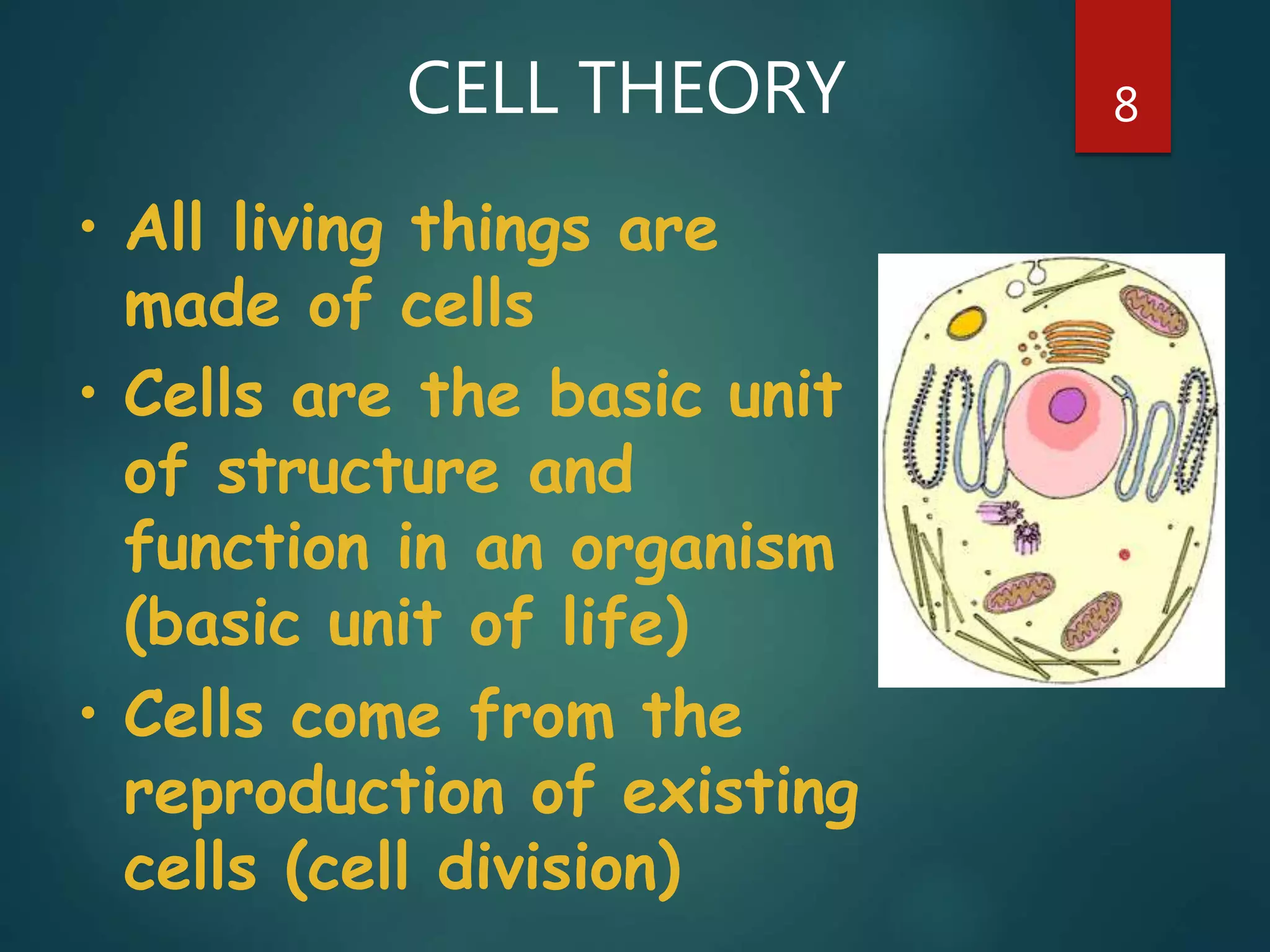
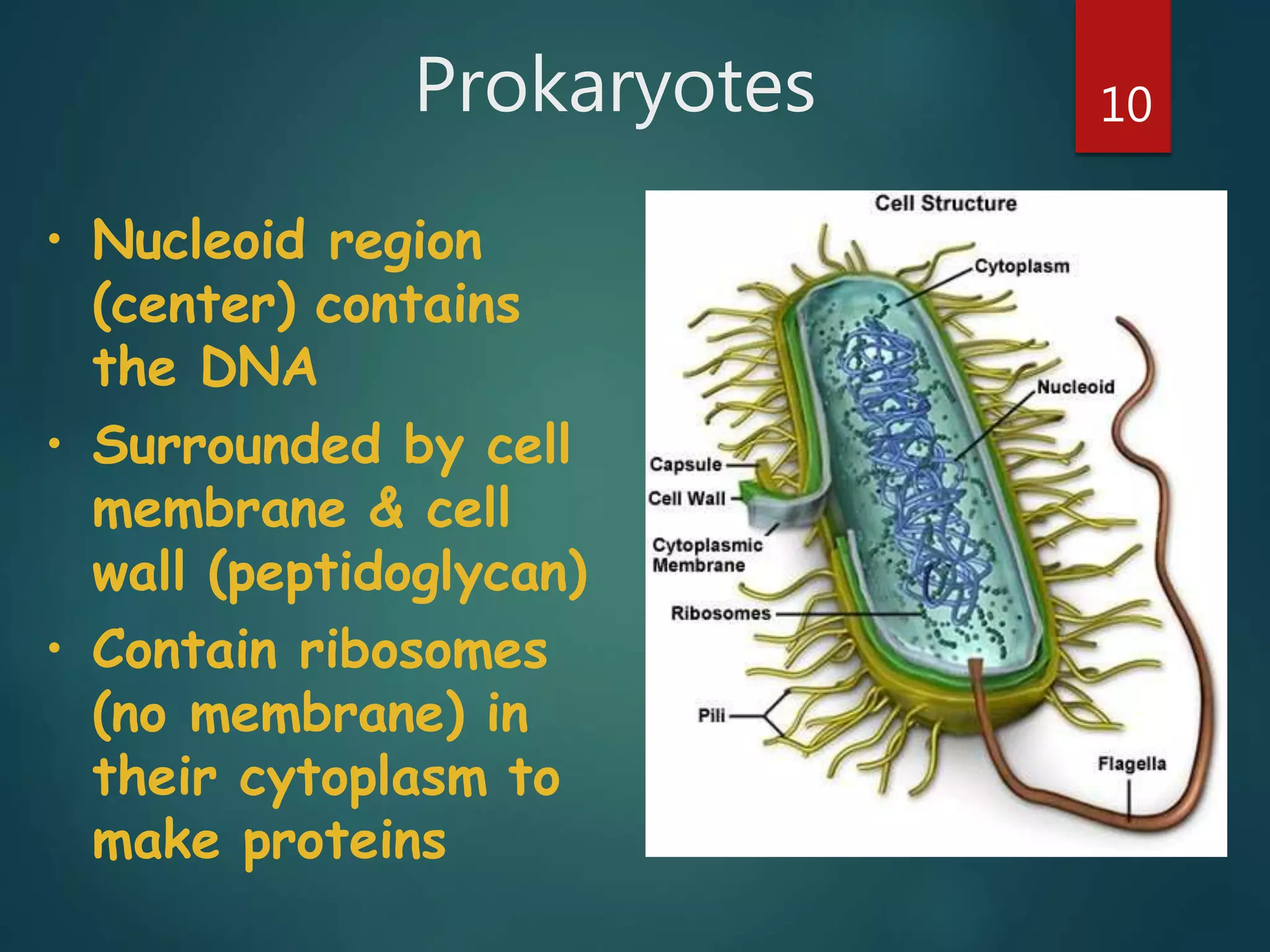
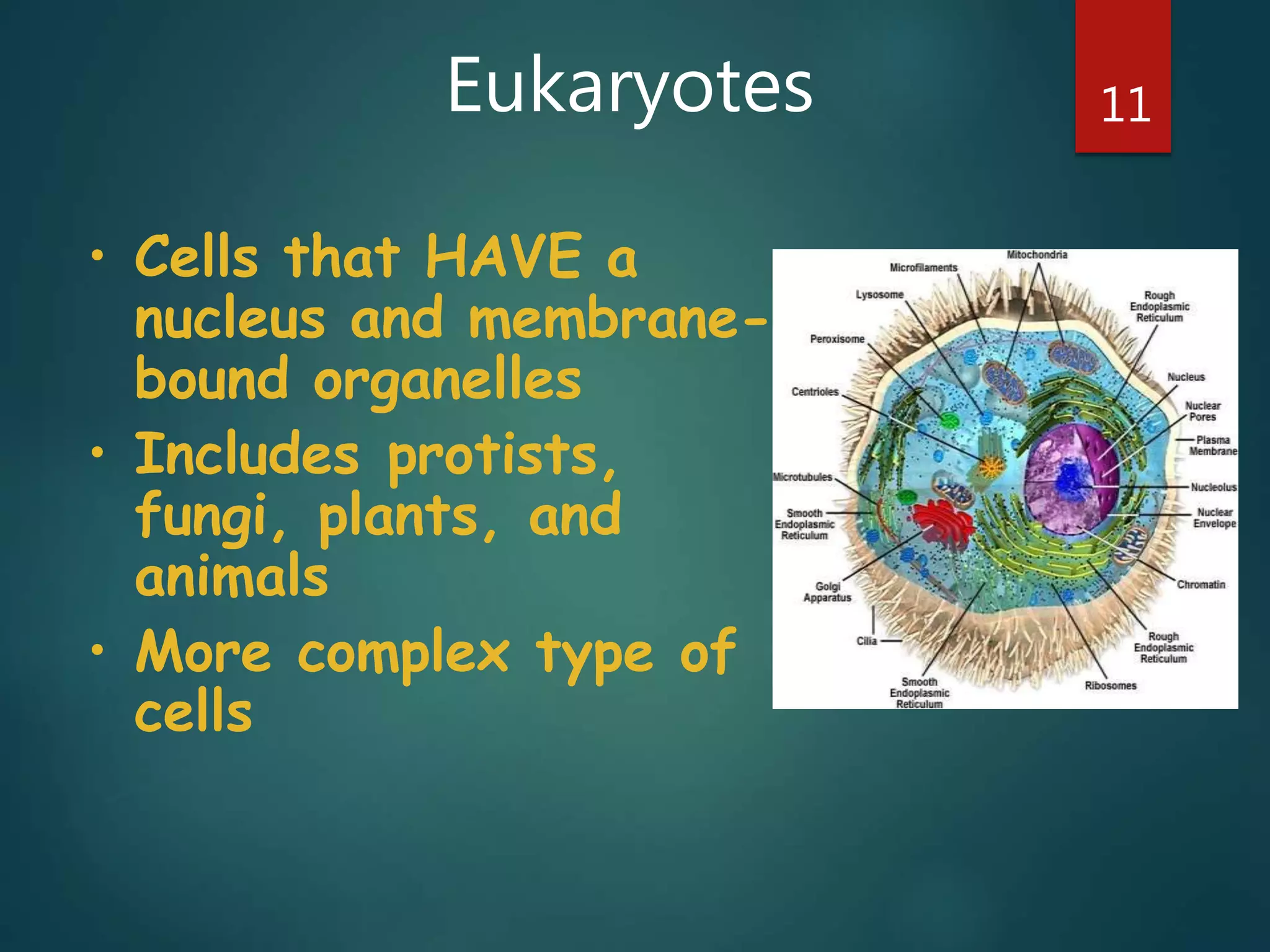
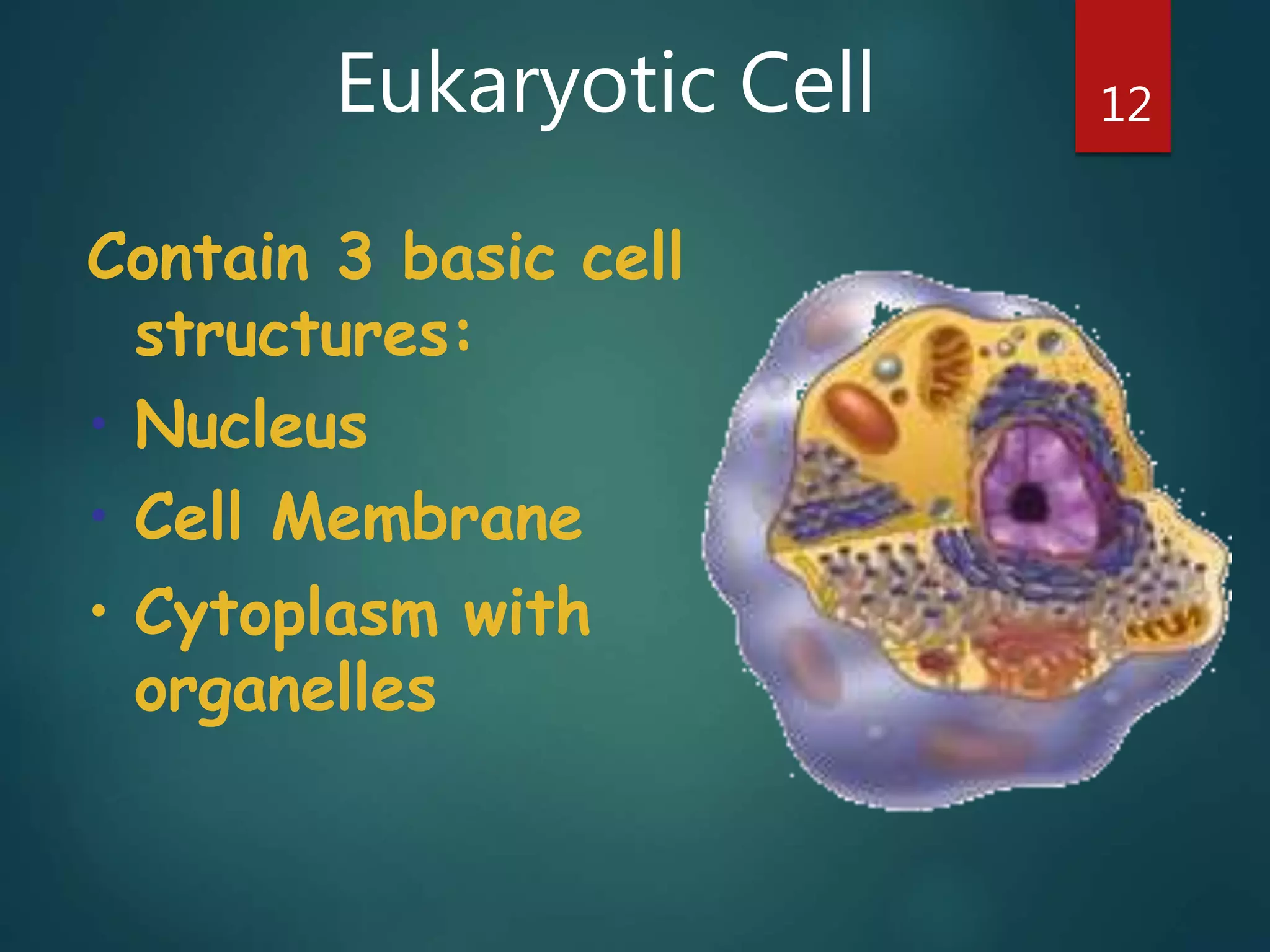
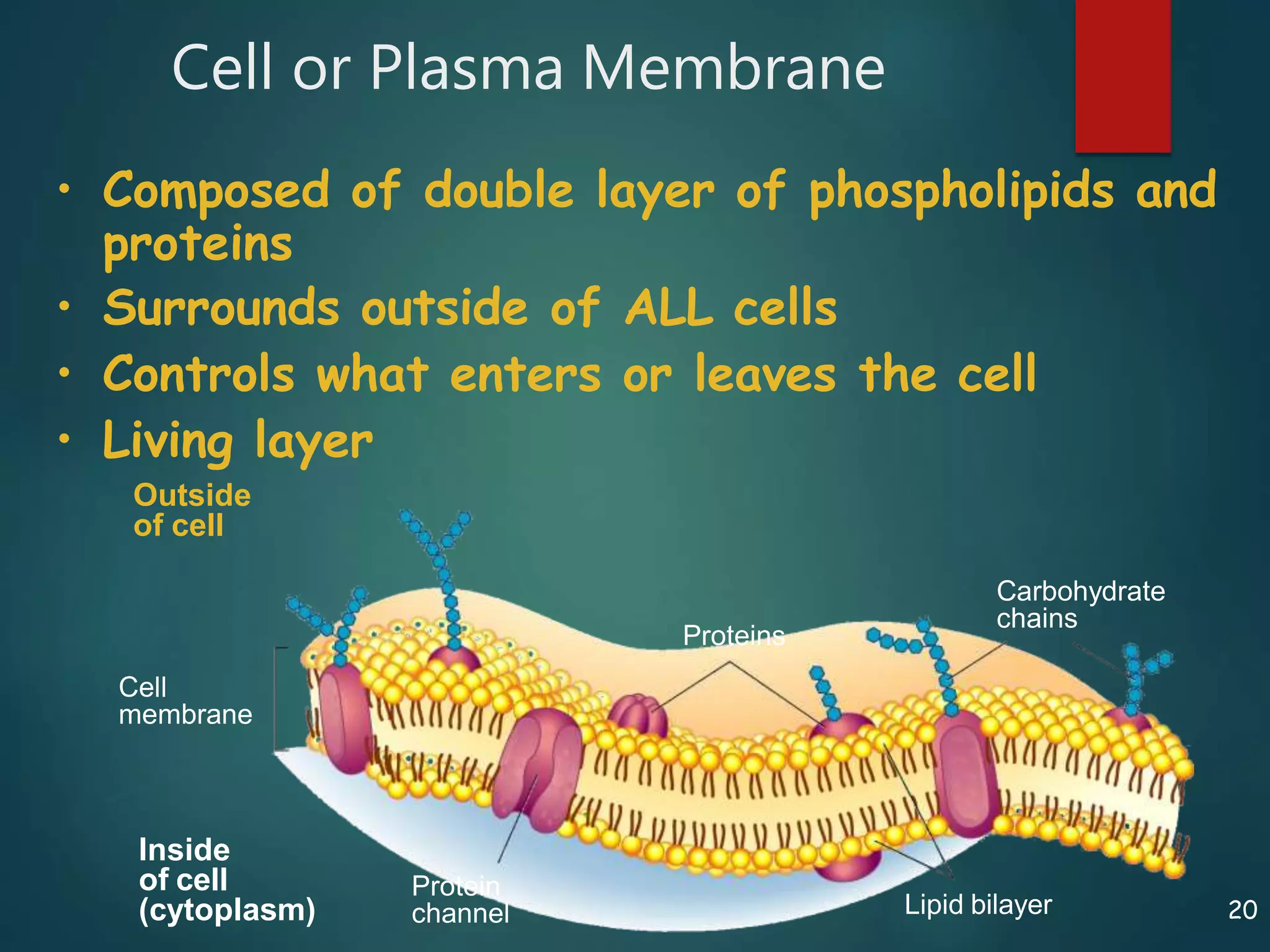
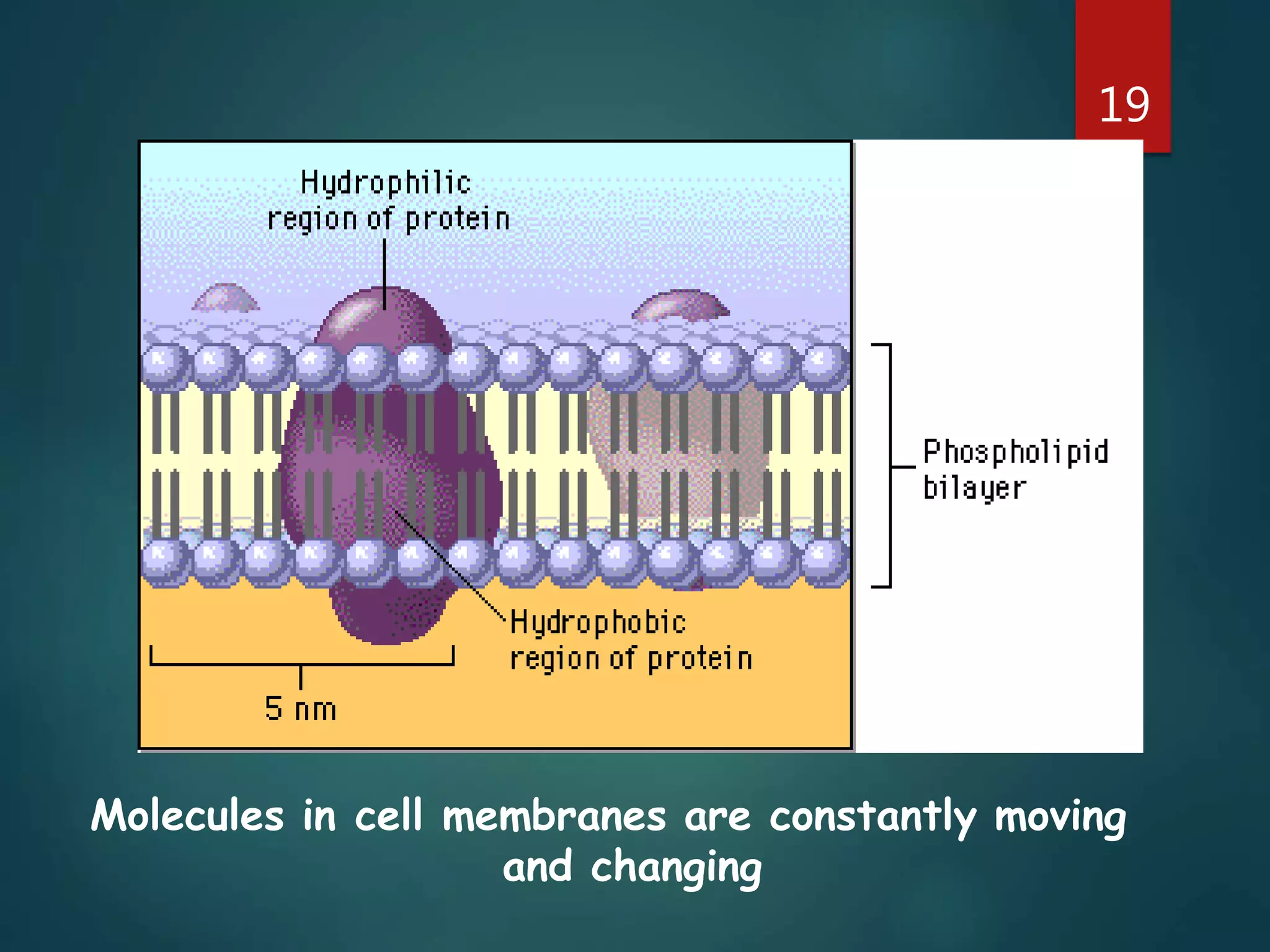
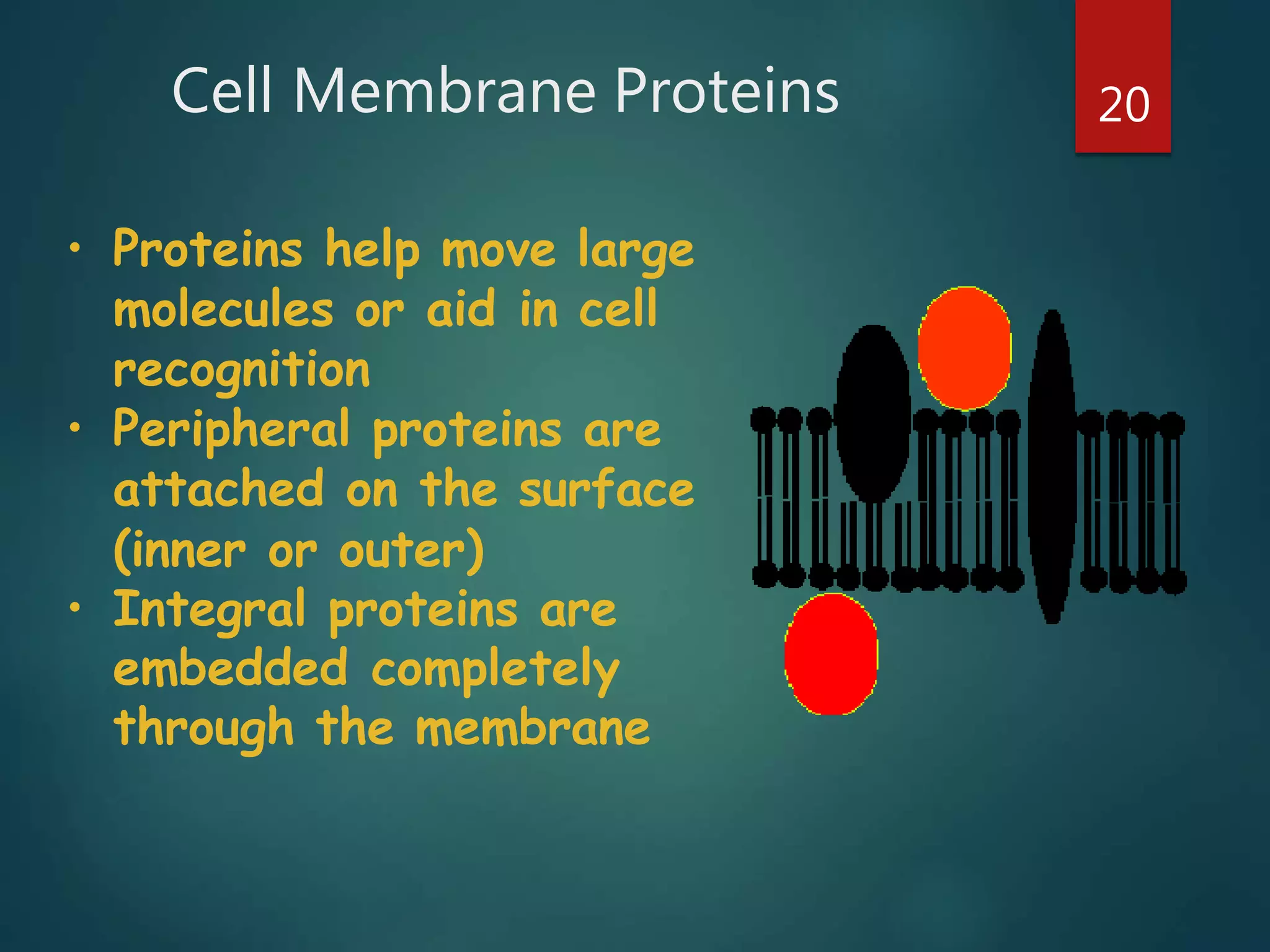
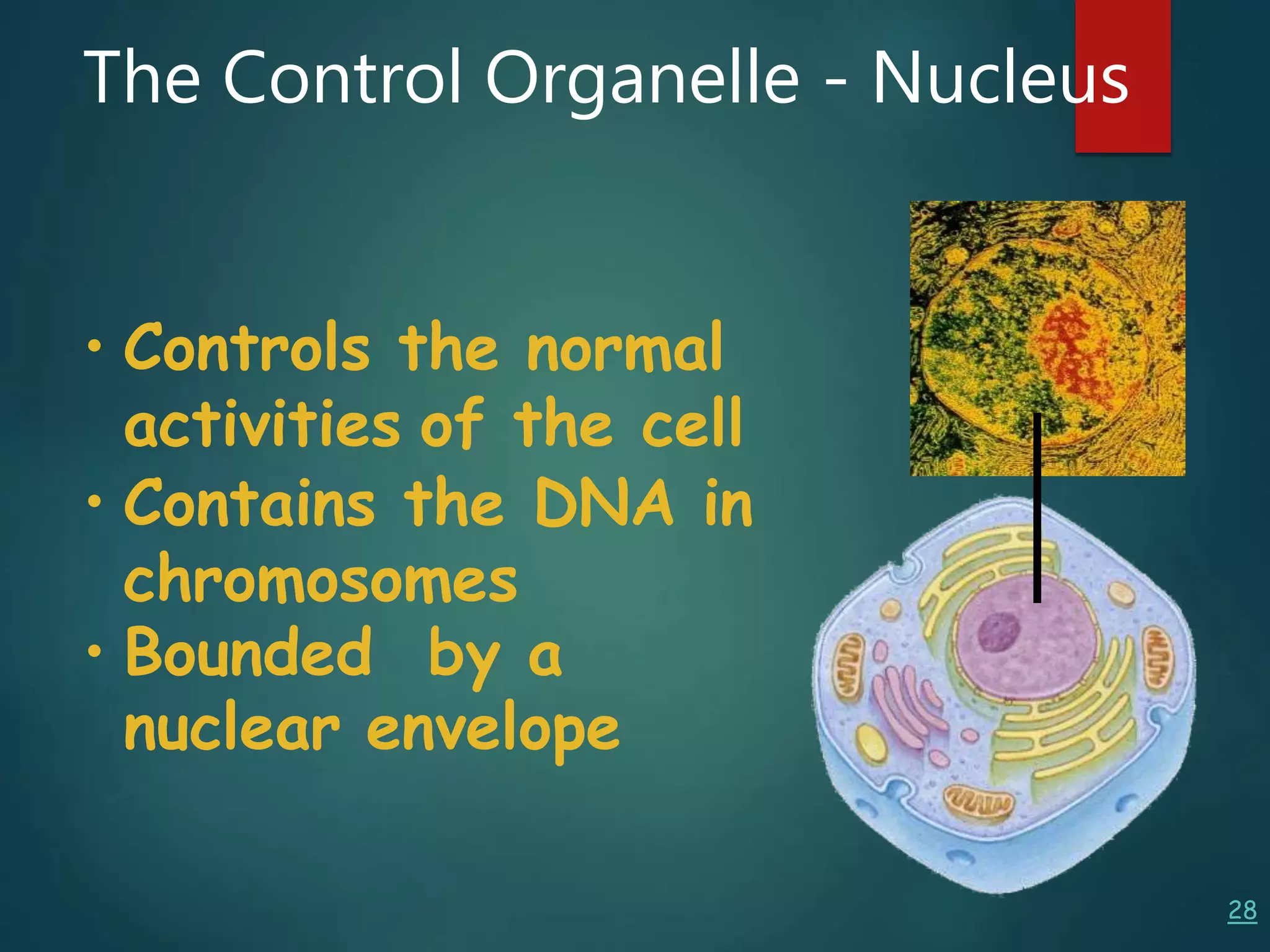
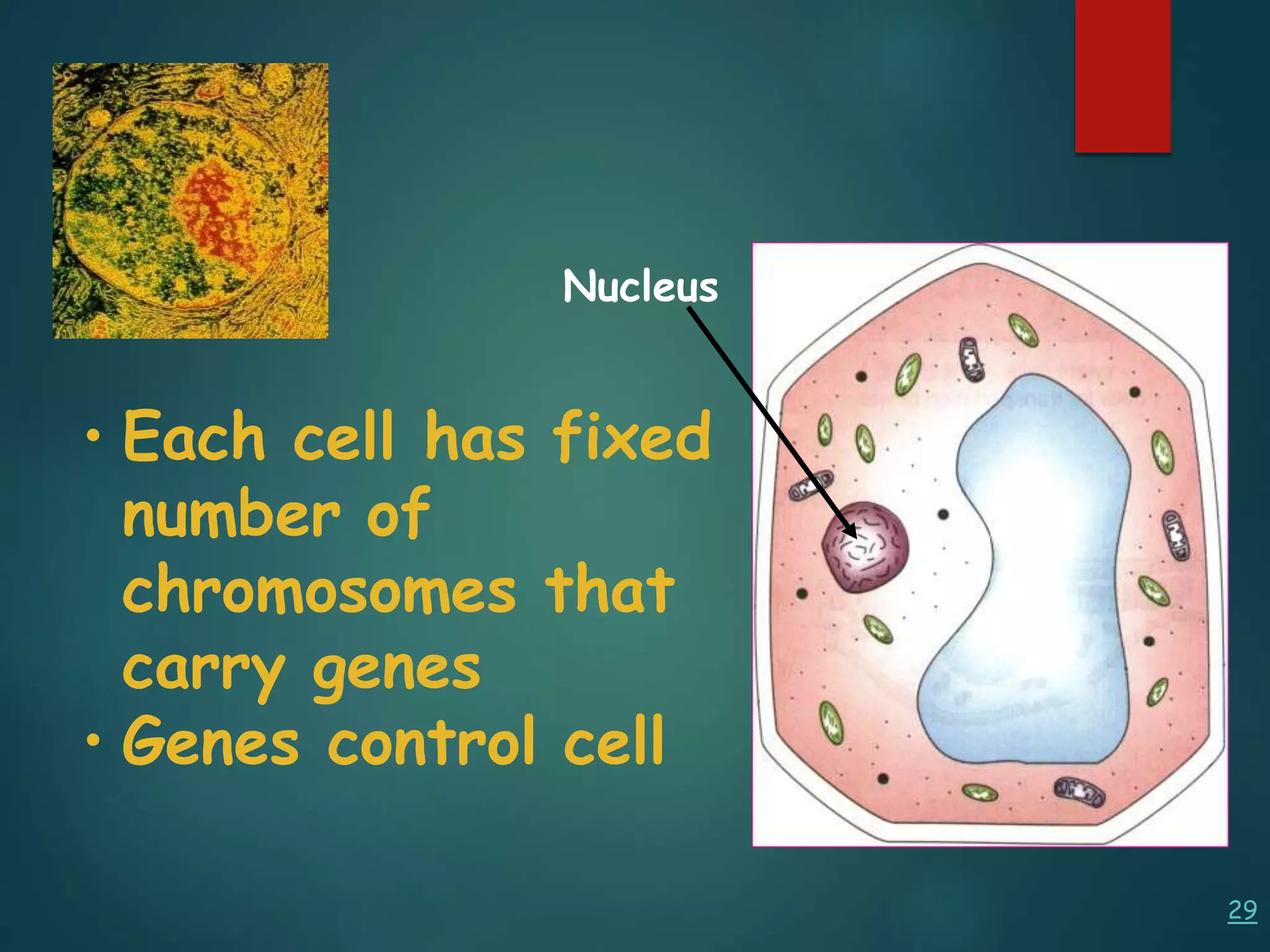
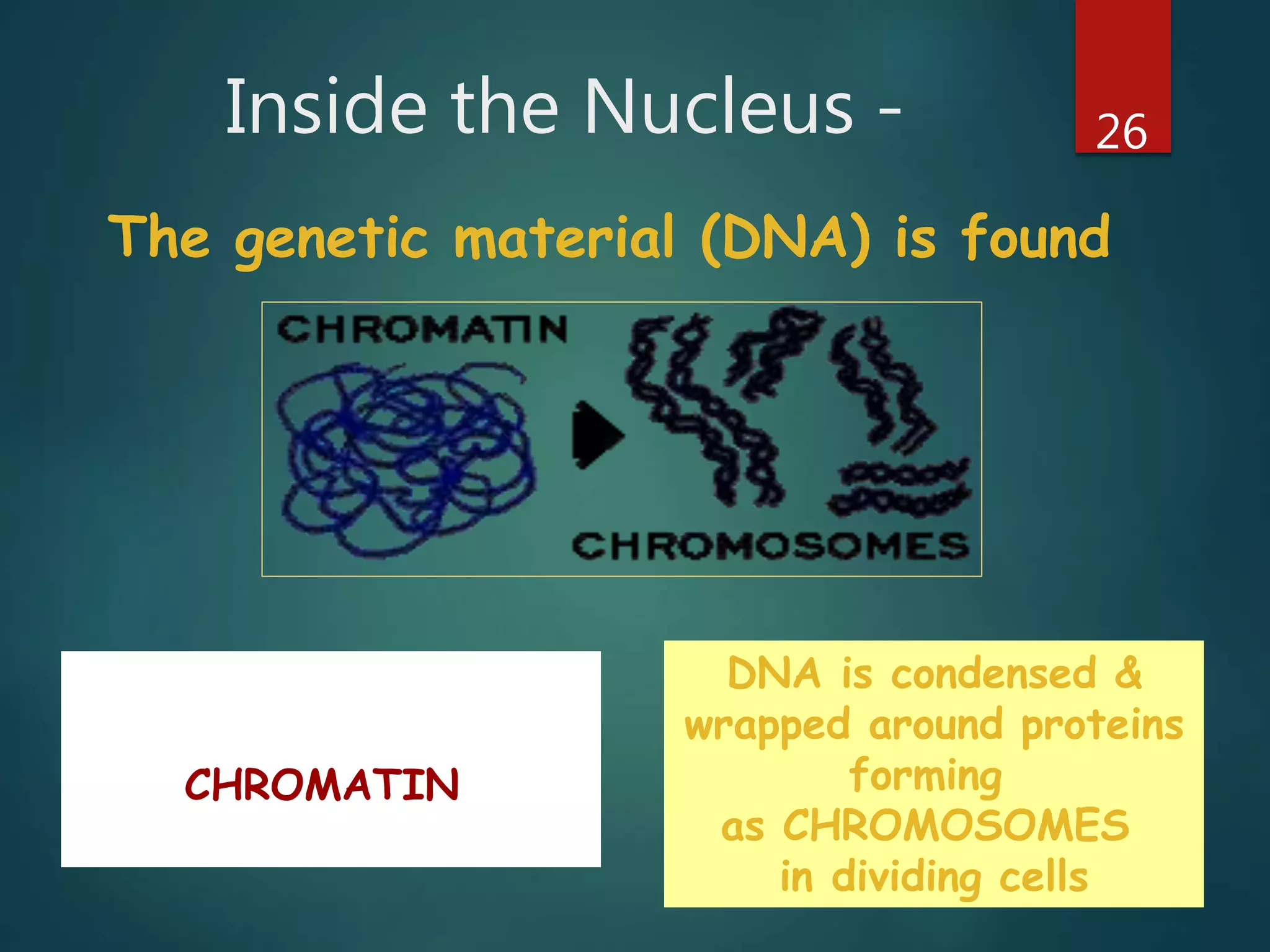
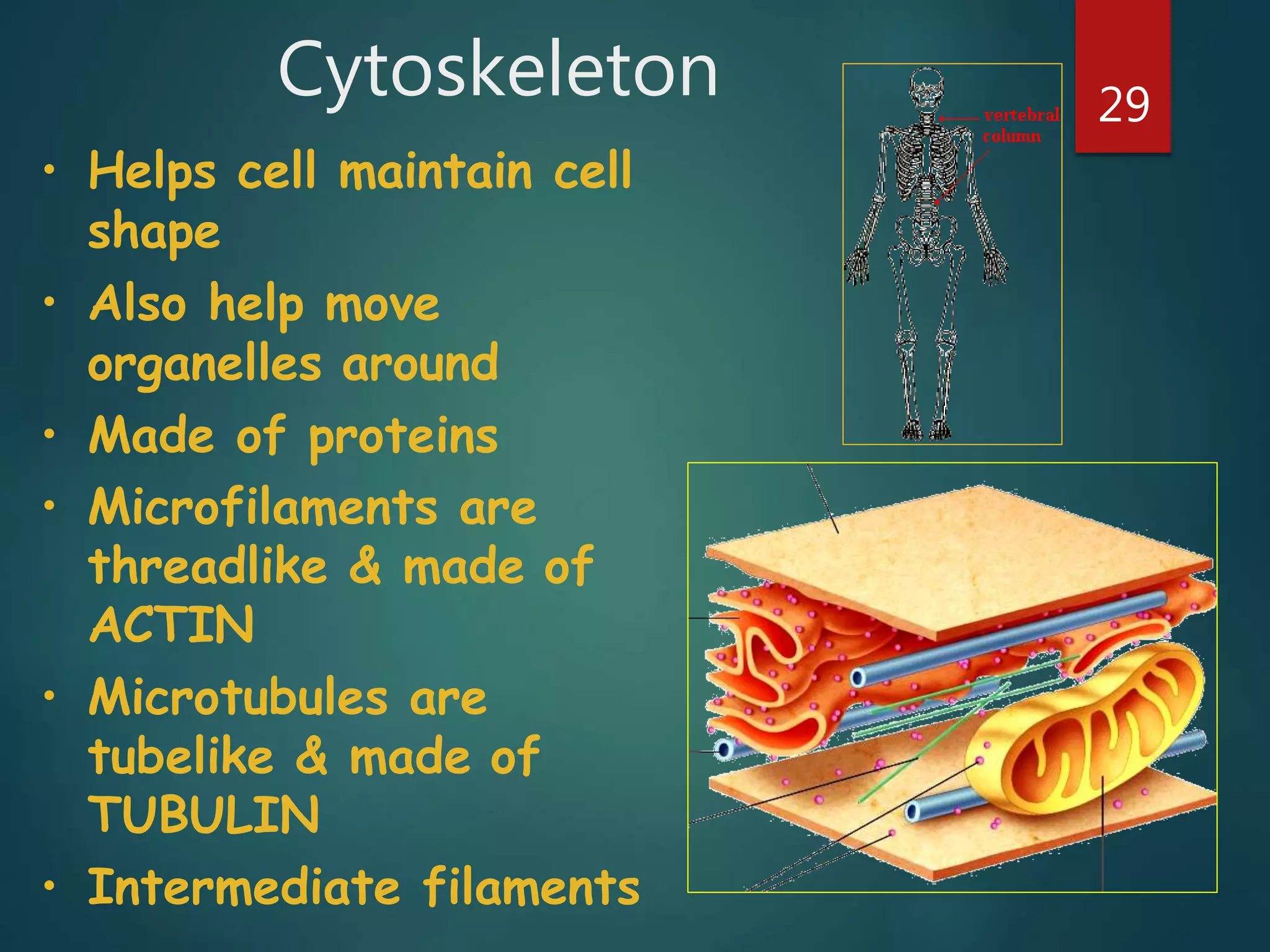
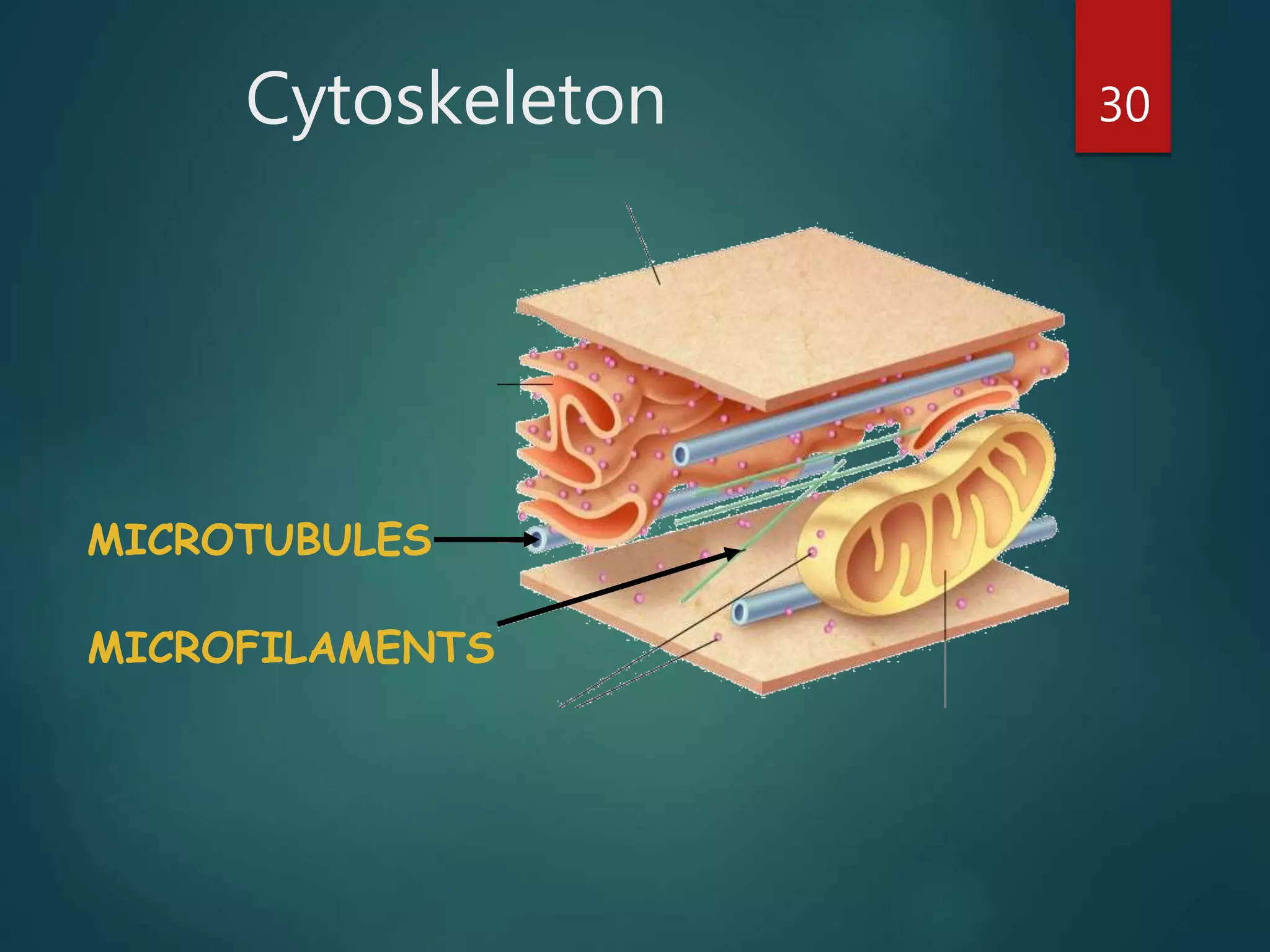
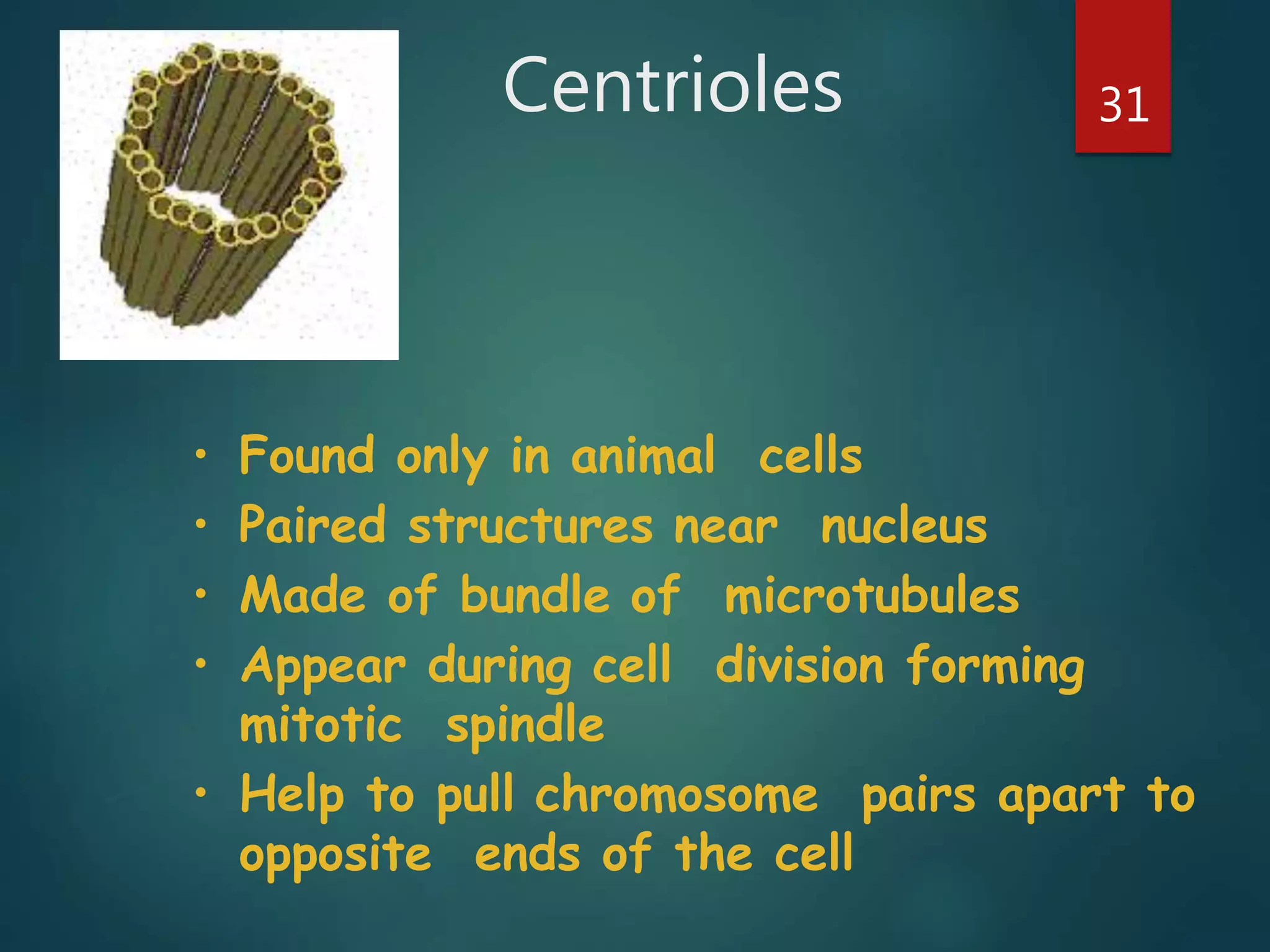
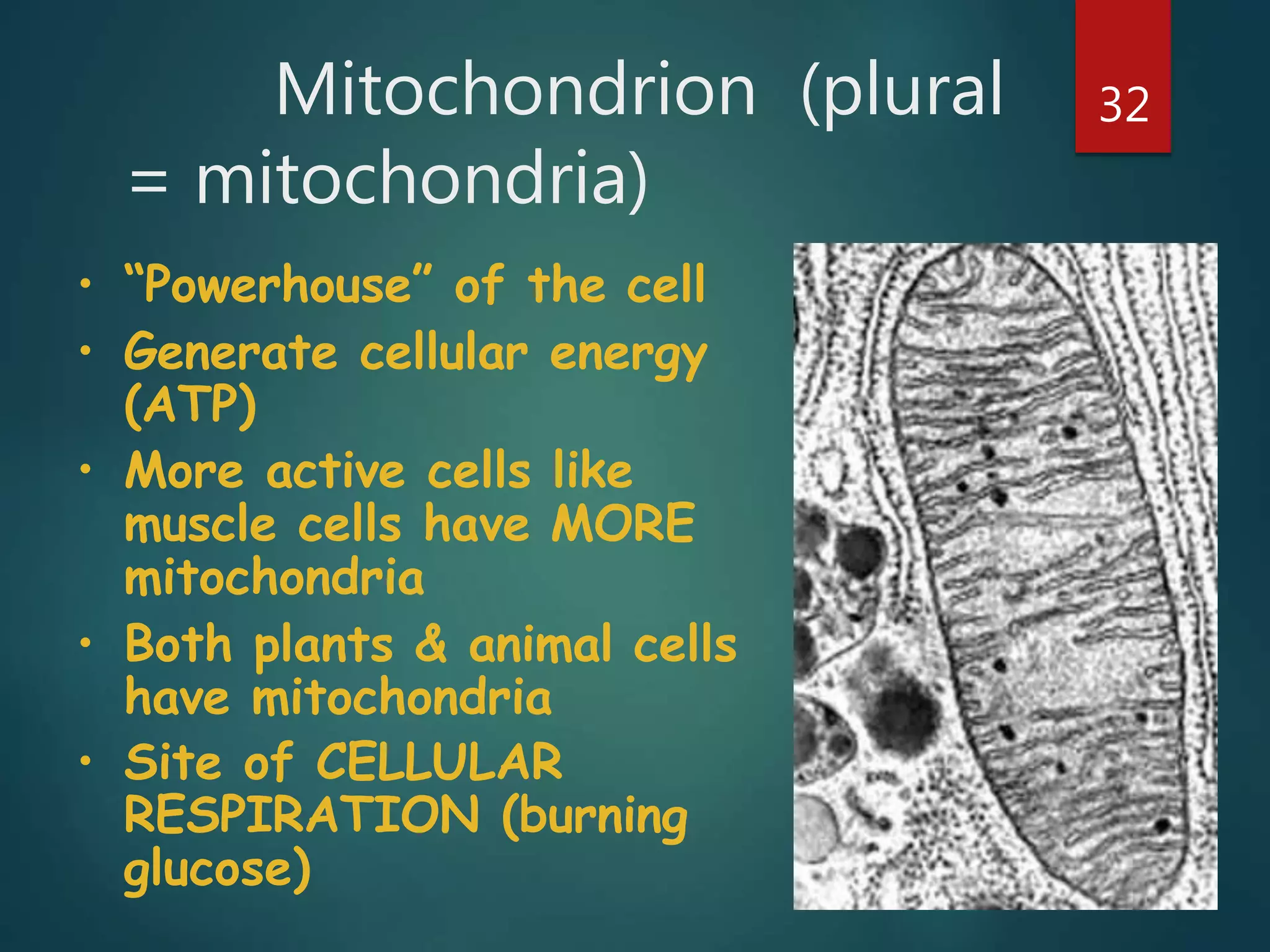
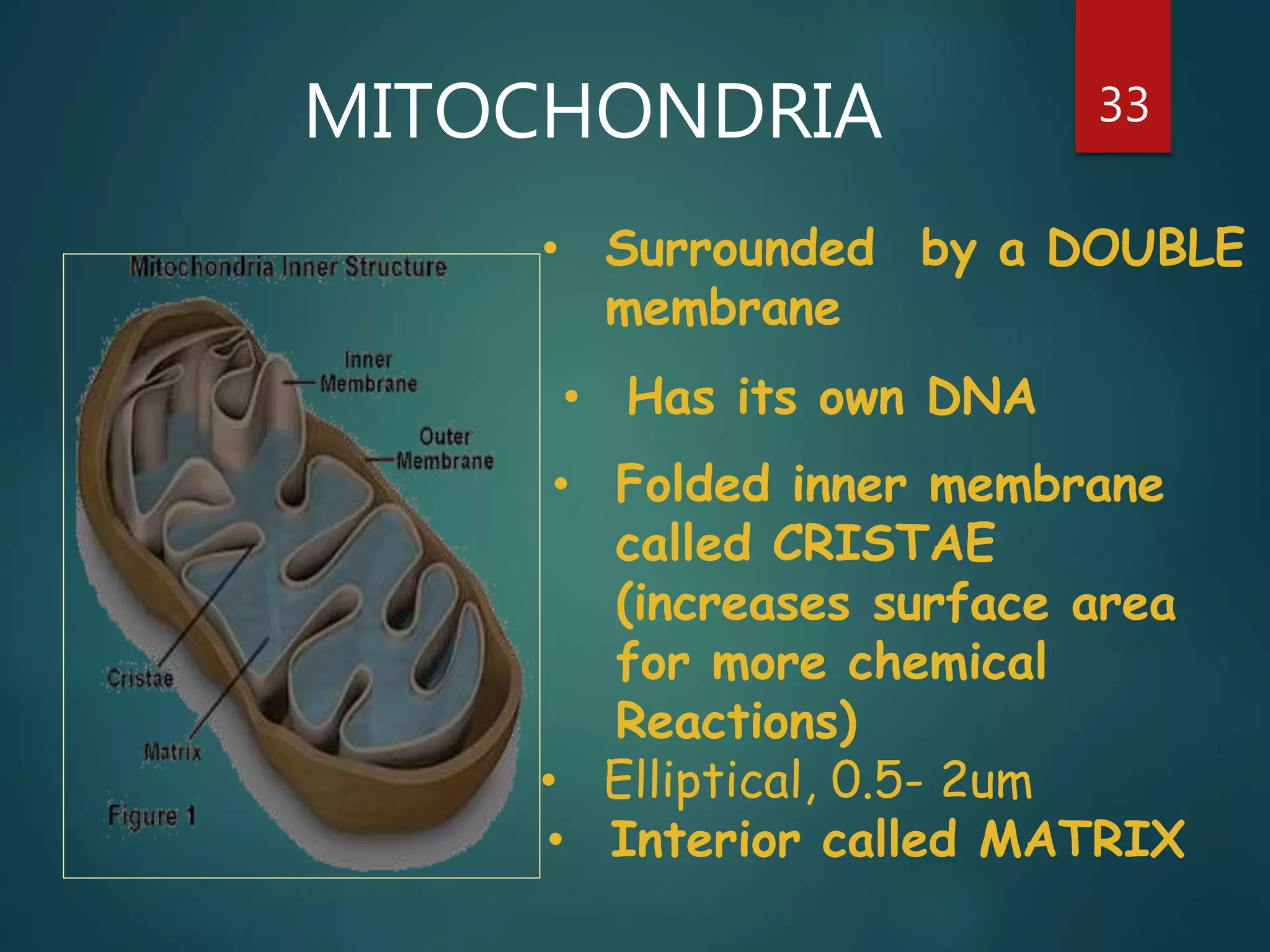
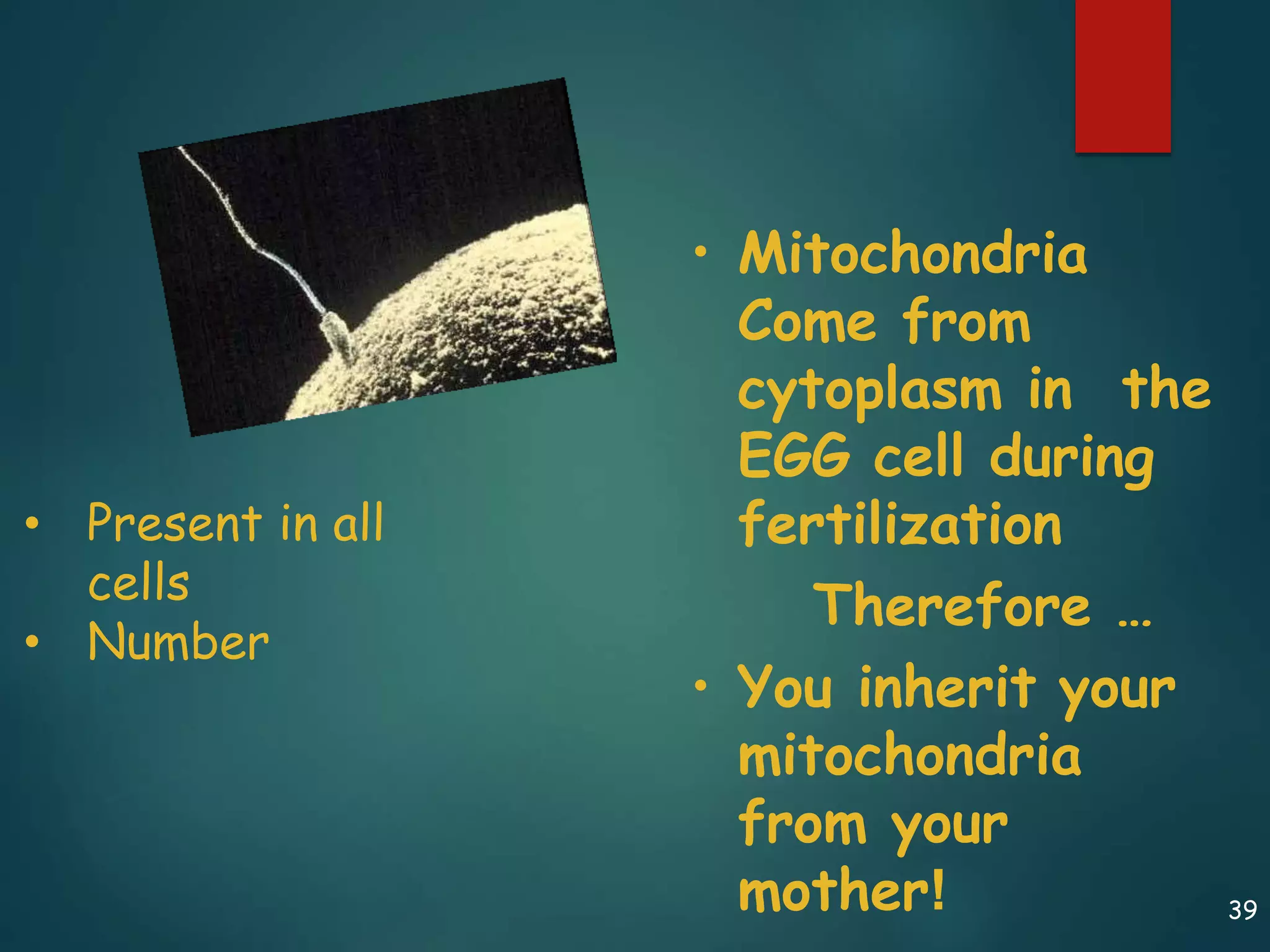
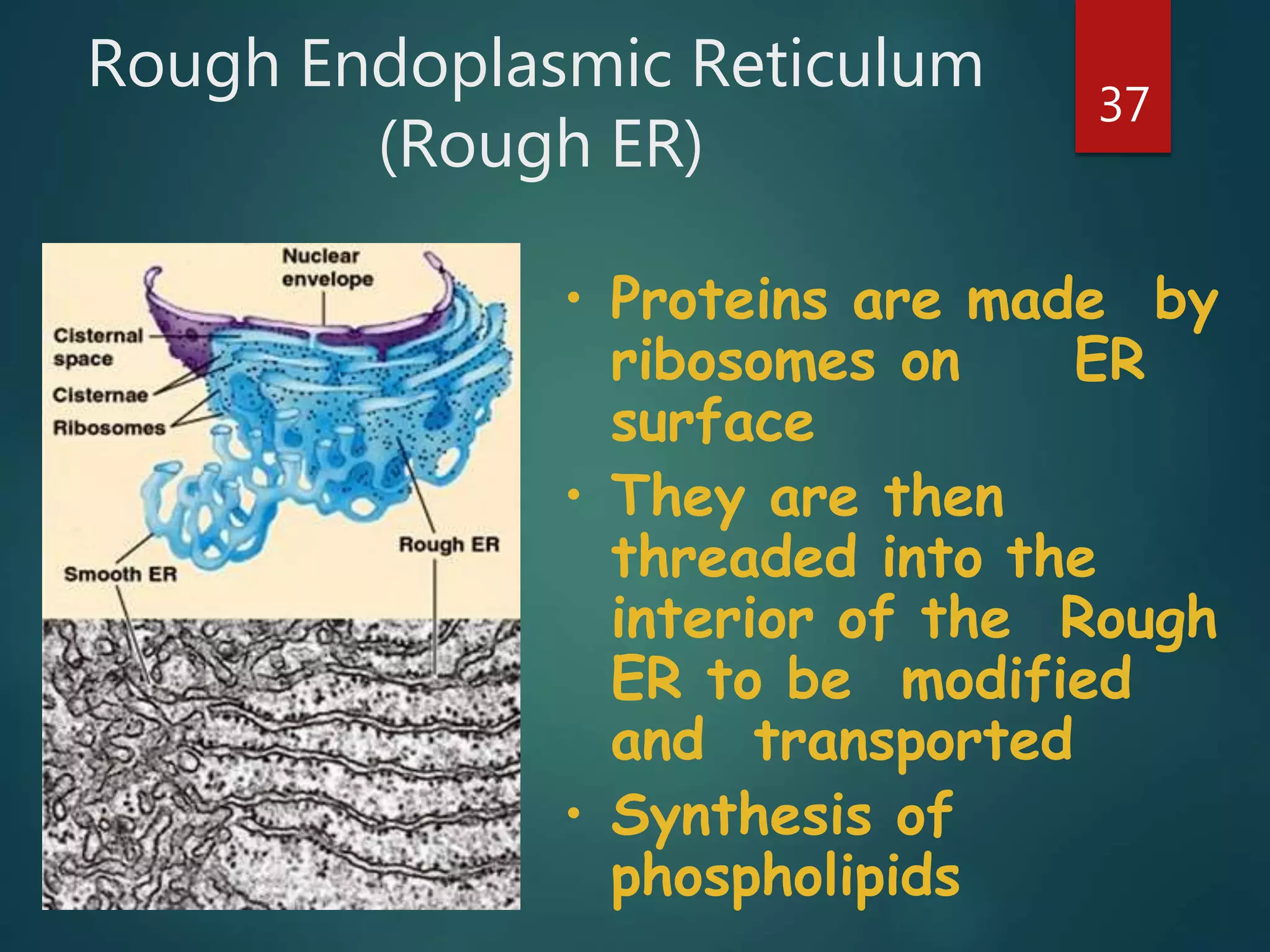
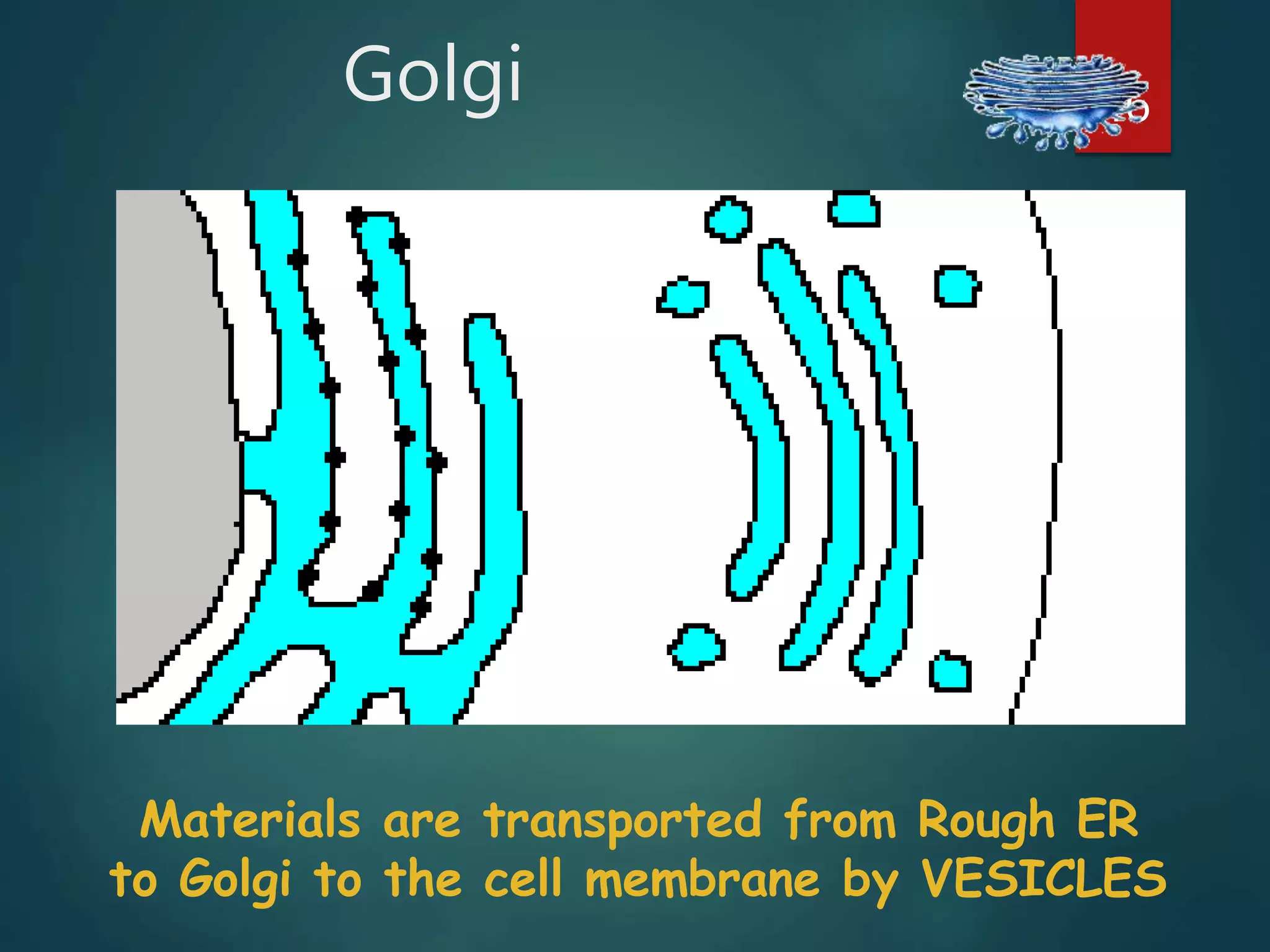
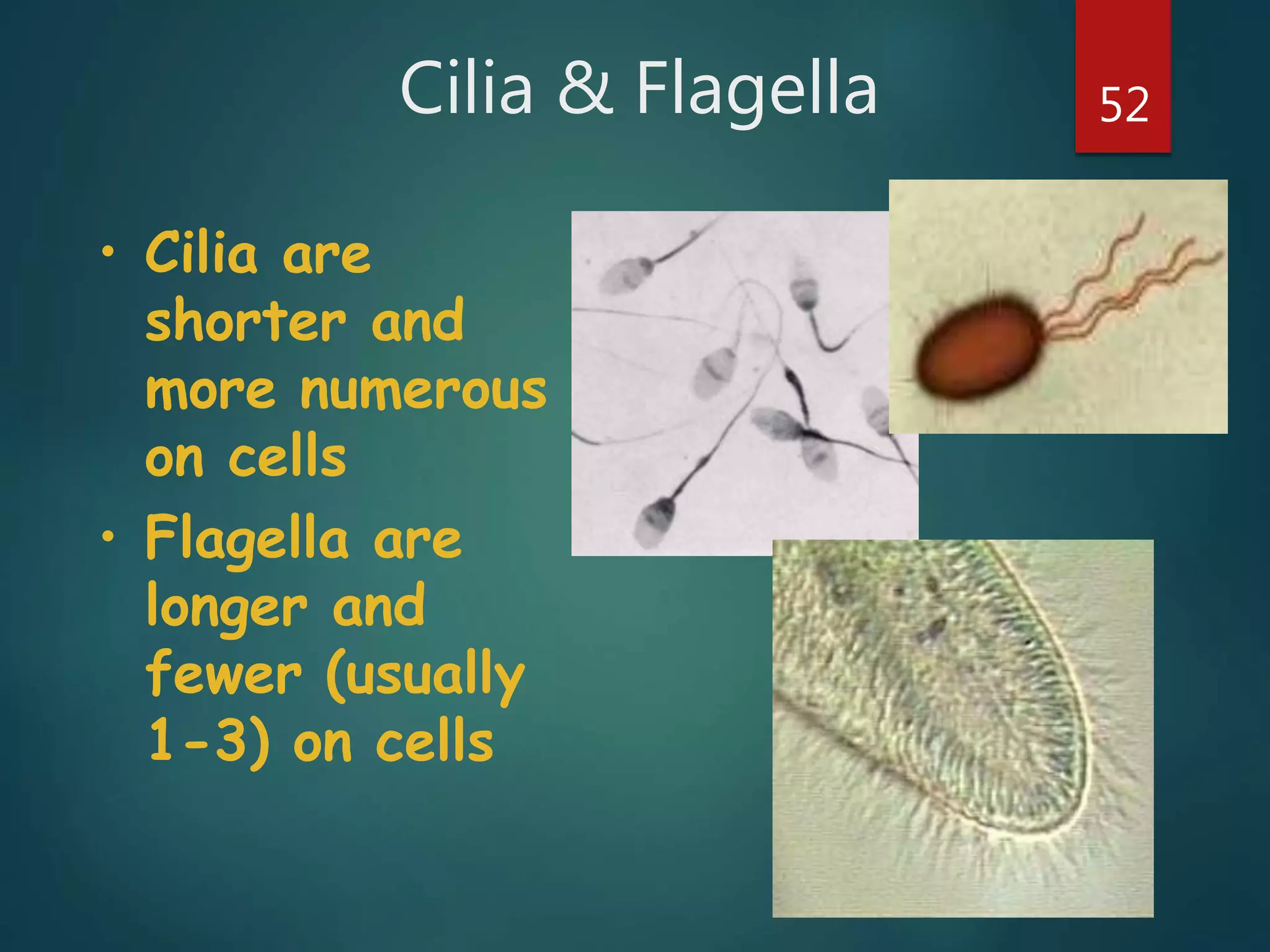
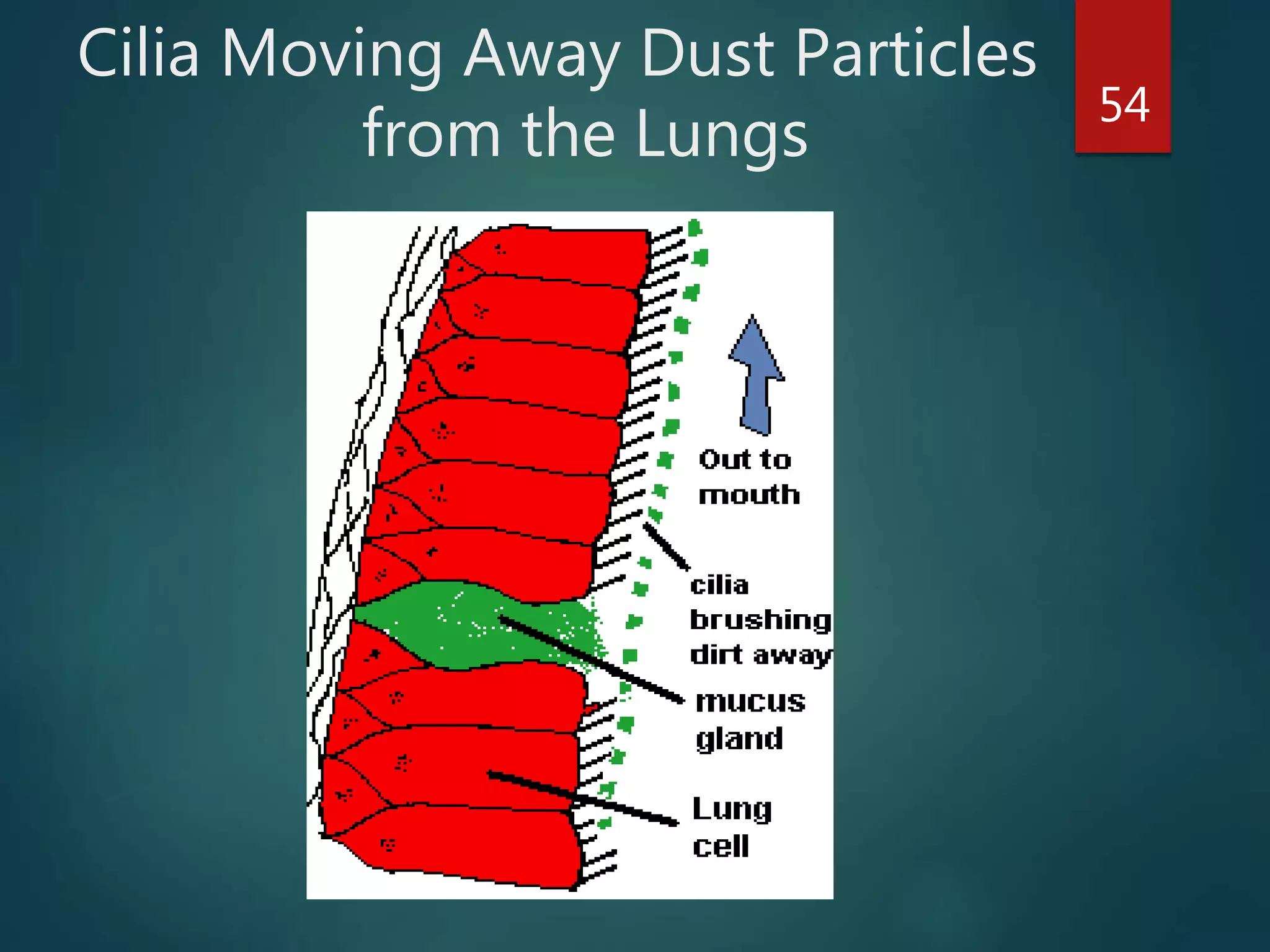
Robert Hooke first observed cells in 1665 using a microscope and named them for their resemblance to monks' rooms called cells. Anton van Leeuwenhoek was the first to observe living cells in 1673 using a simple microscope. In the 1830s, botanist Matthias Schleiden and zoologist Theodore Schwann developed the cell theory which states that all living things are made of cells, cells are the basic unit of structure and function, and new cells are produced from existing cells. Rudolf Virchow later added that cells divide by cell division. The cell contains organelles that perform various functions and is enclosed by a cell membrane that regulates what enters and leaves the cell.