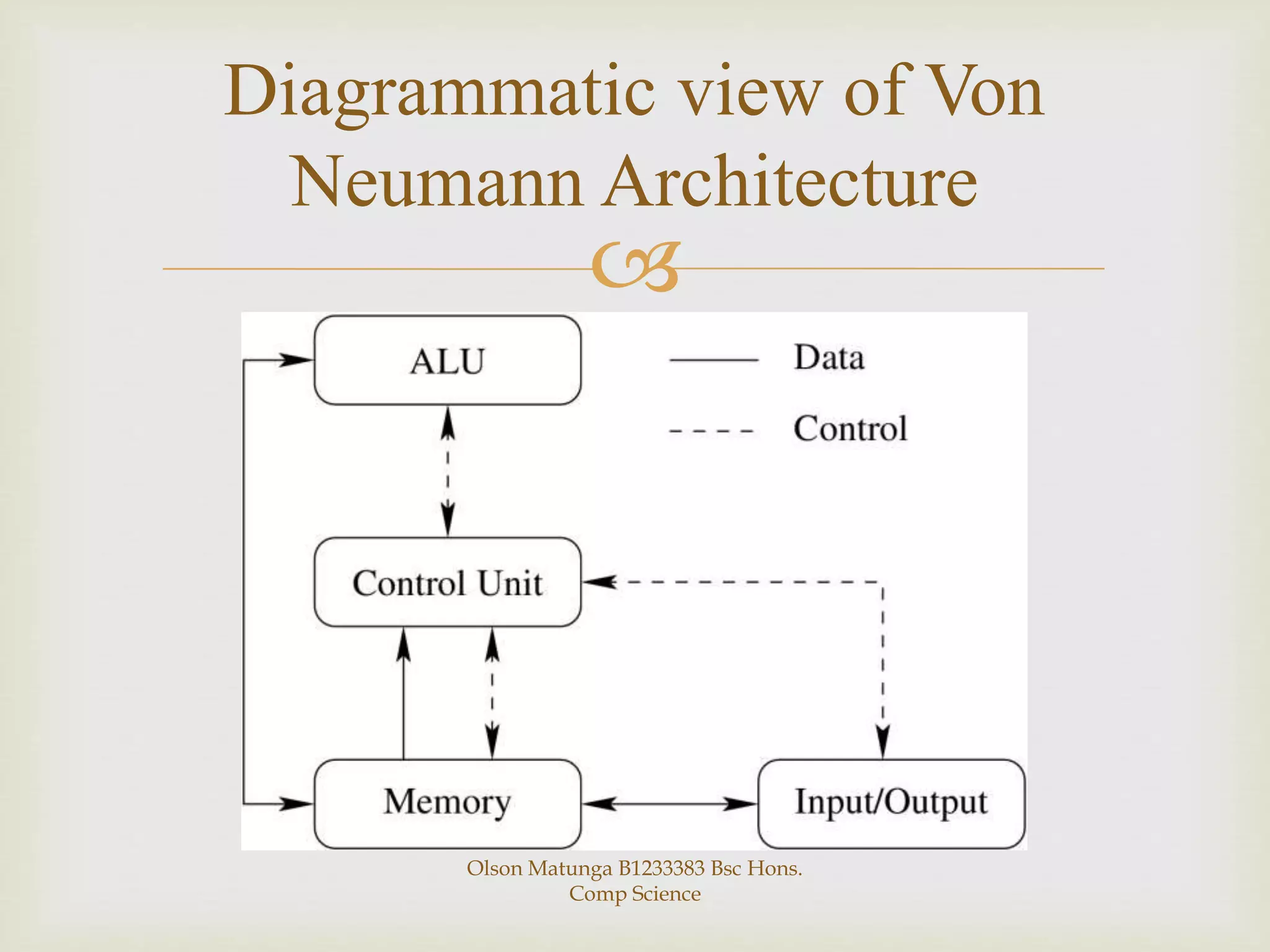
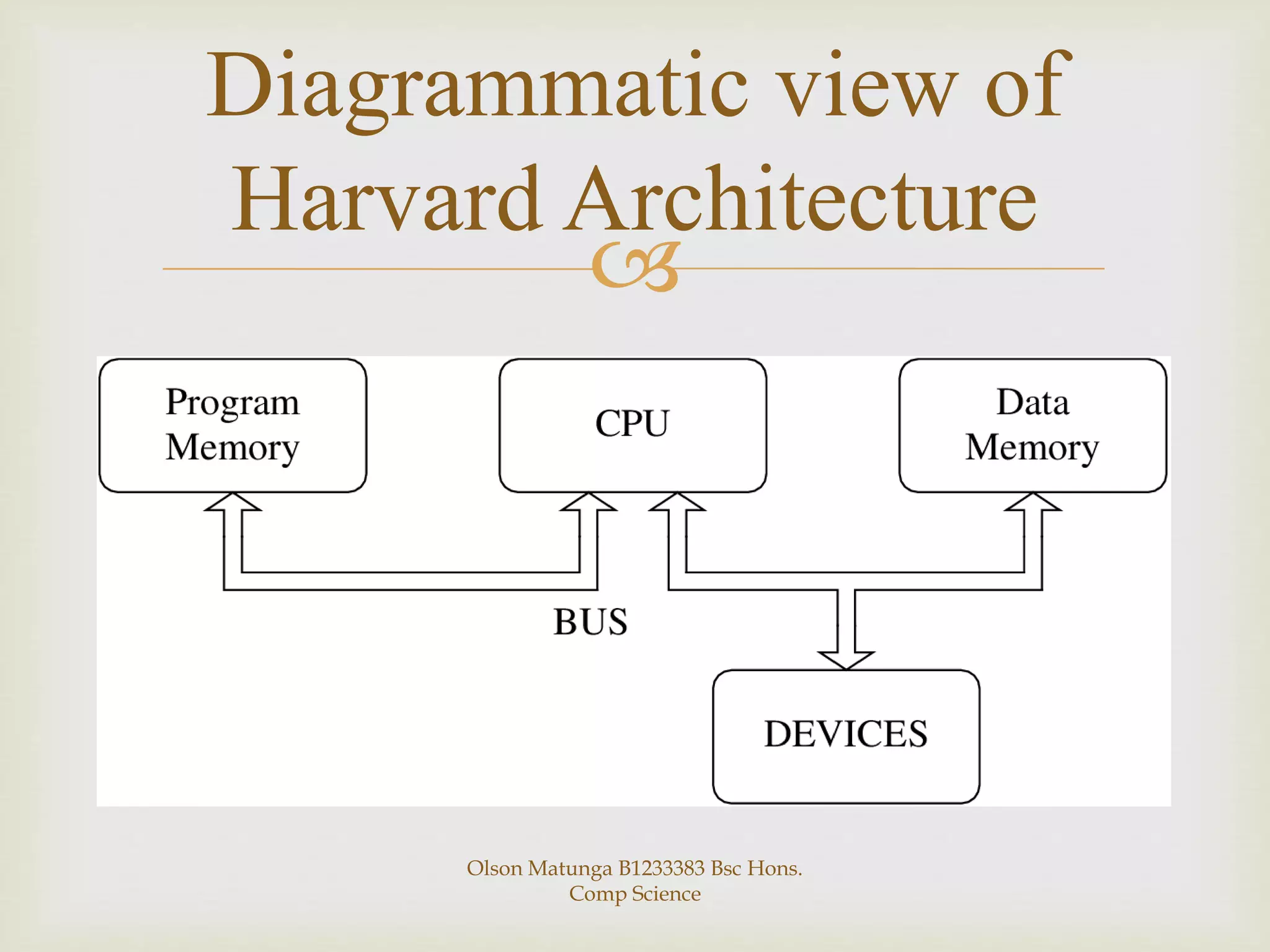
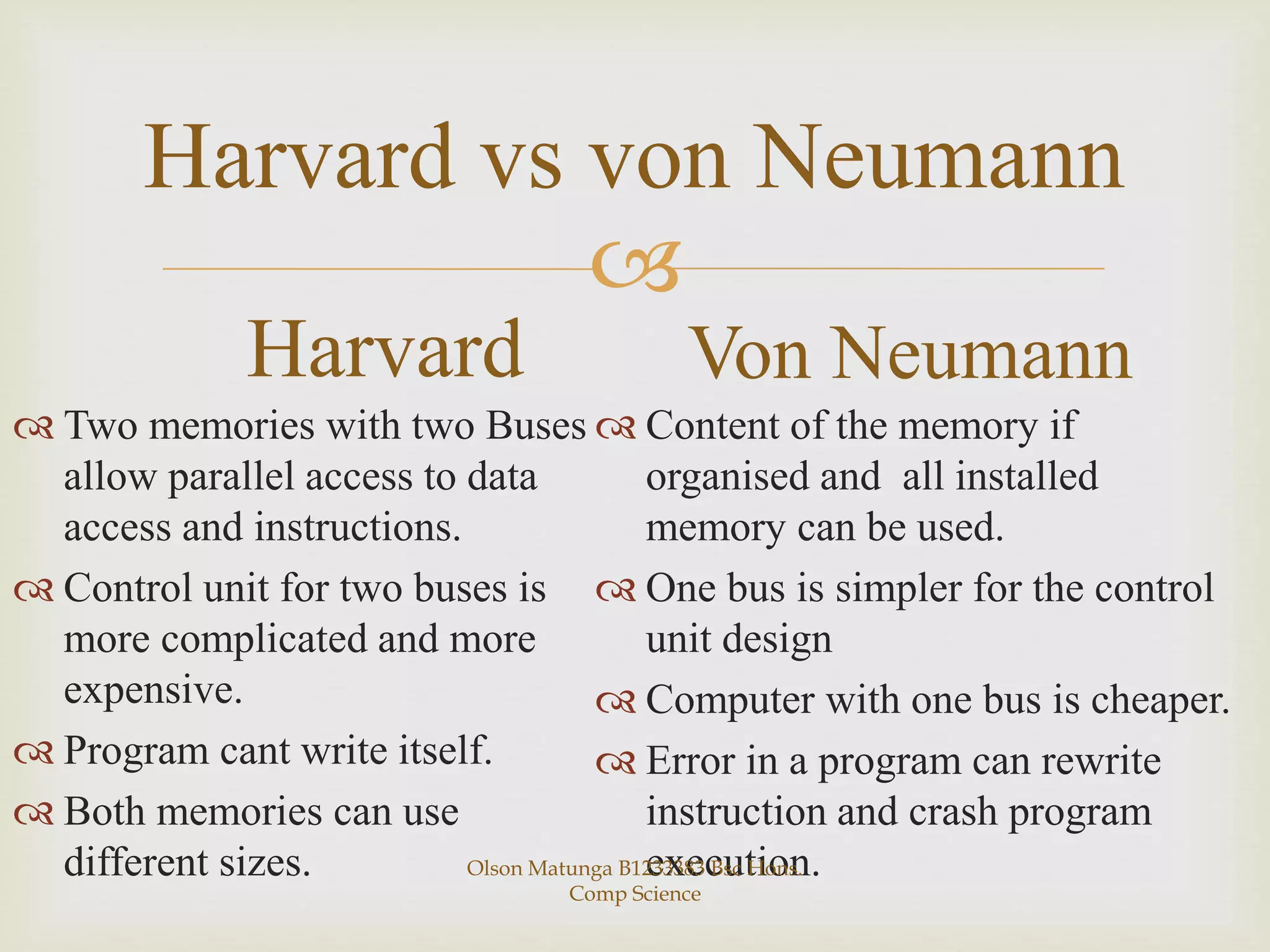
The Von Neumann and Harvard architectures are two common computer architectures. The Von Neumann architecture uses a single memory to store both programs and data, accessed via a shared bus, while the Harvard architecture separates memory and uses two separate buses for program and data access. The Von Neumann architecture has advantages of simpler design and lower cost while the Harvard allows parallel instruction and data processing but has higher development costs. They differ primarily in their memory structure and bus configurations.