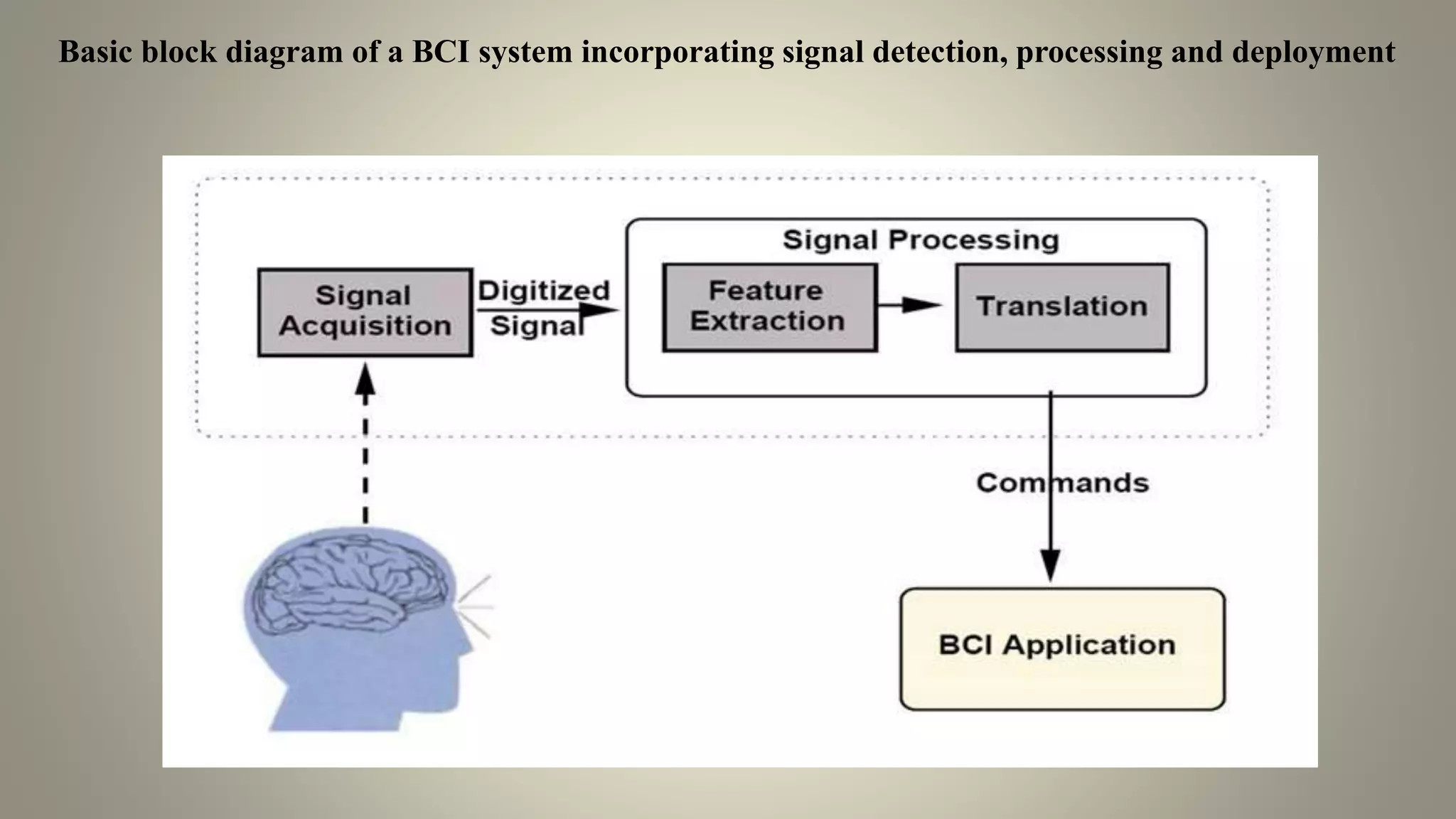
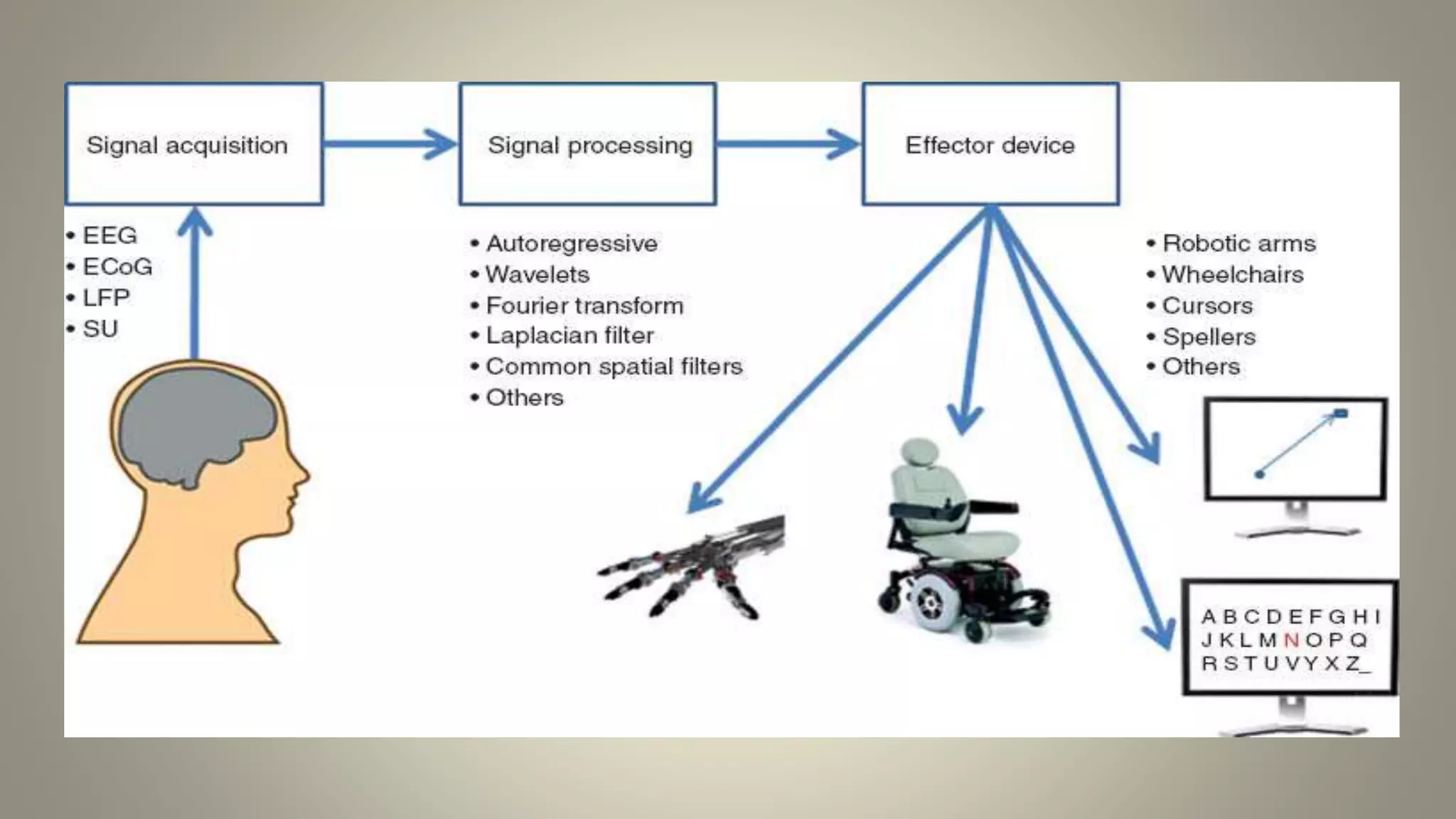
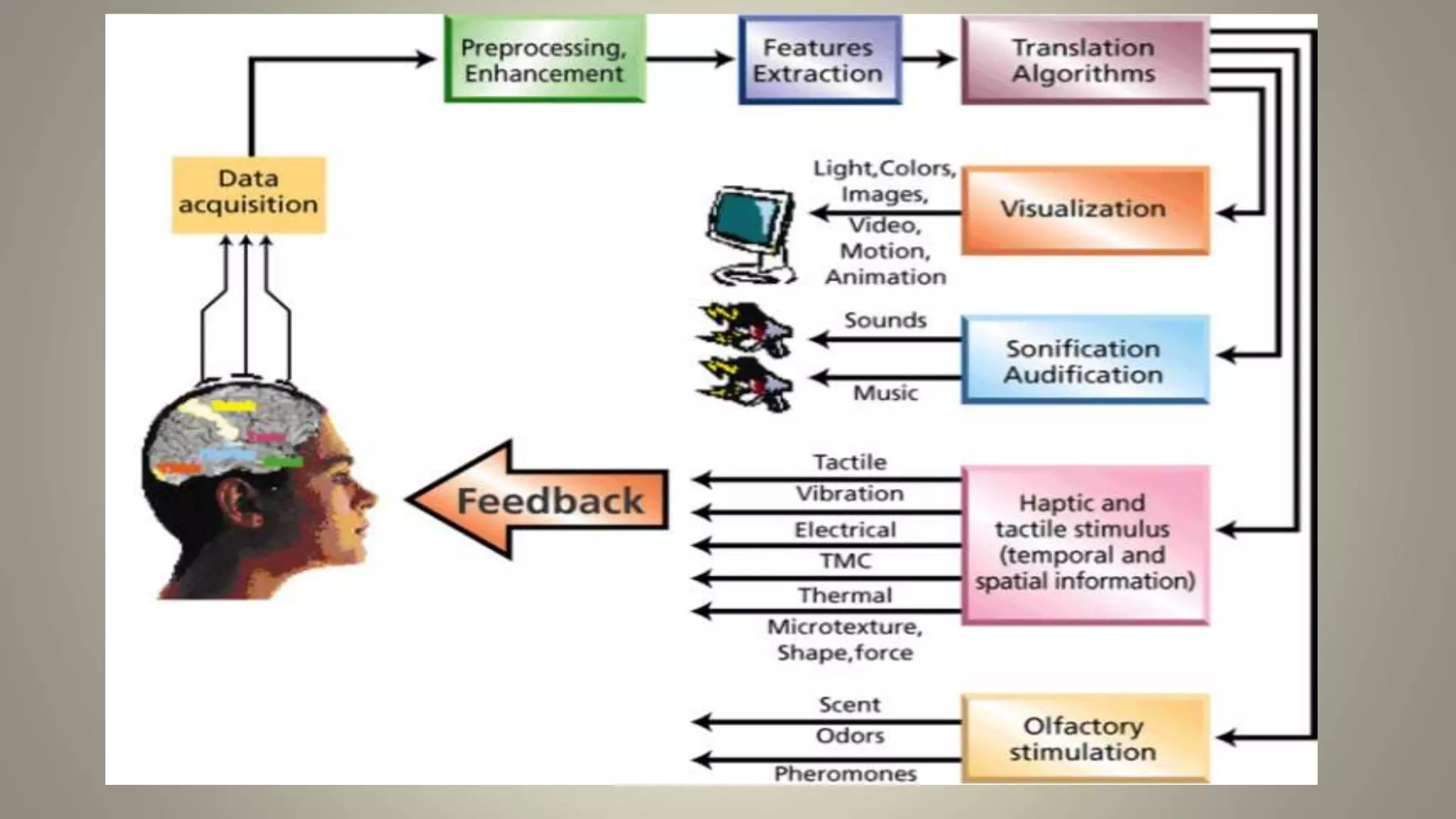
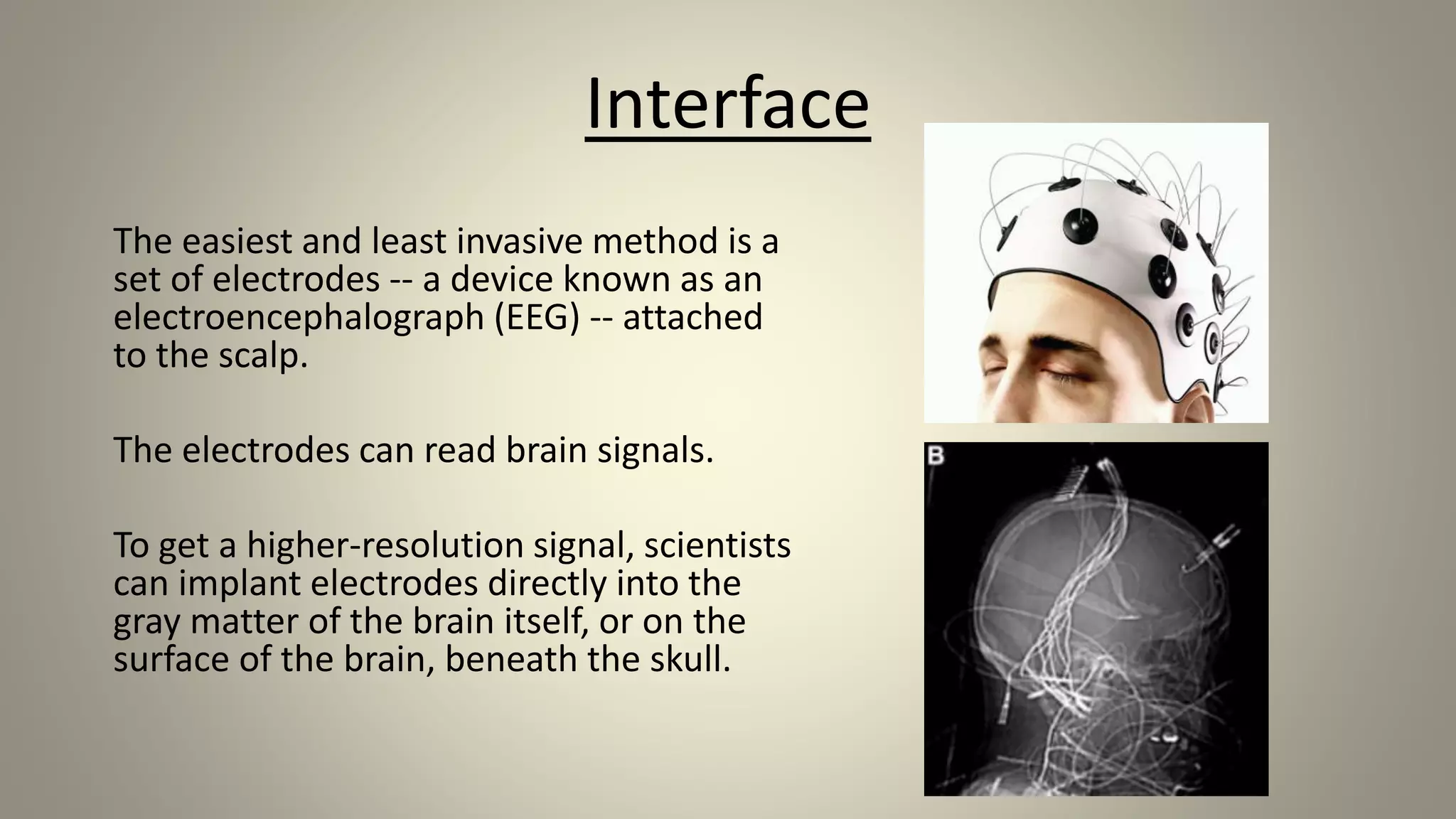
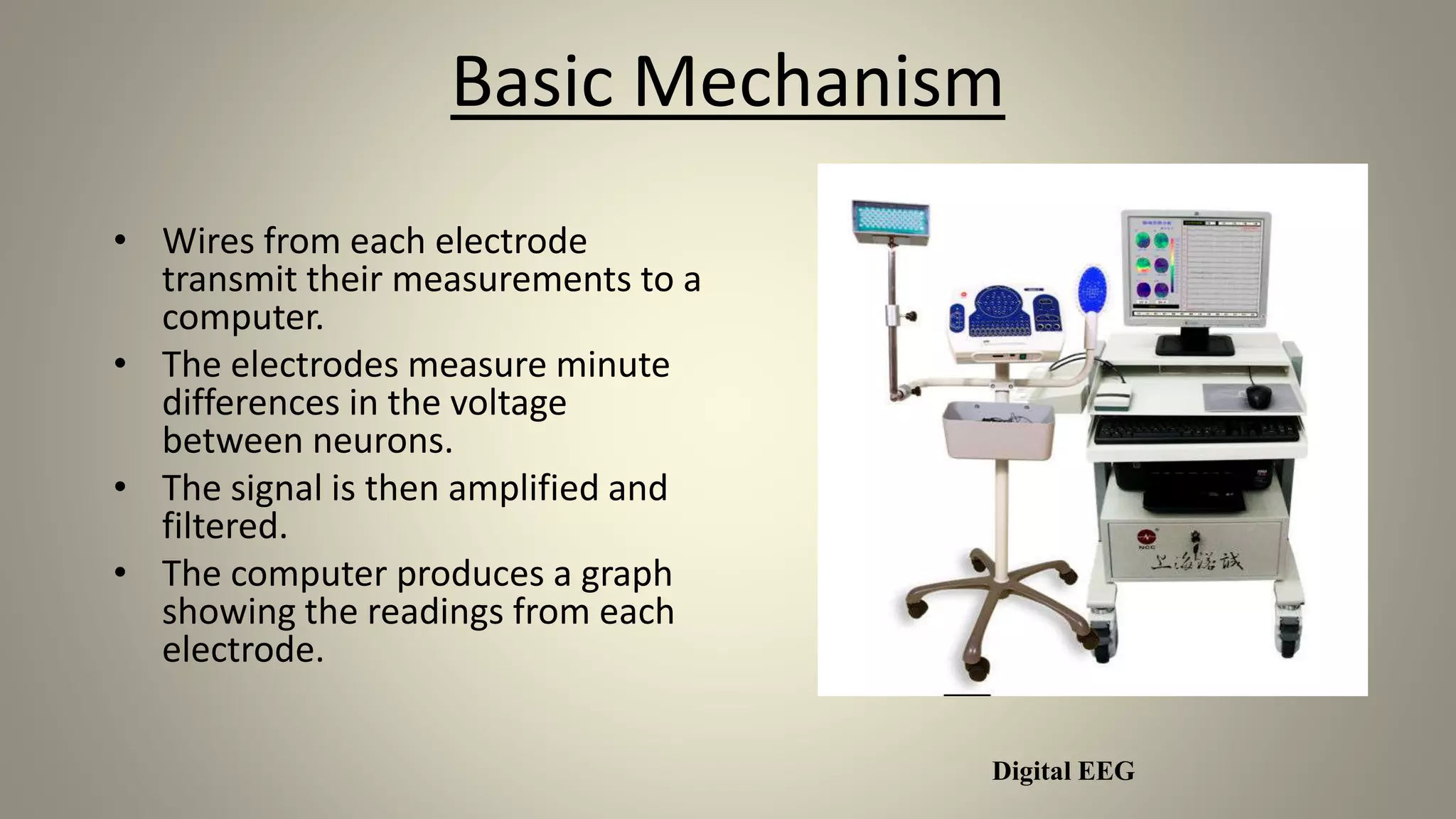
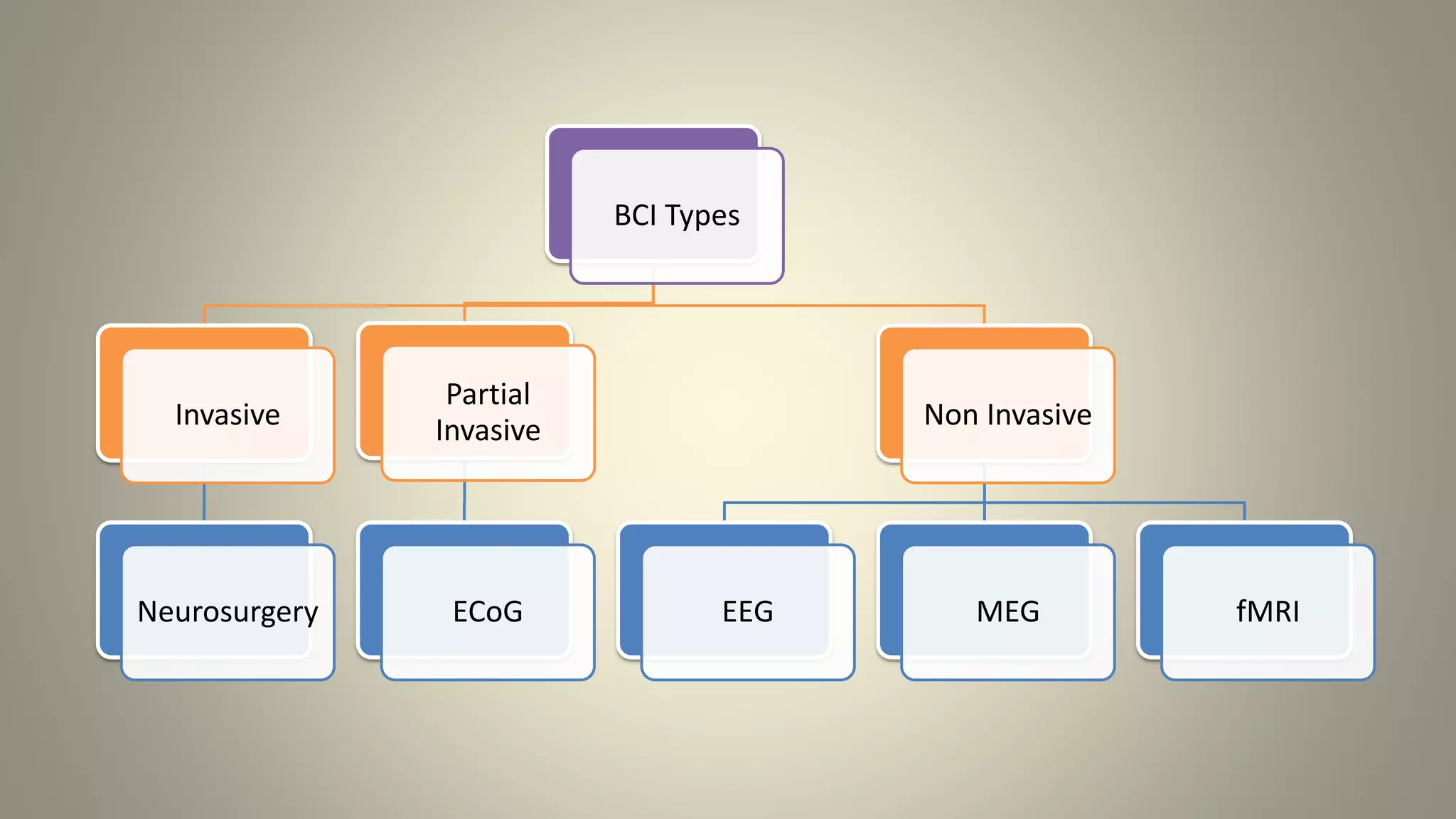
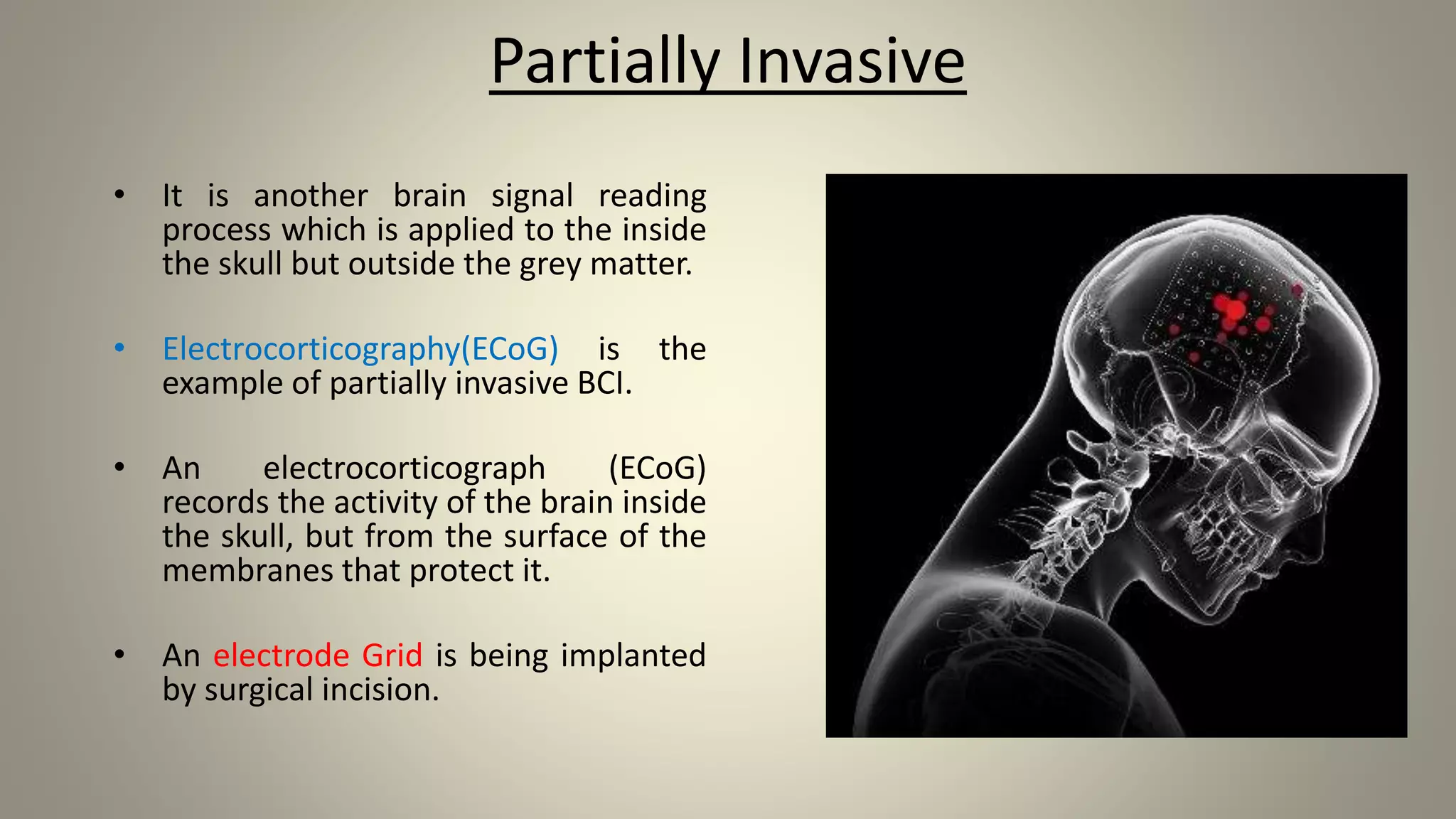
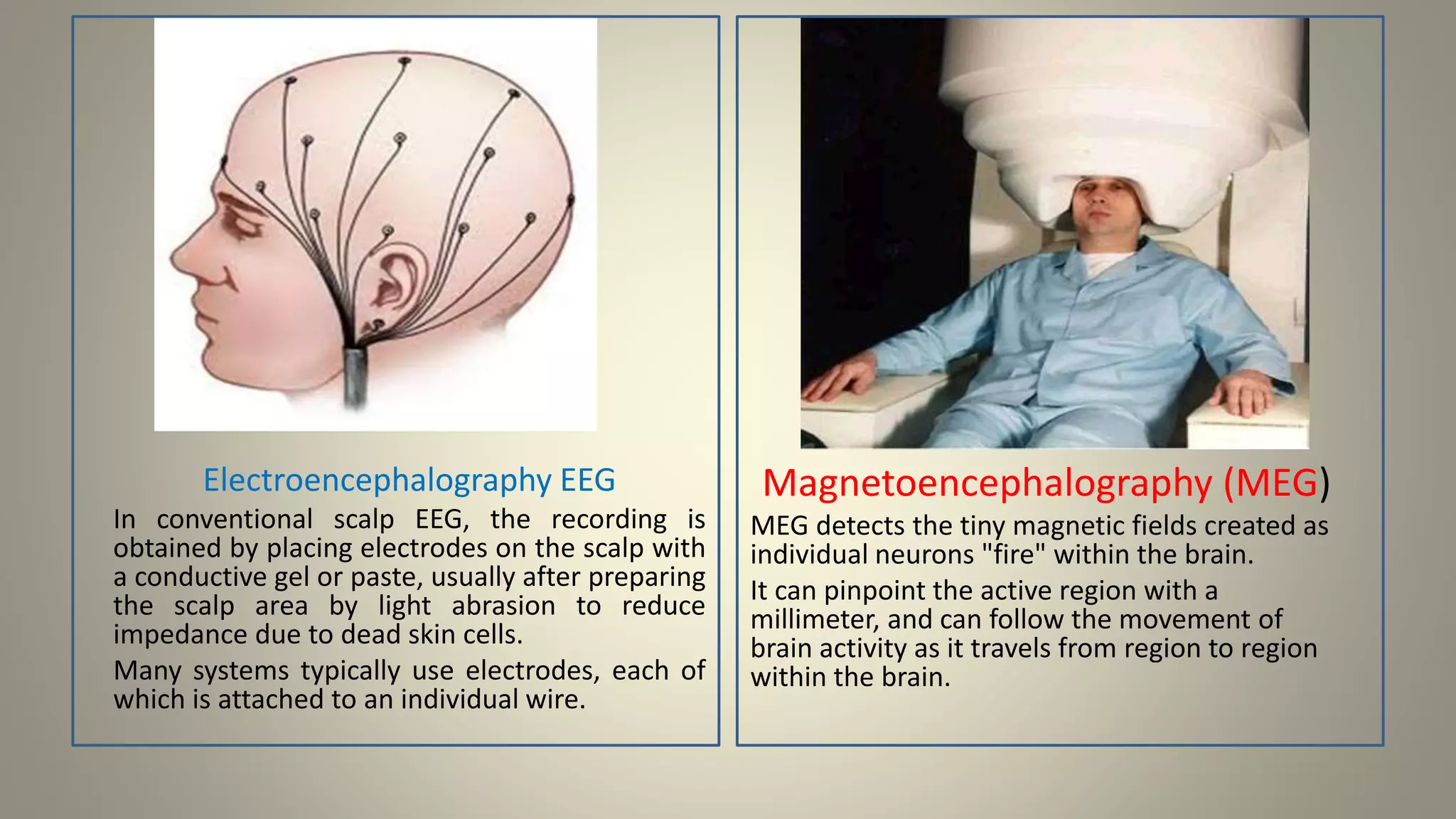
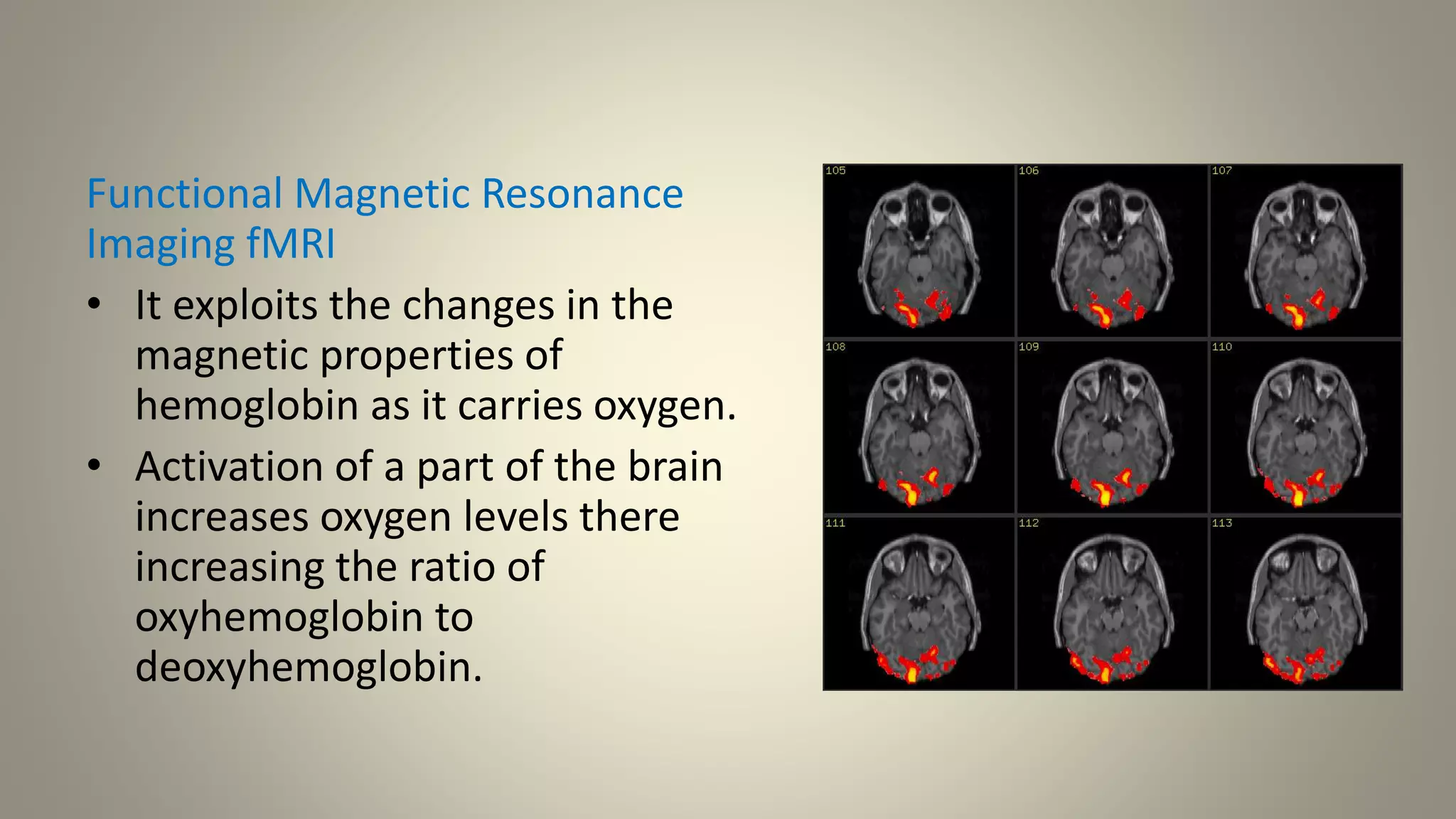
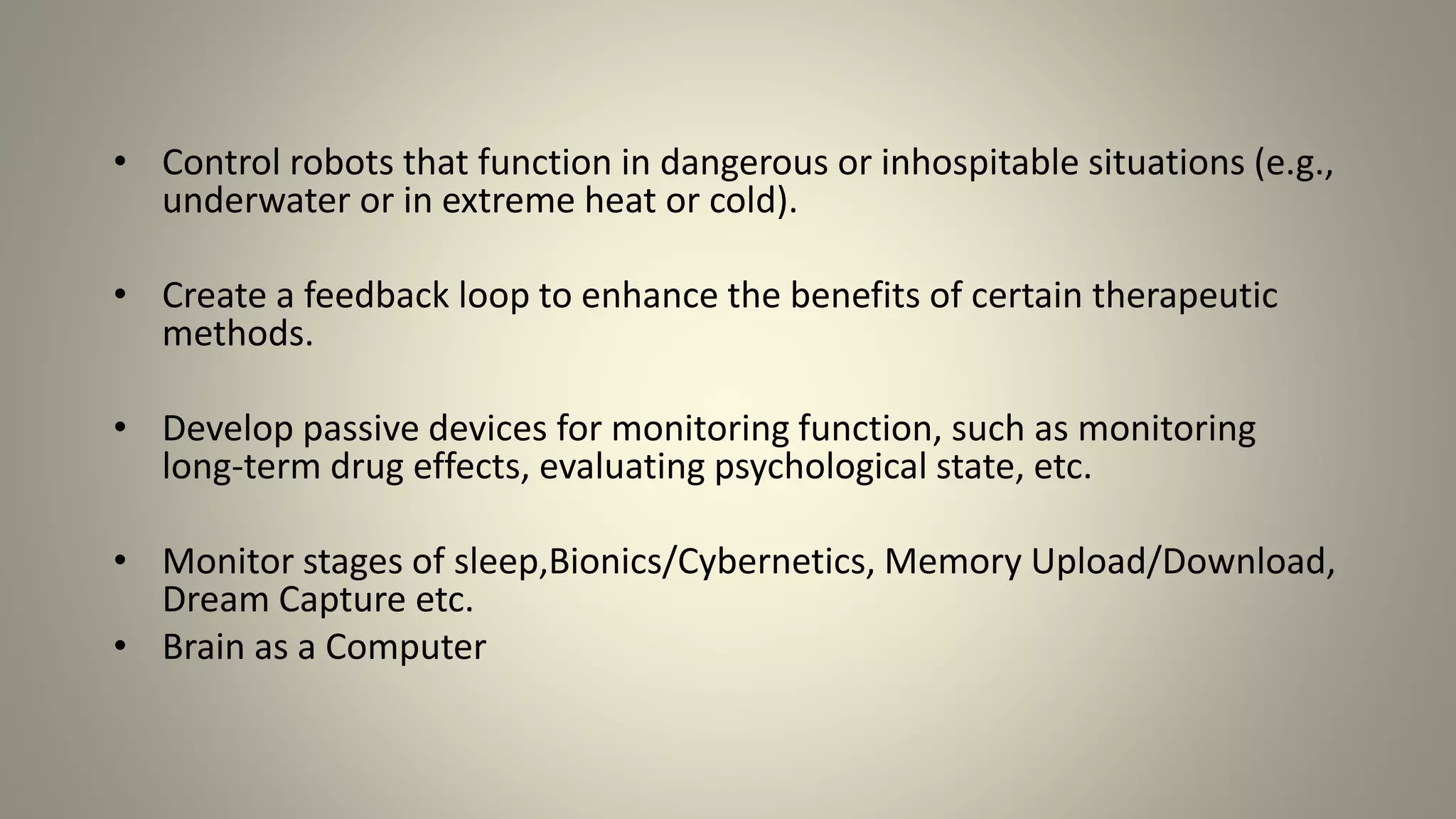
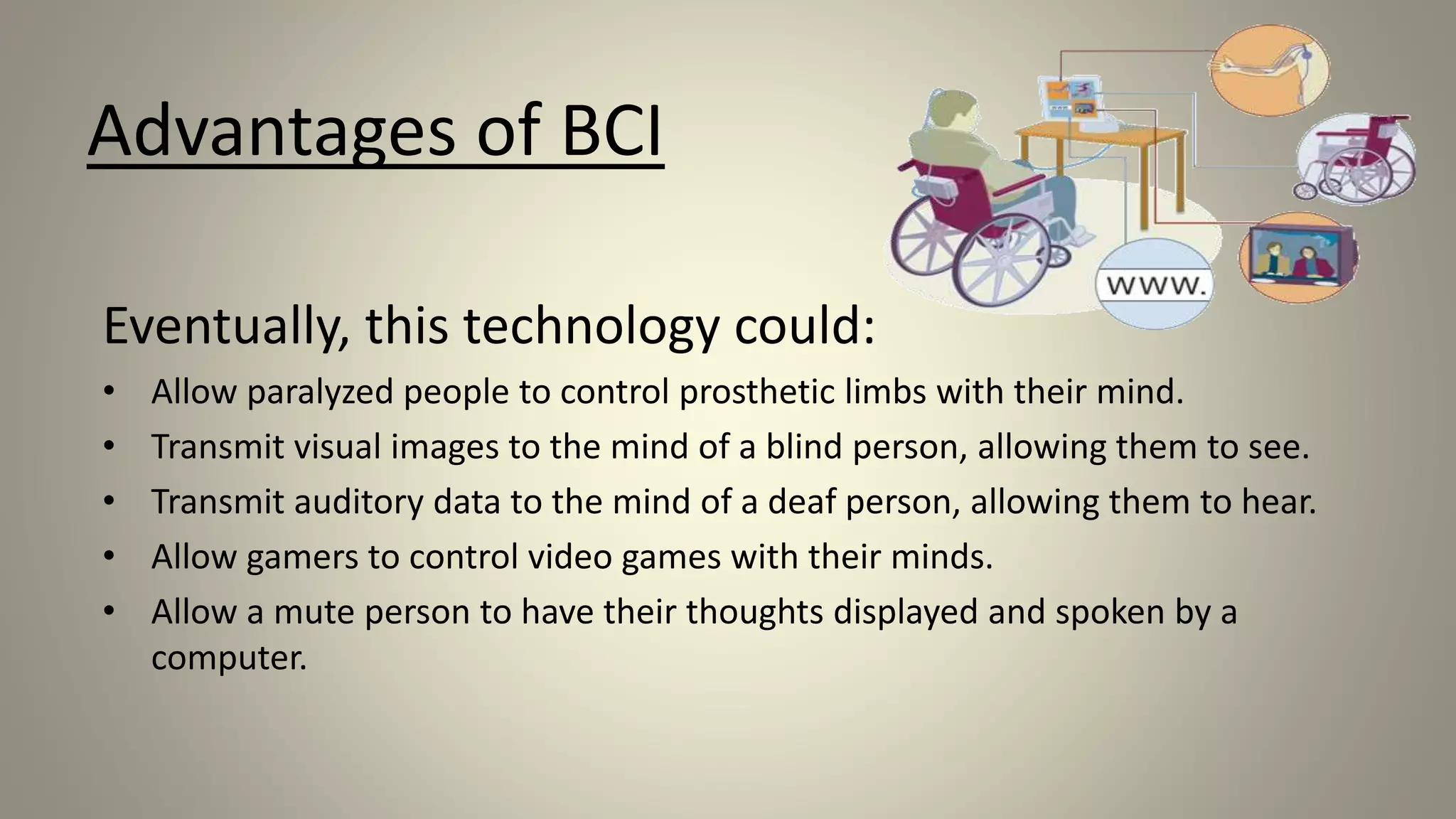
A brain-computer interface allows humans to control devices with their thoughts by detecting electric signals in the brain. BCI systems use electrodes to measure brain signals, which are translated into computer commands. There are invasive, partially invasive, and non-invasive types of BCI. Non-invasive systems use EEG, MEG, or fMRI to read brain activity through the skull. Potential applications include helping disabled people communicate and restoring movement, while advantages are aiding the paralyzed or blind. However, research challenges remain in improving crude technology and addressing ethical issues.
![SHEETAL G. PATEL
MSc. BIOTECHNOLOGY
[SEM II]
201504101110001](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/d6c5bbe0-c77b-438e-859e-a111948a0e64-160503043623/75/BCI-1-2048.jpg)