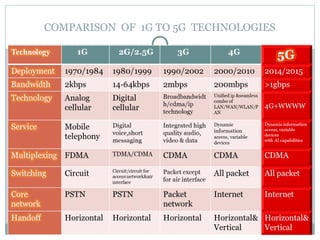
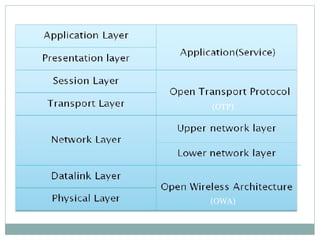
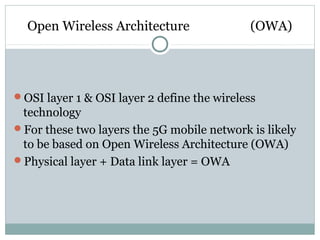
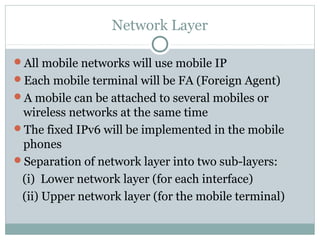
5G technology will provide significantly faster wireless speeds up to 1 Gbps, lower latency, and better support for wireless connectivity between devices. It evolved from 1G to 5G networks with increasing speeds and capabilities. 5G uses new hardware like ultra wideband networks and smart antennas and software like a unified global standard and open transport protocol. Key benefits of 5G include high data bandwidth, global accessibility, and support for applications like wearable devices, media streaming, and virtual reality.