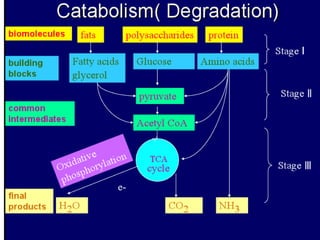
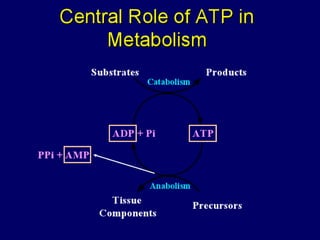
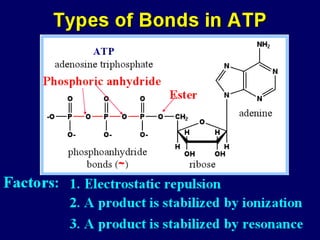
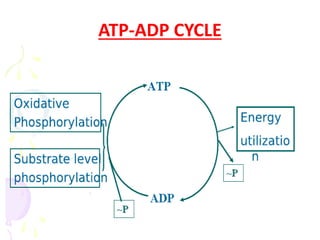
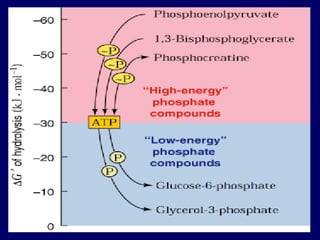
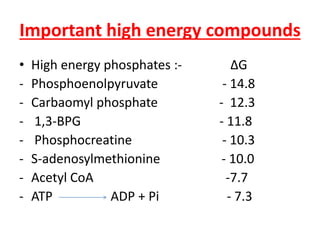
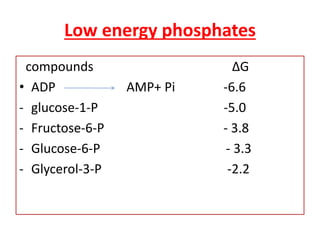
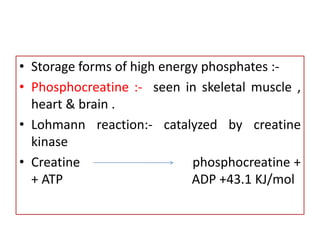
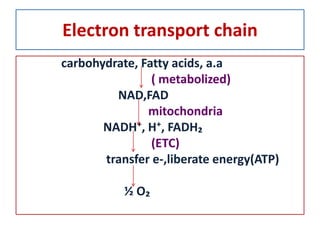
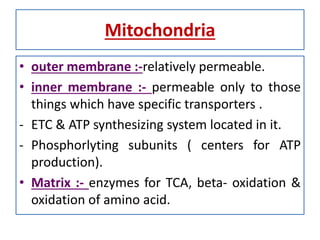
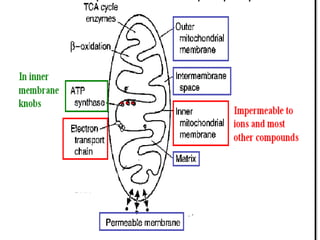
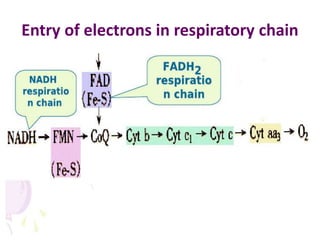
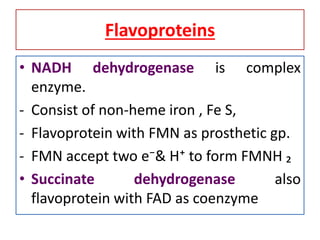
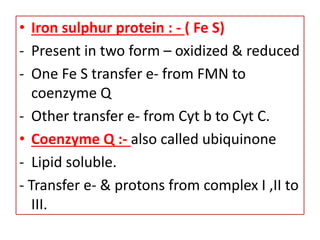
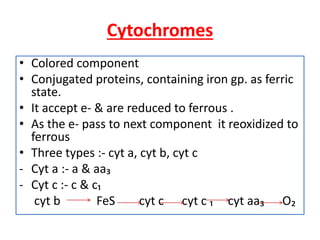
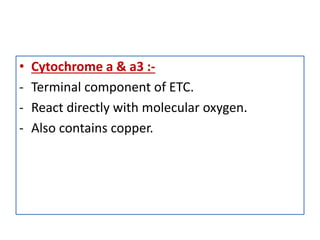
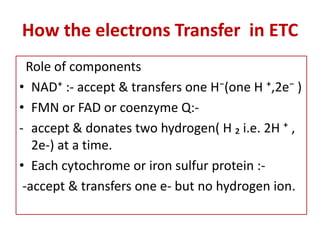
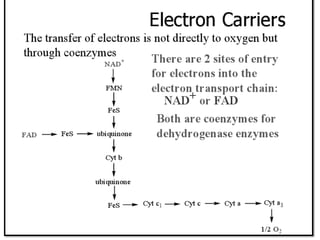
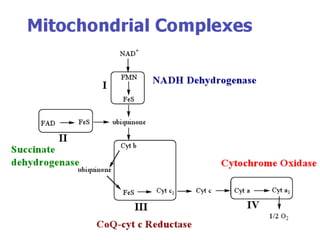
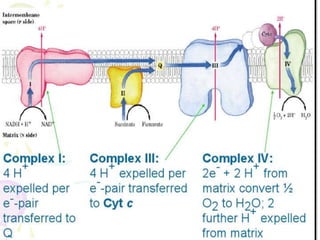
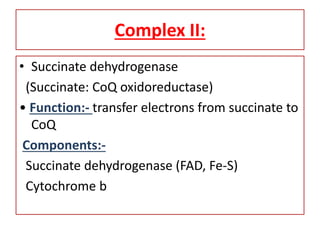
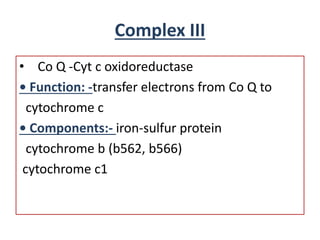
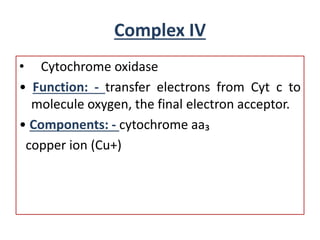
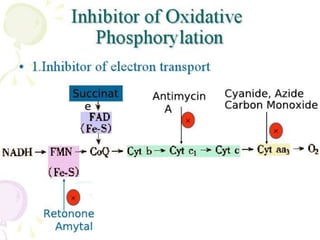
Biological oxidation is the process by which organic substances like carbohydrates, fats, and proteins release energy through redox reactions in cells. This energy is captured in the form of ATP, which is used to power various cellular processes. The electron transport chain located in the inner mitochondrial membrane facilitates the transfer of electrons from electron carriers like NADH and FADH2 to oxygen. This releases energy to synthesize ATP through oxidative phosphorylation and substrate-level phosphorylation. Key components of the electron transport chain include complexes I-IV which contain enzymes, cofactors, and cytochromes that sequentially pass electrons from one to the next until they reach oxygen, the final electron acceptor.