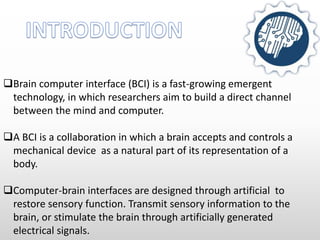
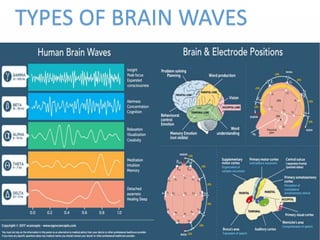
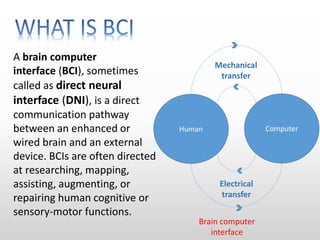
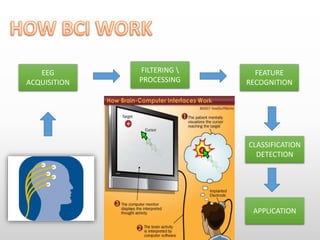
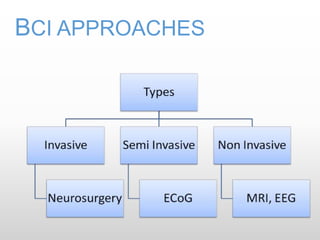
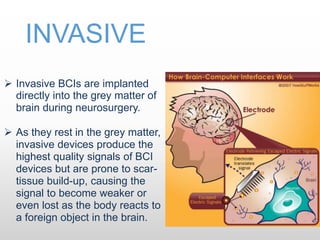
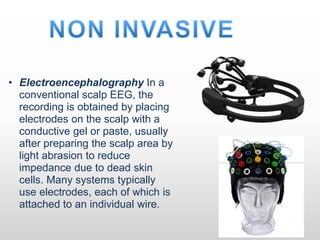
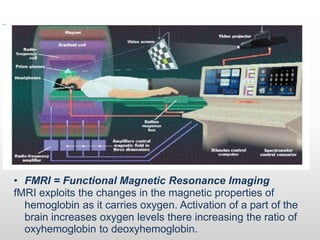
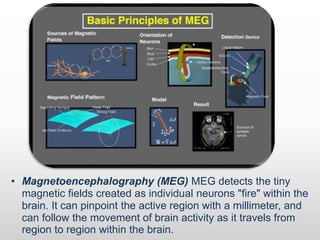
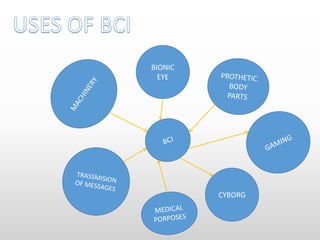
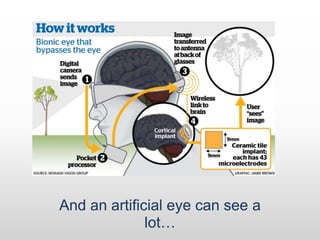
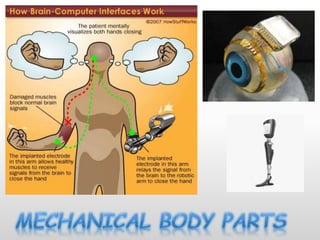
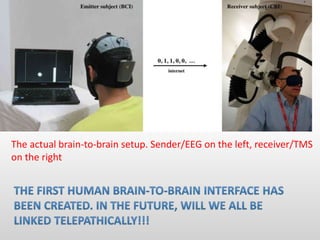
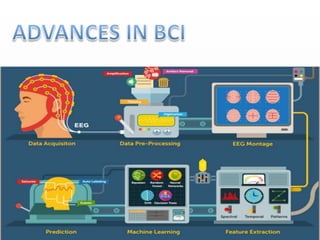
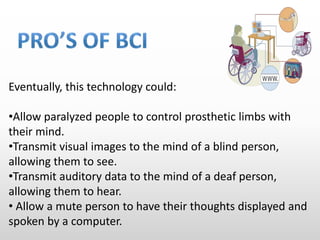
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are emerging technologies aimed at creating direct communication between the brain and computers, facilitating functions like restoring sensory abilities. The history of BCIs began with early research in the 1970s and significant milestones include the first EEG recordings by Hans Berger in 1924. Various BCI approaches exist, ranging from invasive methods to non-invasive techniques, each with pros and cons, and while the technology holds promise for aiding individuals with disabilities, ethical concerns and technological limitations remain prevalent.