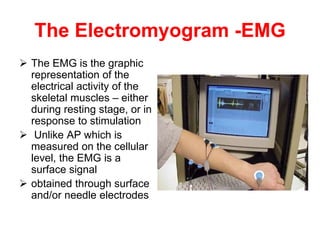
The document provides an overview of commonly used biomedical signals for monitoring physiological processes and detecting pathological conditions. It discusses several key signals including the electrocardiogram (ECG), electroencephalogram (EEG), electromyogram (EMG), electroretinogram (ERG), electrooculogram (EOG) and event-related potentials (ERPs). For each signal, it describes what physiological process is being measured, how the signal is recorded, its typical amplitude and bandwidth, main sources of interference and common applications. The document emphasizes that biomedical signals reflect the electrical, chemical and mechanical activities of cells, tissues and organs, and can provide important diagnostic information when analyzed.