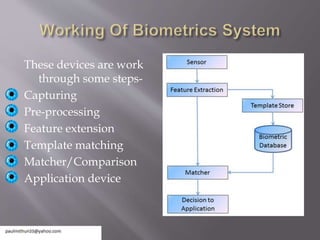
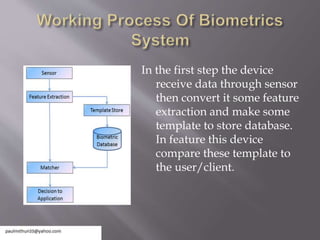
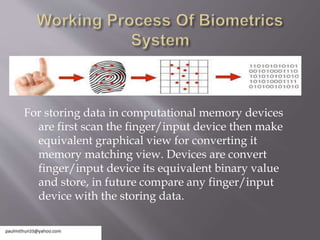
The document discusses biometric systems for security. It defines biometrics as measuring biological traits to identify individuals. It then discusses the history of biometrics using fingerprinting in China in the 14th century. It describes the main types of biometric devices as behavioral (e.g. voice, signature) or physical (e.g. fingerprint, face) and lists their common uses including banking, attendance tracking, and data security. Finally, it compares biometric security to other methods and outlines some limitations such as noise in data and variations over time.