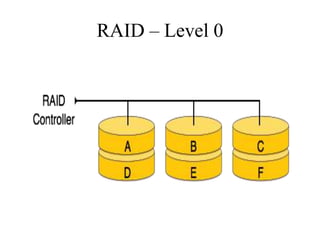
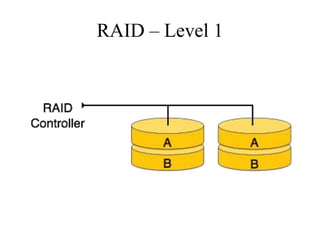
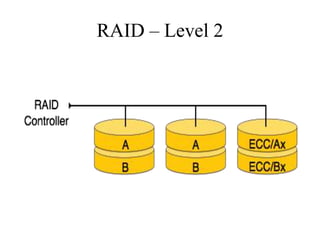
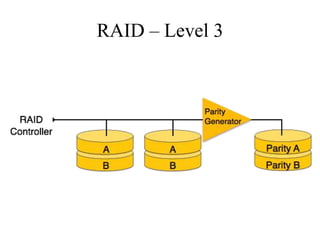
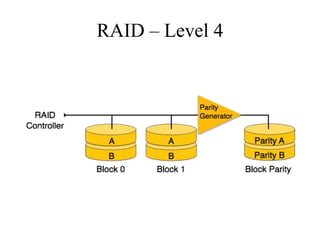
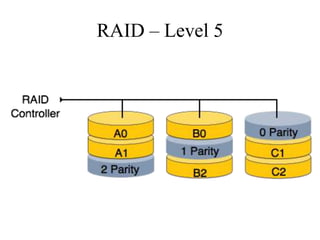
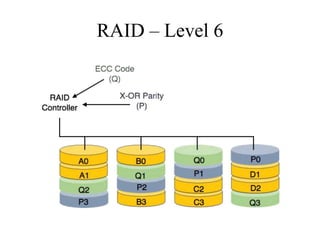
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) connects multiple disks together to increase performance and reliability. It provides increased I/O throughput, data redundancy if a disk fails, and allows data to be restored. The main RAID levels are: RAID 0 uses disk striping for performance but no redundancy; RAID 1 uses mirroring for 100% redundancy; RAID 5 uses disk striping with parity data distributed across all disks. Higher RAID levels like RAID 6 provide even more fault tolerance. The best RAID level depends on performance and reliability needs.