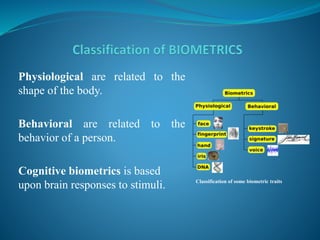
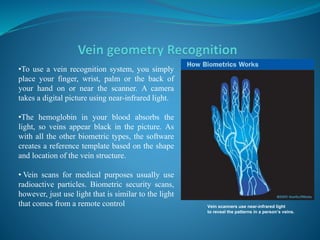
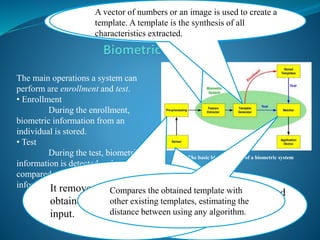
The document provides an overview of biometric security systems. It defines biometrics as measuring unique human characteristics and discusses various physiological and behavioral biometric traits used for identification, including fingerprints, facial recognition, voice recognition, hand geometry, retina and iris scanning. It covers classification of biometric traits, factors for determining their effectiveness, functions of biometric systems, and concerns regarding privacy, standardization and overreliance. The document concludes by discussing potential future applications of biometric technologies in hospitals, forensics and membership programs.