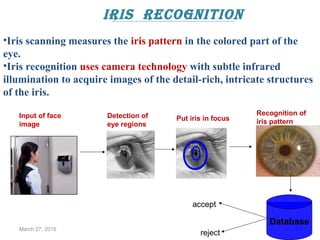
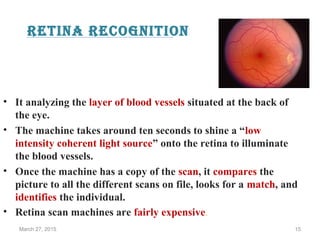
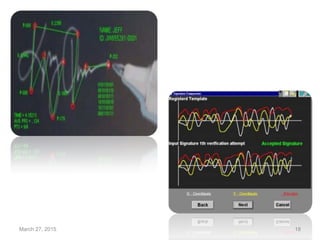
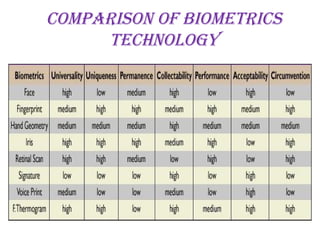
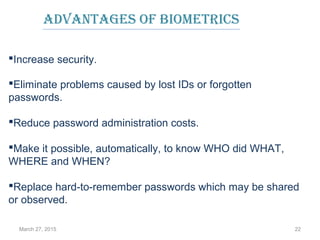
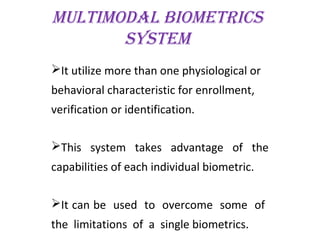
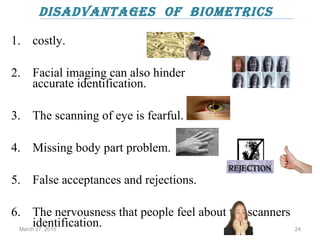
The document provides a comprehensive overview of biometrics, defining it as the automatic identification of individuals through physiological and behavioral characteristics. It covers the history, various recognition techniques (such as fingerprint, face, iris, and voice recognition), applications, and the advantages and disadvantages of biometrics. The conclusion highlights the potential growth of biometrics technology and its promise to enhance privacy and security in the future.