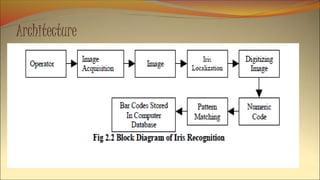
The document provides a comprehensive overview of iris recognition as a biometric technology, highlighting its accuracy, unique characteristics, and applications in security and personal identification. It discusses the process of iris recognition, including image acquisition, preprocessing, analysis, and recognition, along with the advantages and disadvantages of the technology. Additionally, it compares iris recognition with other biometric systems and emphasizes its growing relevance in various security applications.