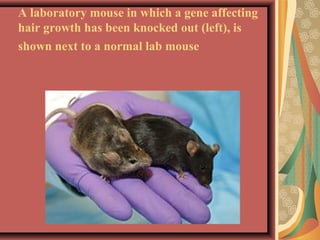
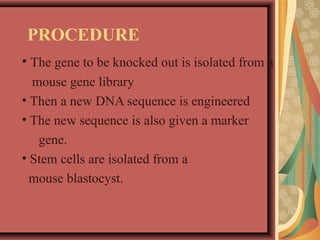
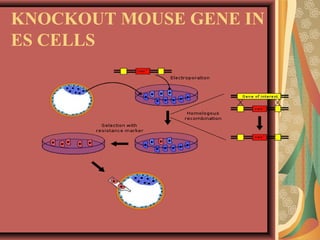
Gene knock out technology involves replacing or disrupting an existing gene with artificial DNA to study gene function. The first knockout mouse was created in 1989. Knockout mice and microorganisms are commonly used animal models for studying genes in the laboratory. The procedure involves isolating the target gene, engineering a new DNA sequence with a marker gene, introducing this into stem cells via electroporation, and breeding mice with the knocked out gene. Knockout technology allows determining gene functions, creating mouse models of human diseases, and characterizing genetic regulatory regions.