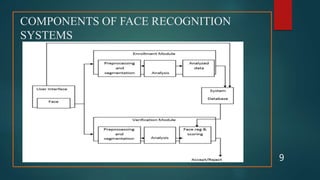
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on face recognition technology. It begins with an introduction to facial recognition systems and what biometrics are. It then discusses why facial recognition is chosen over other biometrics, the differences between facial recognition and face detection, and how facial recognition systems work. Application areas are identified, such as security, government ID, casinos. Advantages include convenience and cost-effectiveness, while disadvantages include issues with lighting, pose, and privacy concerns. The growth rate of the facial recognition market is projected to be nearly 14% annually through 2022.