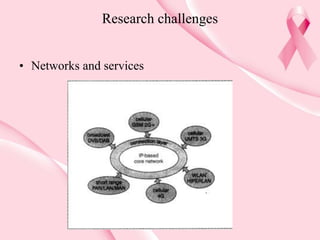
This document summarizes a seminar on 4G wireless systems. It discusses the limitations of 3G networks and the drivers for 4G, including fully converged services, ubiquitous access, diverse devices, and autonomous, software-defined networks. The document outlines research challenges in networks/services, software systems, and wireless access technologies to achieve the 4G visions. These include adaptive reconfigurability, spectral efficiency, all-pervasive coverage, and software-defined radios and networks. While the exact 2010 scenario may change, the key 4G elements of converged services, ubiquitous access, diverse devices, and software-driven networks will remain goals for research.