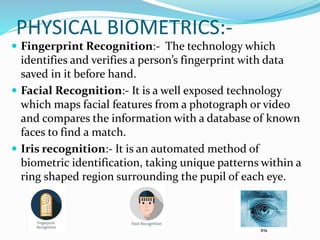
The document discusses biometric technology. It begins with a brief history of biometrics, noting that the first real biometric system was created in 1870 and fingerprints were first used for identification in 1892. It then defines biometrics as automated methods of identifying individuals based on physiological or behavioral characteristics. The document outlines the main components of a biometric system including modes of operation, typical blocks, and types of biometrics. It provides details on specific biometric technologies like fingerprint, facial, and iris recognition. The benefits, advantages and disadvantages as well as applications of biometric systems are also summarized.
![Sardar Patel Memorial Society’s (Trust)
RAJIV GANDHI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING,
RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY,
CHANDRAPUR
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
SEMESTER- III
SESSION-2022-23
A SEMINAR ON
BIOMETRIC TECHNOLOGY
Under the guidance of
Prof. MINAKSHI GETKAR
AND
SEMINAR IN-CHARGE
Prof. RUPATAI LICHODE
Presented By-
GAURAV MANOHAR WANKAR[CSEC322]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminaronbiometrictechnology-230217122410-5a6a8f60/75/SEMINAR-ON-BIOMETRIC-TECHNOLOGY-1pptx-pptx-1-2048.jpg)