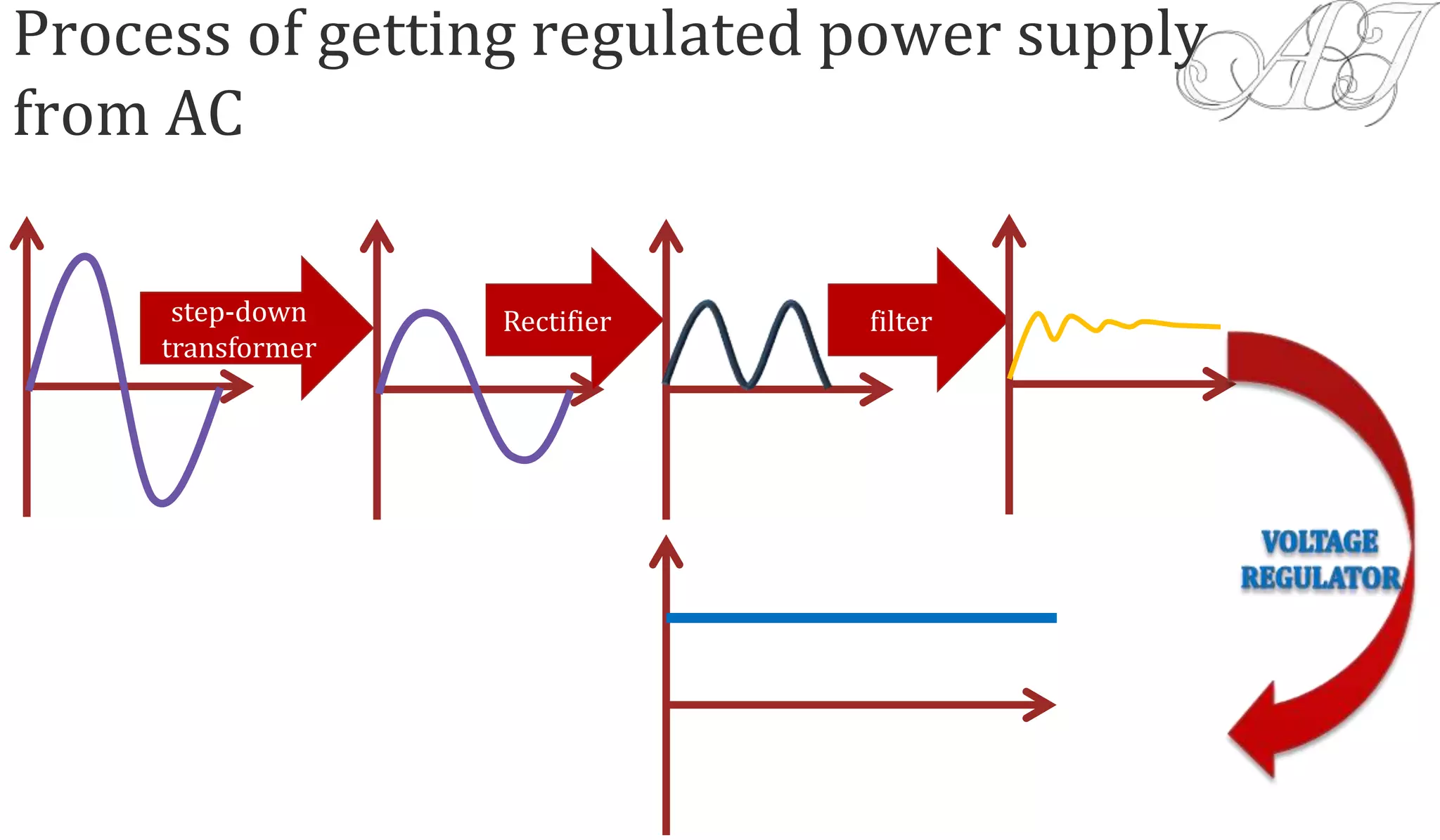
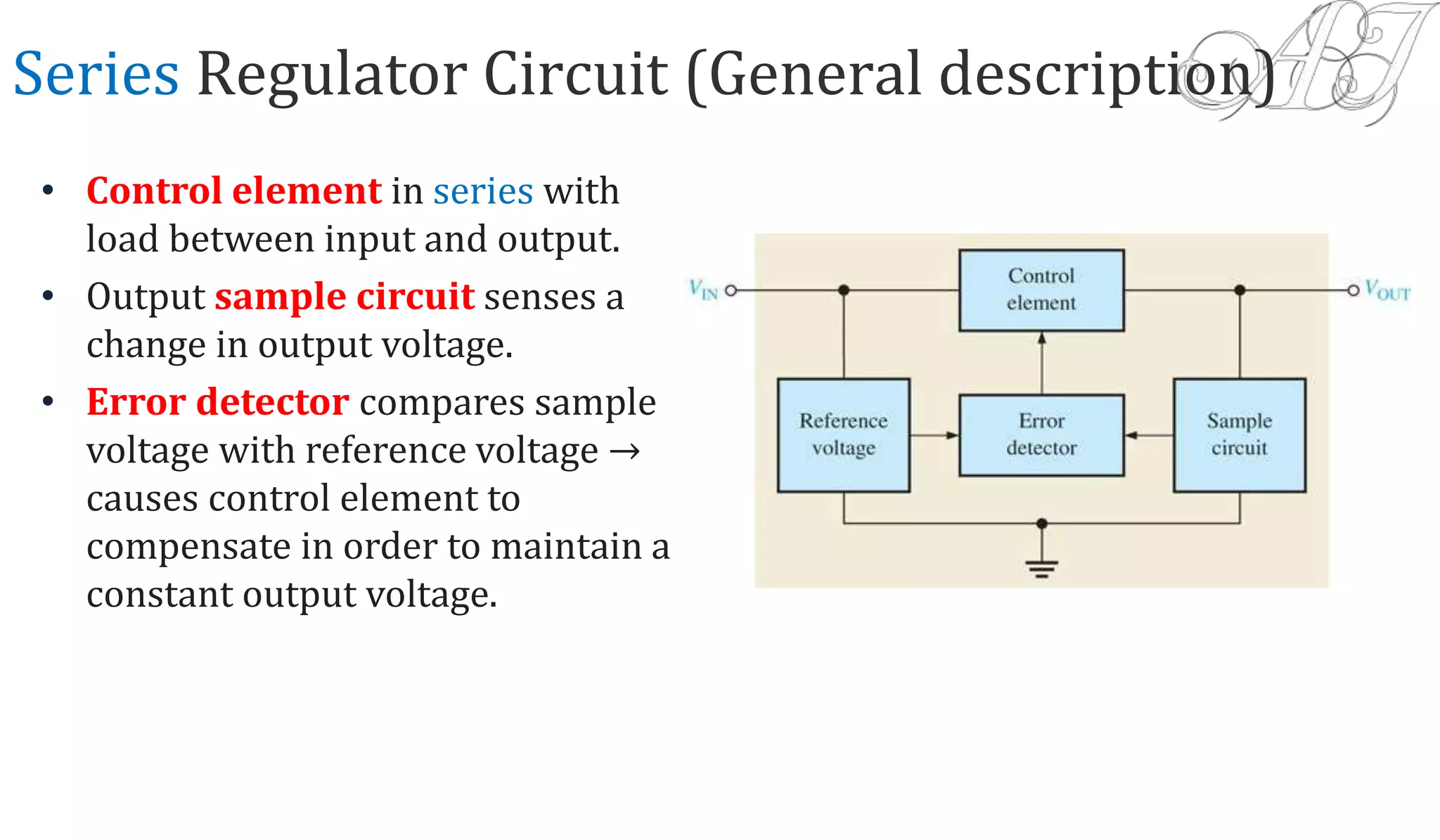
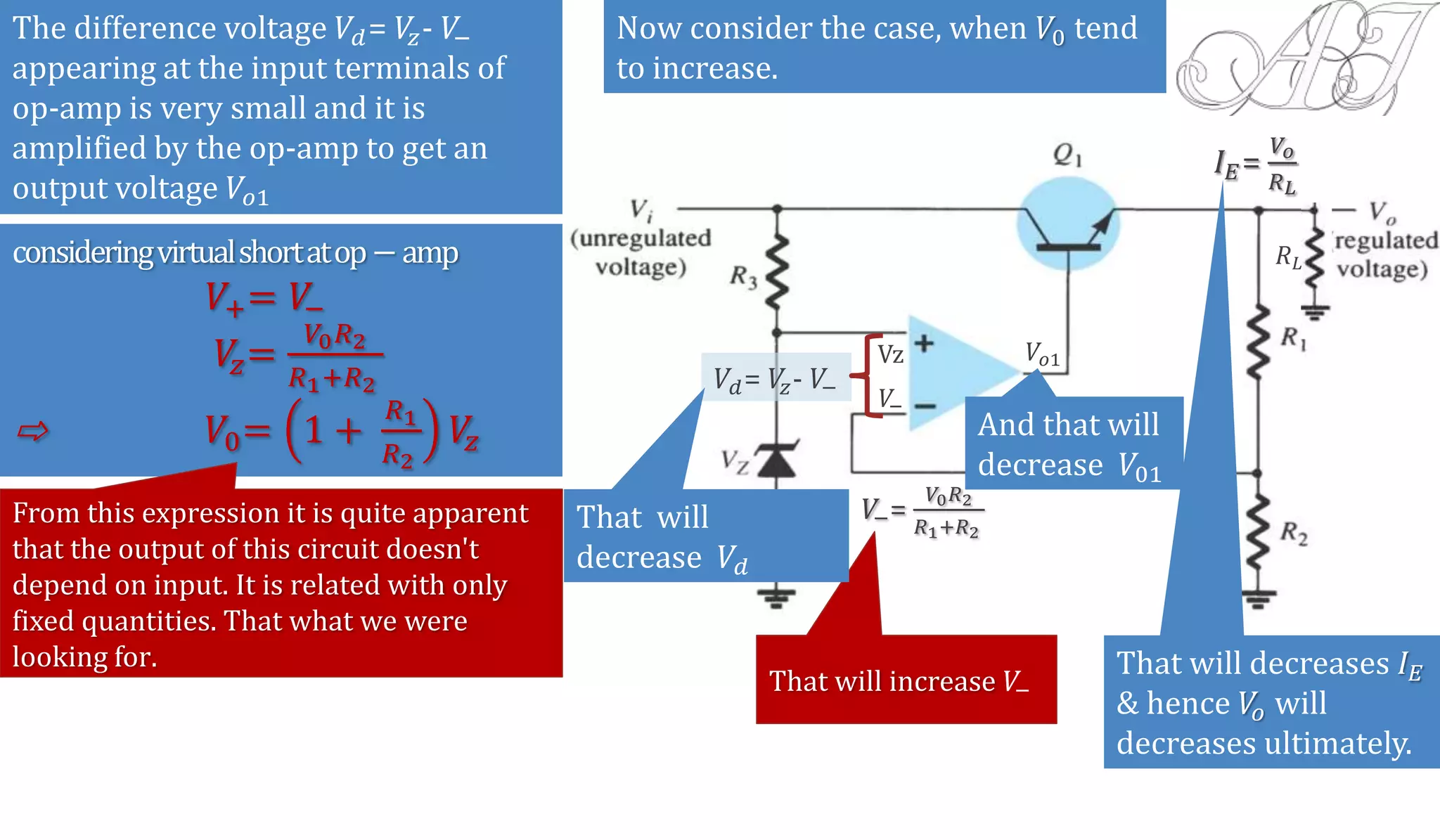
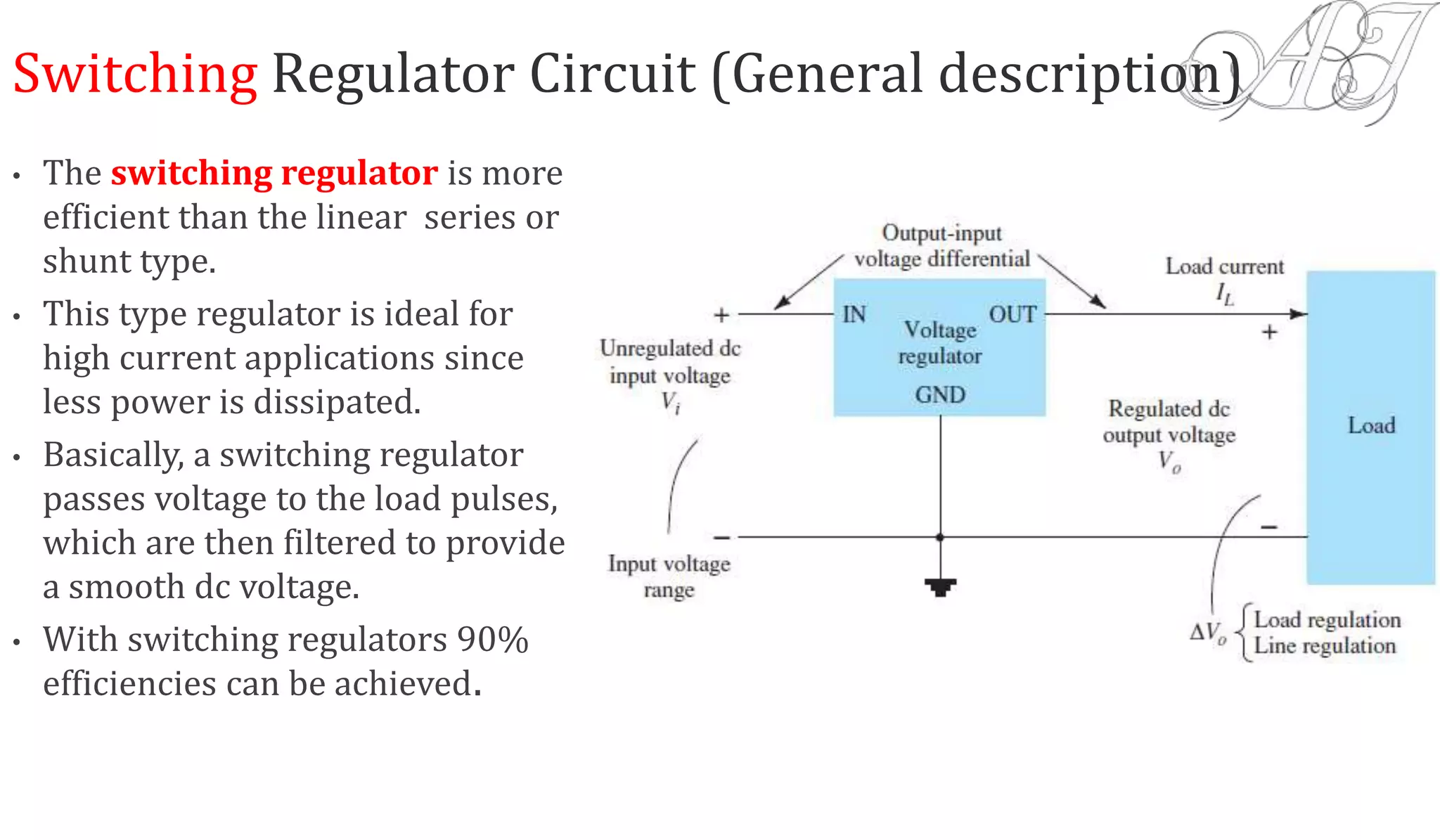
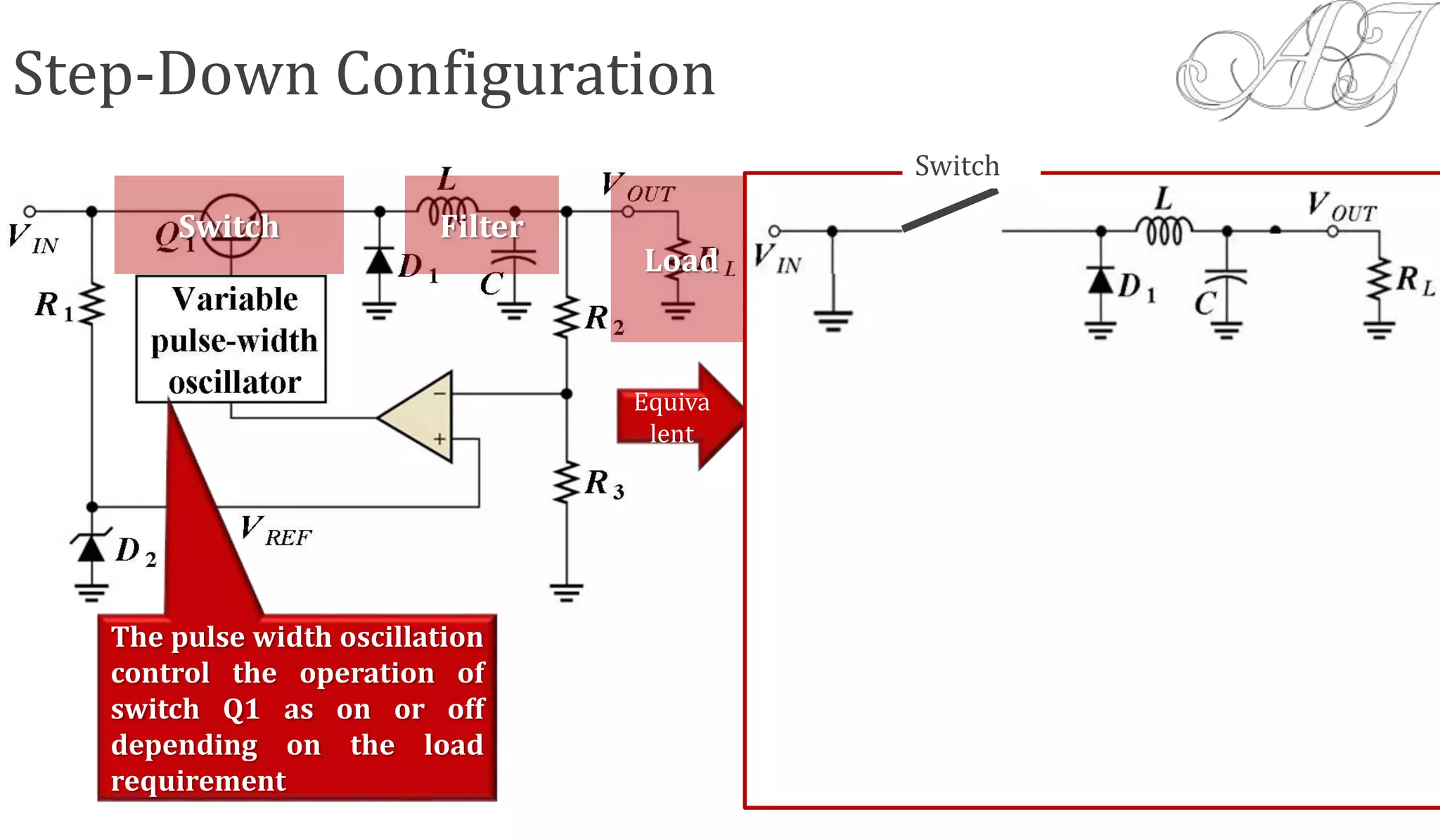
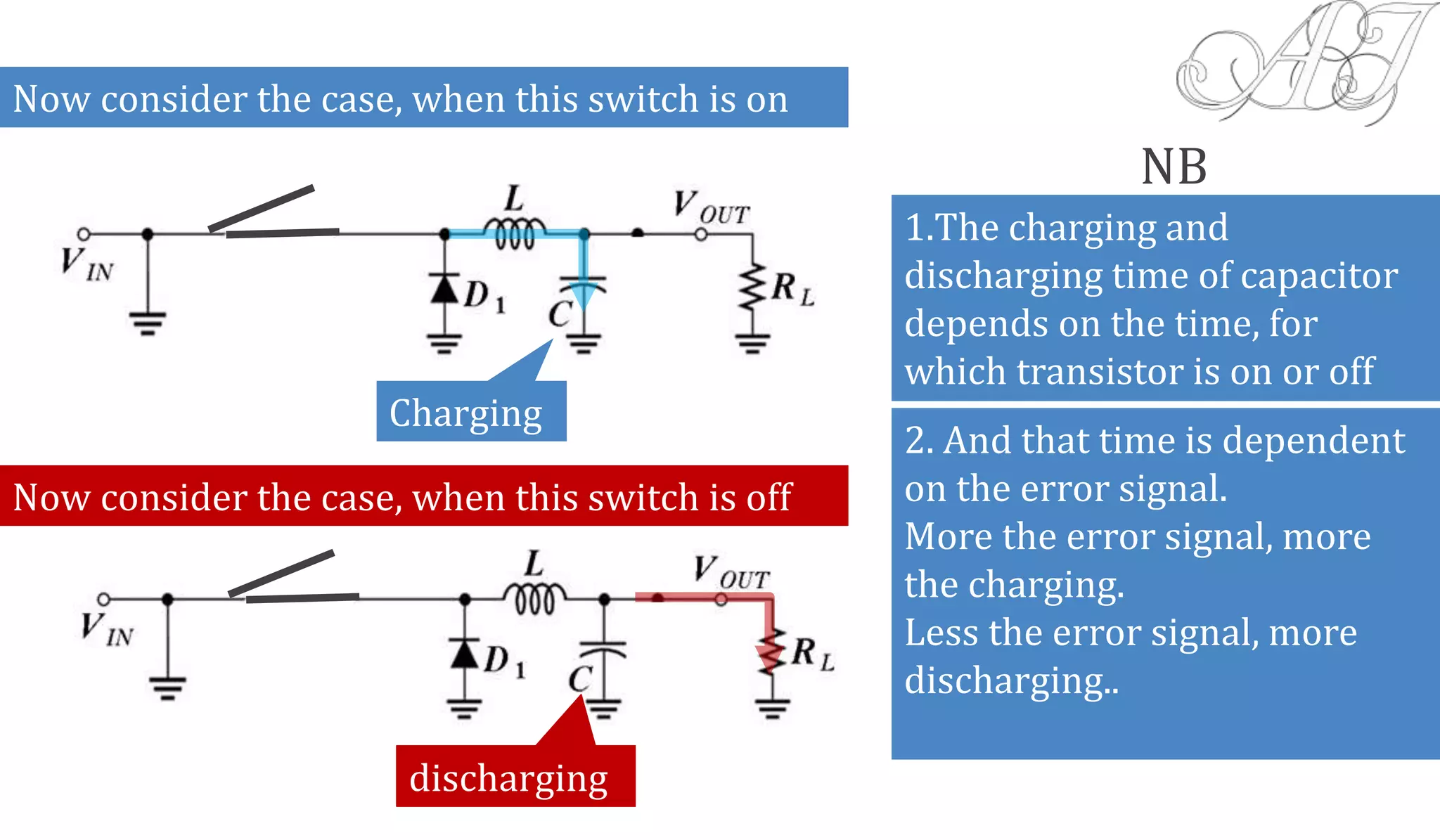
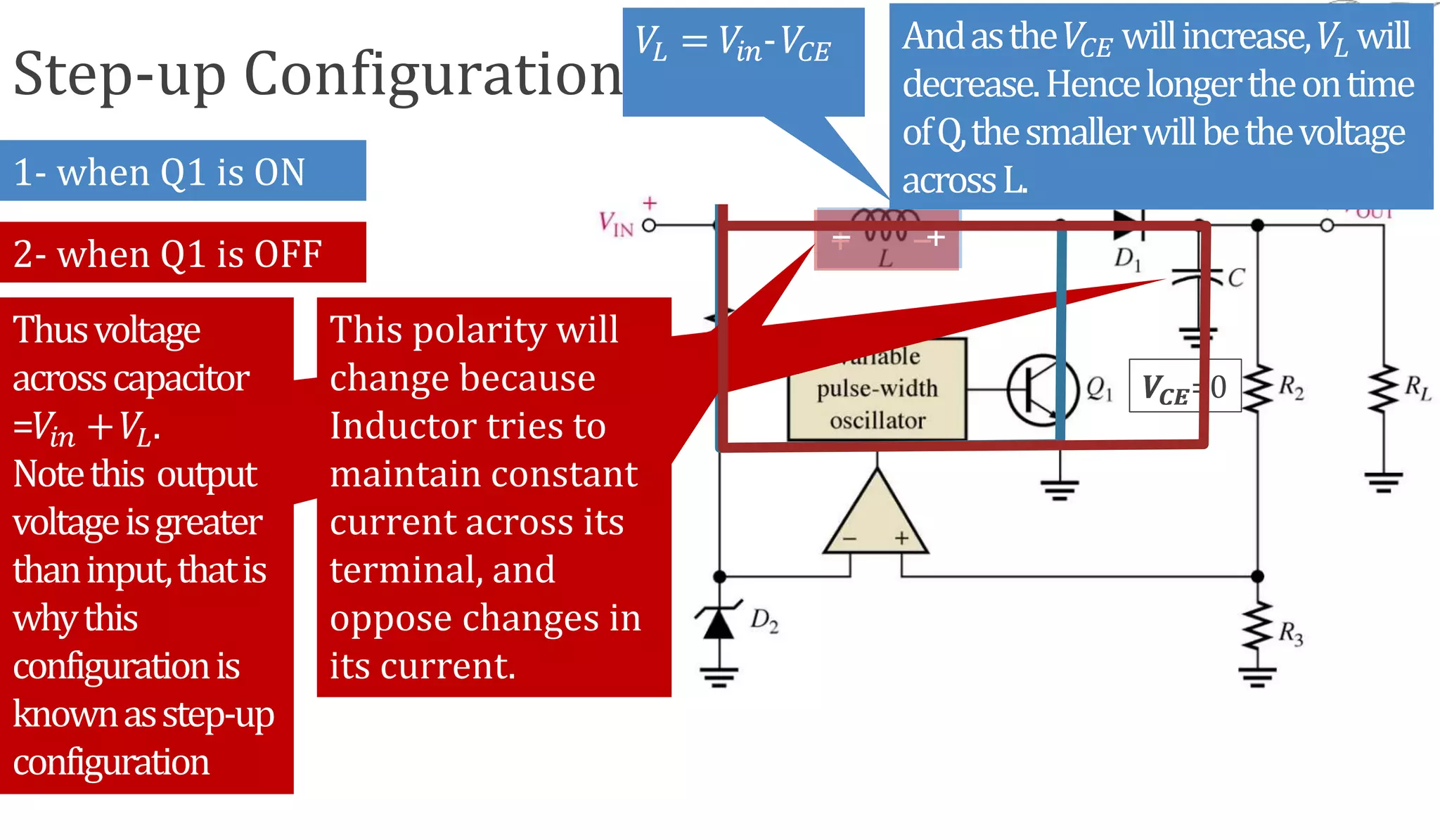
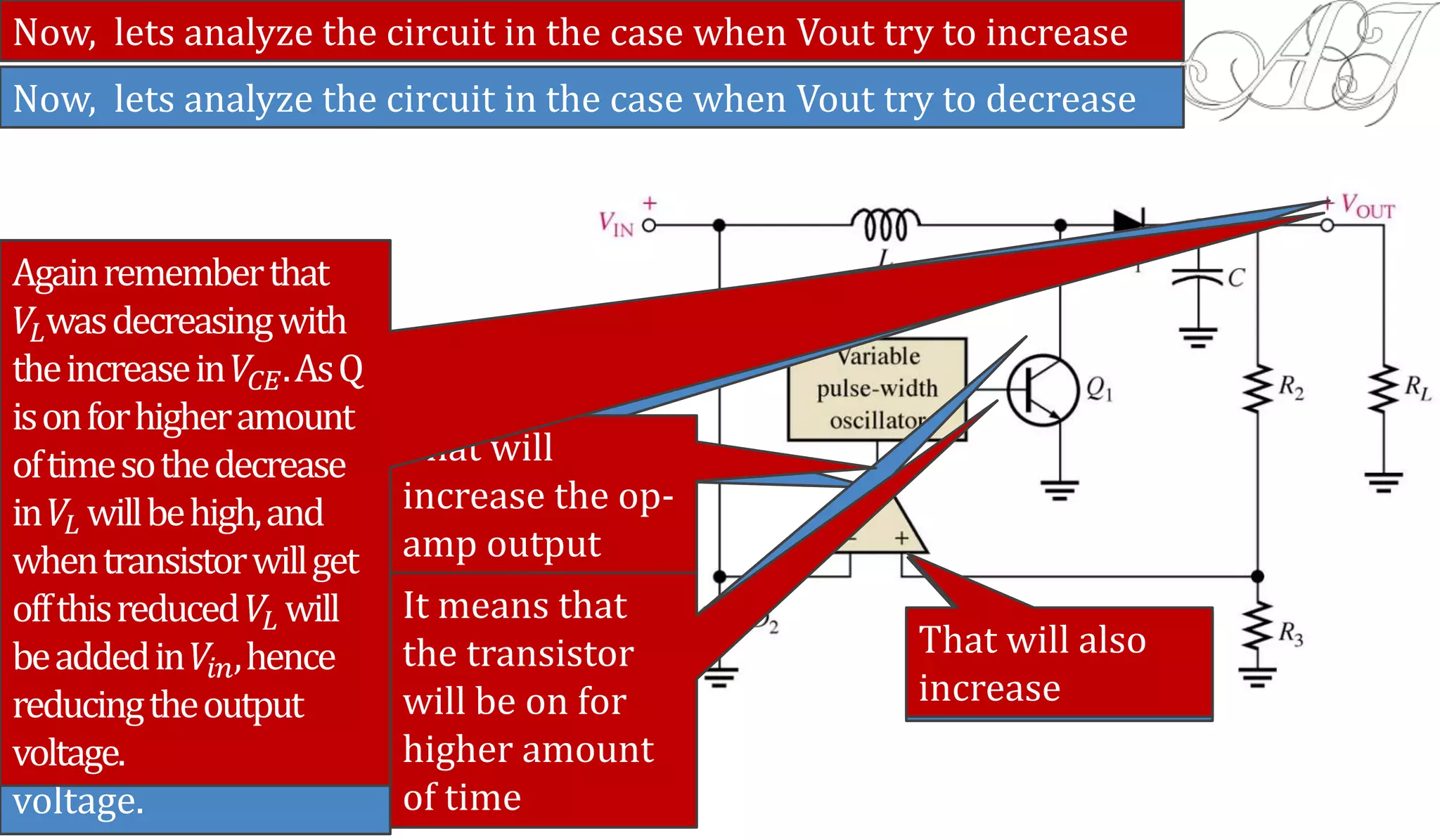
The document discusses various methods for obtaining regulated DC power from AC sources, focusing on the roles of voltage regulators, transformers, and different regulator configurations including linear and switching regulators. It provides a detailed analysis of series and shunt regulators, highlighting their feedback mechanisms for maintaining constant output voltage under varying load conditions. Additionally, it explains the operational principles of switching regulators, emphasizing their efficiency in high-current applications.