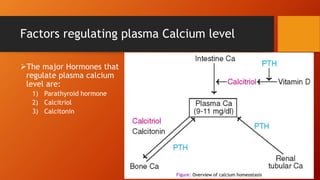
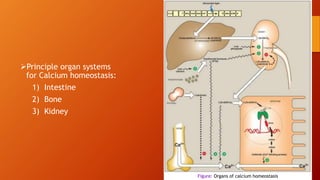
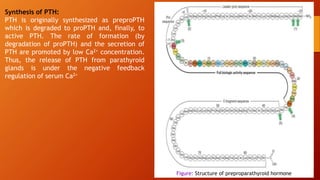
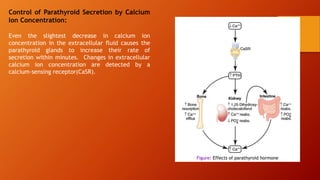
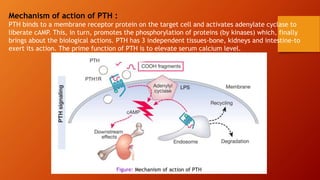
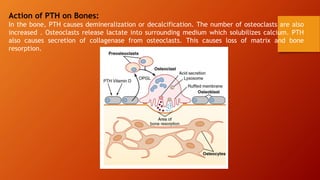
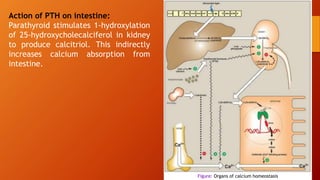
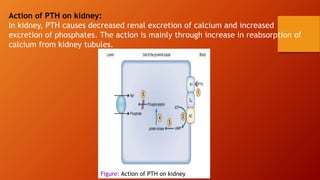
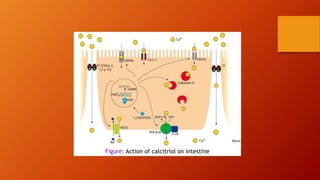
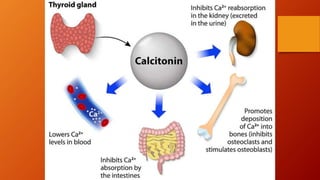
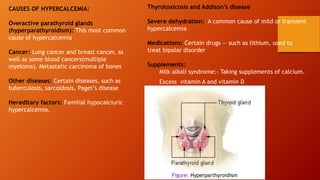
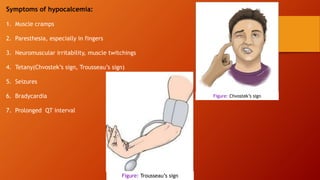
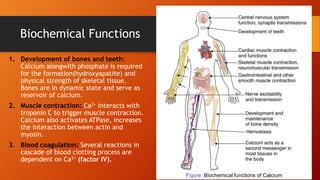
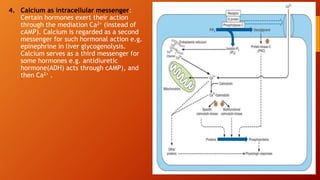
Calcium homeostasis involves tightly regulating plasma calcium levels through a complex interplay of hormones like parathyroid hormone (PTH), calcitriol, and calcitonin. PTH acts to raise calcium levels by stimulating bone resorption and renal reabsorption of calcium. Calcitriol promotes intestinal calcium absorption. Calcitonin lowers calcium levels by inhibiting bone resorption. The body maintains 99% of its calcium stores in bones. Imbalances can result in hypercalcemia from overactive PTH or hypocalcemia from vitamin D deficiency.



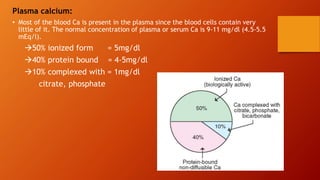
![In bones:
• 99% of body calcium is present in bones.
• Bone is composed of a tough organic matrix
that is greatly strengthened by deposits of
calcium salts. Average compact bone
contains by weight about 30 percent matrix
and 70 percent salts. Newly formed bone
may have a considerably higher percentage
of matrix in relation to salts.
• The crystalline salts deposited in the
organic matrix of bone are composed
principally of calcium and phosphate.
• Major crystaline salt is calcium
hydroxyapatite{Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2]
Distribution of calcium](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calciumhomeostasis-1-210527175040/85/Calcium-homeostasis-4-320.jpg)

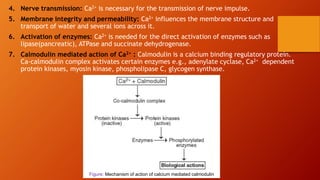

![Calcium homeostasis
Calcium homeostasis refers to the maintenance of a constant concentration
of calcium ions in the extracellular fluid. It includes all of the processes that
contribute to maintaining calcium at its “set point.” Because plasma [Ca2+]
rapidly equilibrates with the extracellular fluid, ECF [Ca2+] is kept constant
by keeping the plasma [Ca2+] constant.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calciumhomeostasis-1-210527175040/85/Calcium-homeostasis-11-320.jpg)