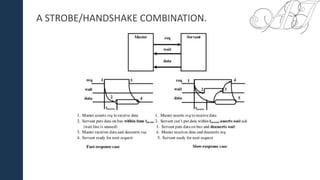
The document outlines a presentation on bus communication methods in electronics, covering definitions, structures, and characteristics. It discusses parallel vs. serial communication, synchronous vs. asynchronous buses, basic protocol concepts, and bus arbitration methods. The focus is on the advantages and disadvantages of each type, as well as practical applications and transactions involved in bus communication.