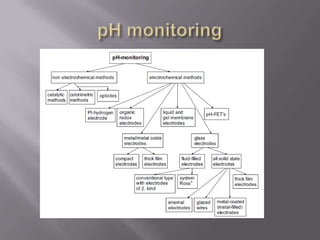
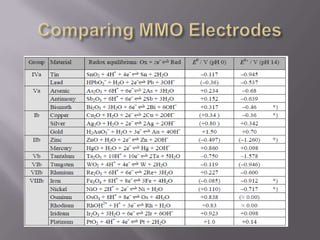
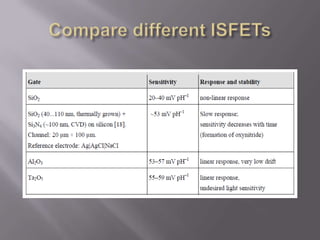
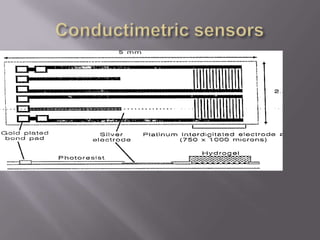
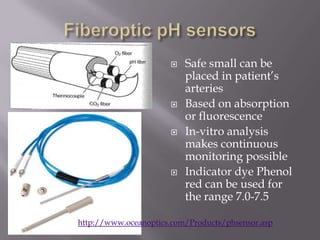
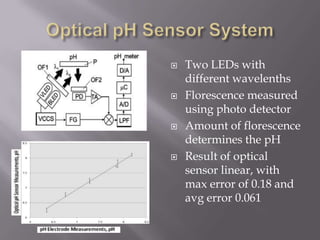
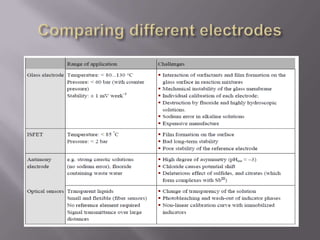
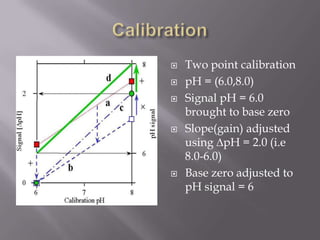
Blood pH is tightly regulated in the human body and generally lies between 7.3-7.5. pH monitoring is important in medical diagnosis and treatment, including for major diseases, surgeries, and drug effects. Various methods exist for measuring pH, including glass electrodes, metal-metal oxide electrodes, pH sensitive FETs, conductimetric sensors, and fiber optic sensors. Each method has advantages and limitations for different applications such as invasiveness, accuracy, and ability for continuous monitoring. Temperature also affects pH measurement so calibration is required.


![pH DefinedChemically: measure of acidity or basicity of a fluidPhysically: Measure of concentration of H+ ionsMathematically: pH = -log10[H+] Technically: Power or Potential of hydrogen ions in the fluid.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phmeasurementpresentation-12853231682887-phpapp01/85/Blood-pH-Measurement-3-320.jpg)