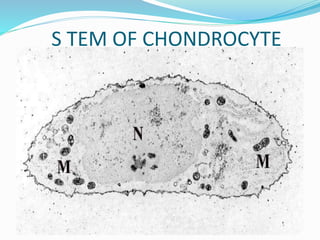
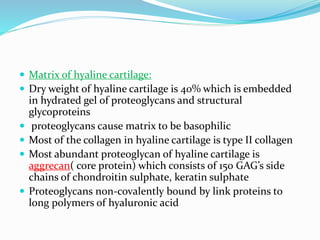
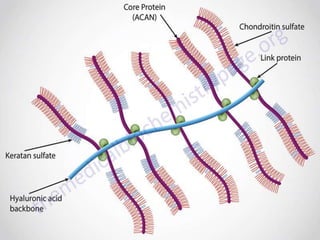
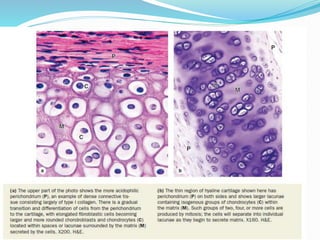
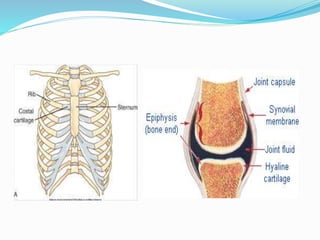
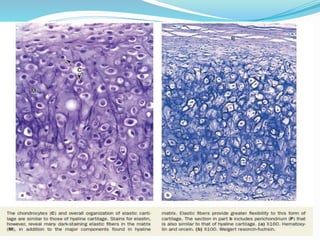
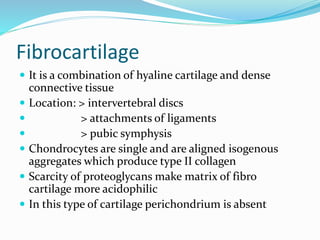
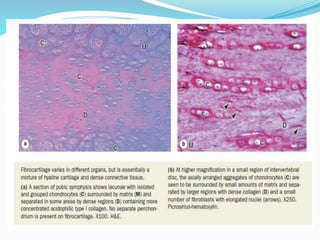
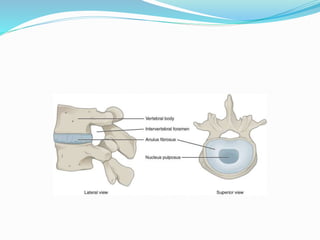
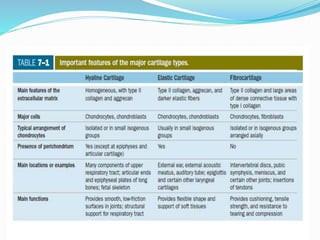
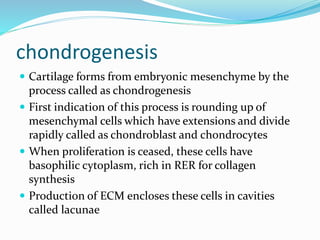
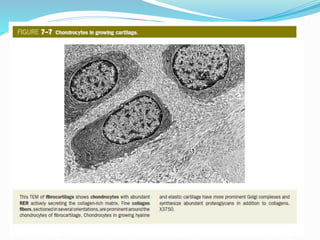
Cartilage is a connective tissue composed of cells called chondrocytes embedded in an extracellular matrix. There are three main types of cartilage - hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage. Hyaline cartilage is found in joints, respiratory airways, and growing bones. It contains type II collagen and proteoglycans that allow it to bear mechanical stress and provide cushioning. Chondrocytes maintain the extracellular matrix by synthesizing its components. Cartilage grows through both interstitial and appositional growth and has limited ability for repair due to its avascular nature.