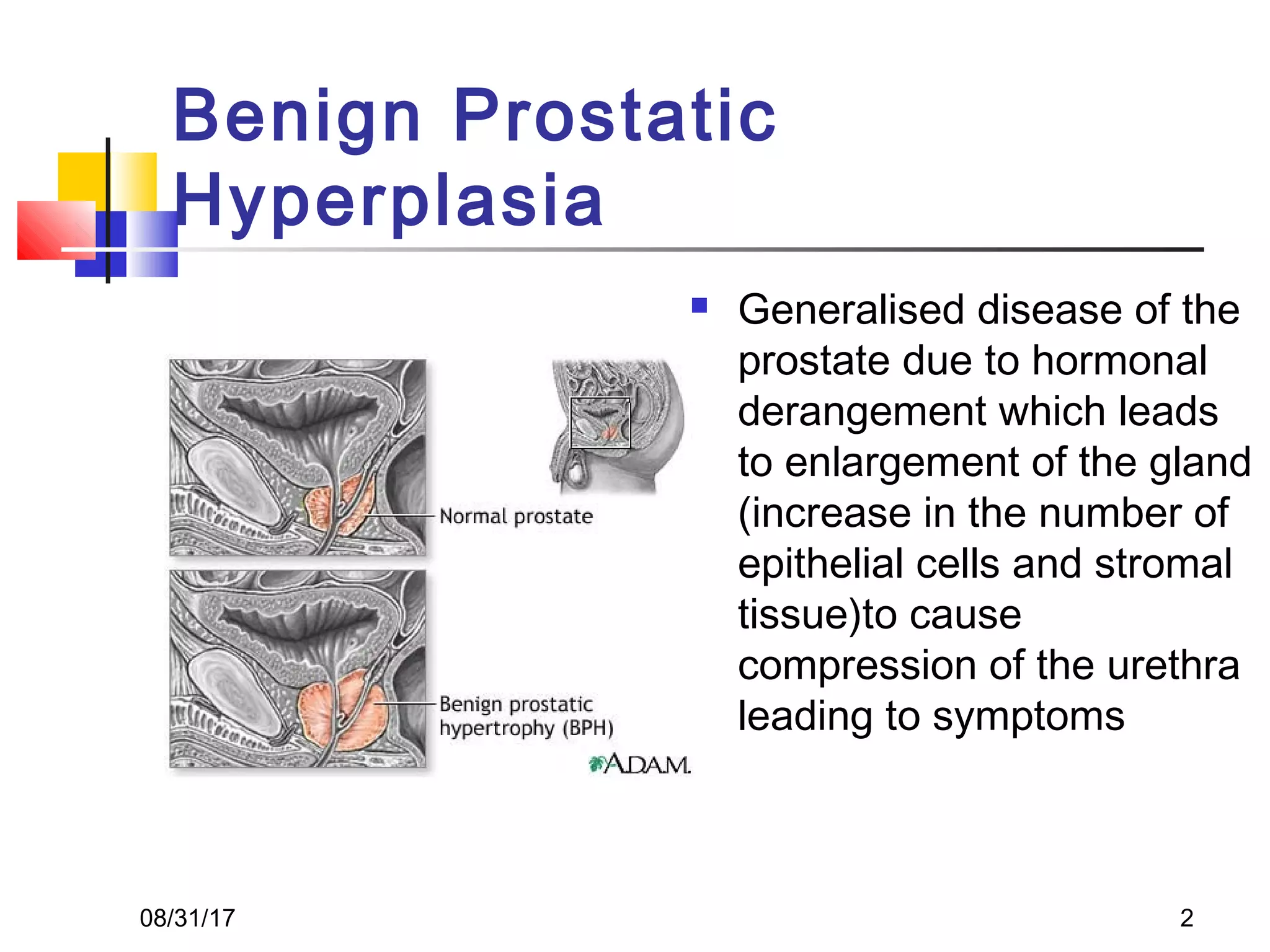
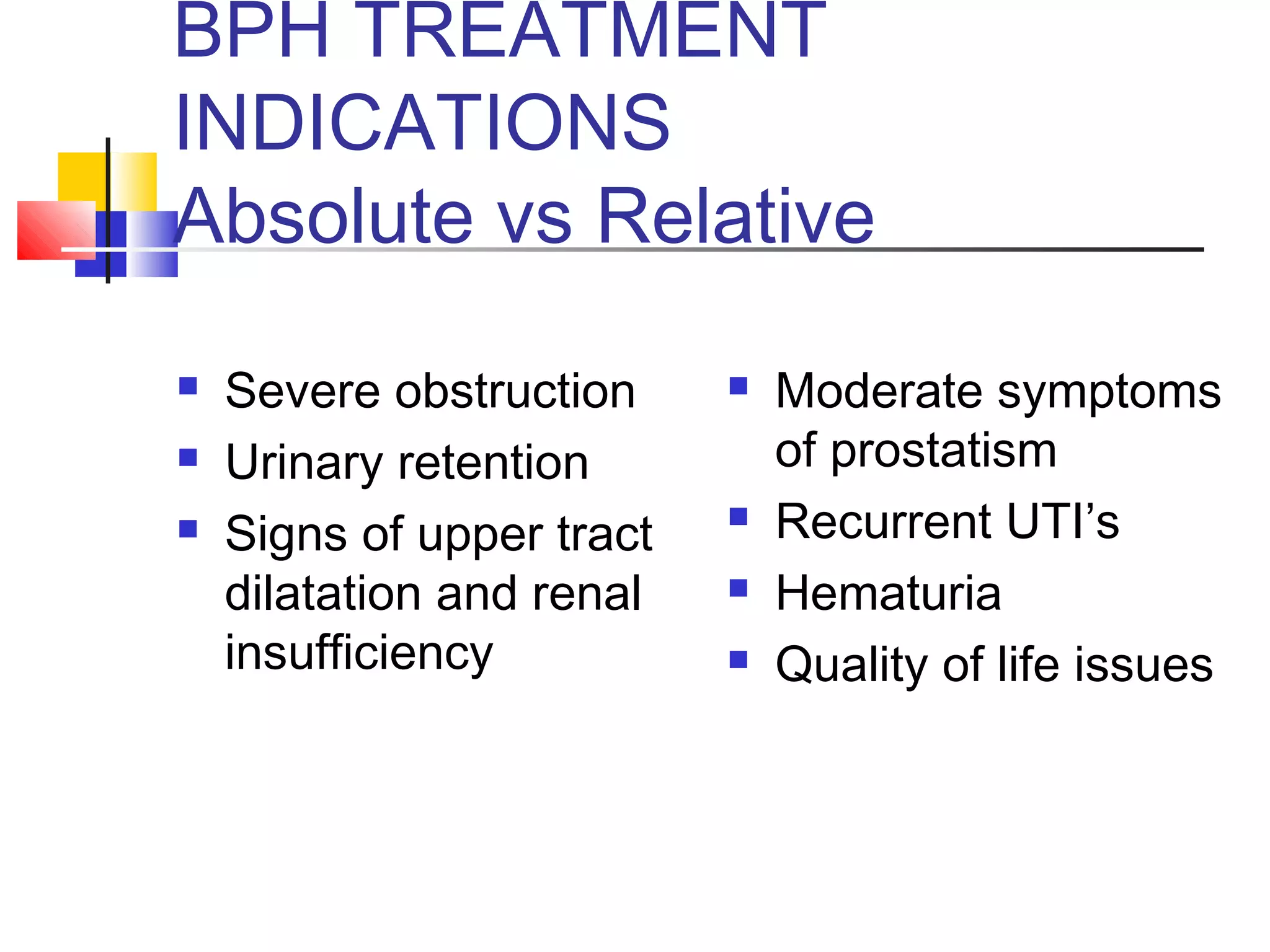
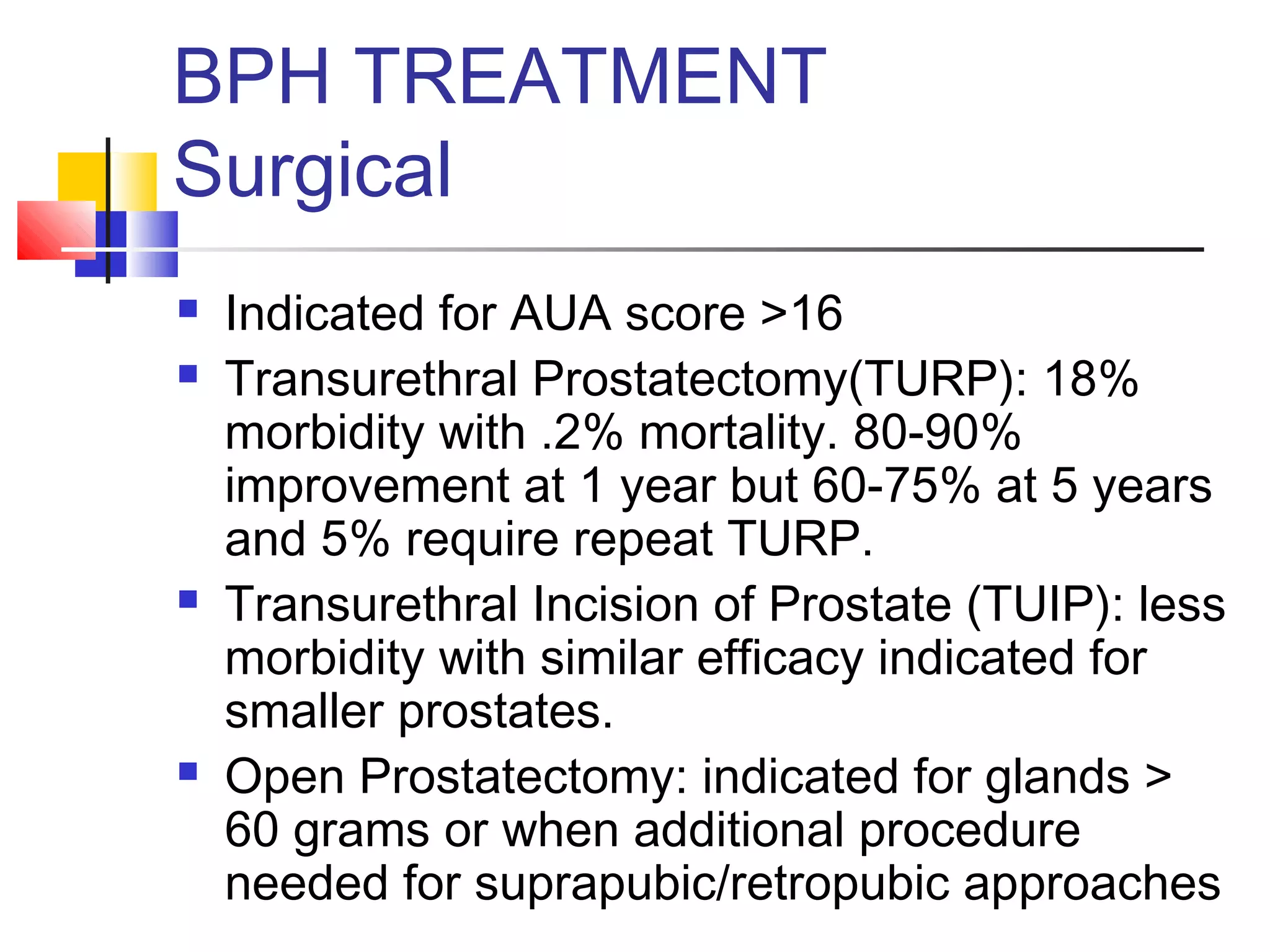
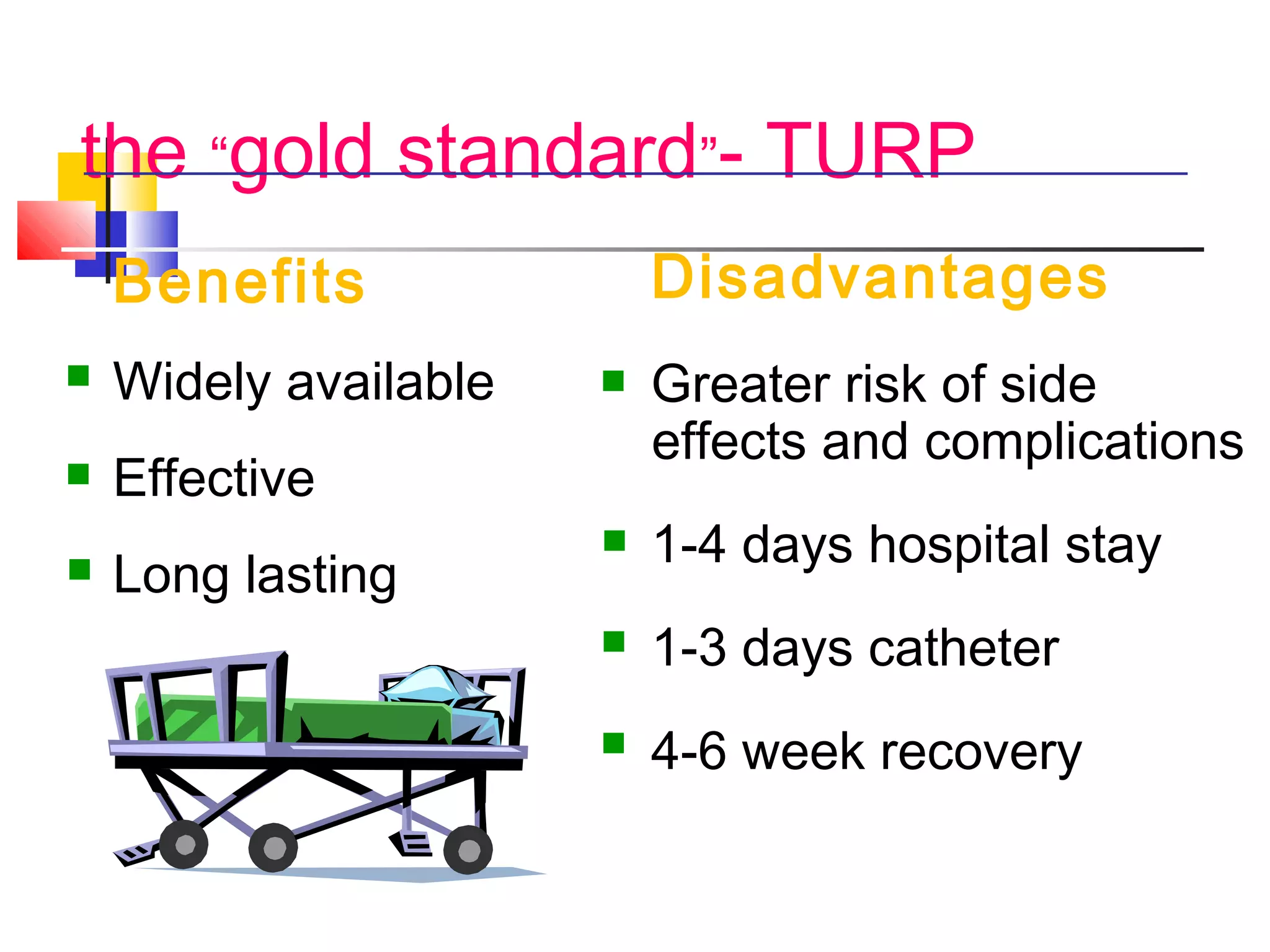
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a noncancerous enlargement of the prostate gland that is common in aging men. It is caused by hormonal changes that lead to increased cell growth in the prostate, compressing the urethra and causing urinary symptoms. Treatment options range from watchful waiting for mild symptoms to medications and surgery for more severe cases. Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is generally the gold standard surgical treatment, providing long-term relief but also risks side effects like retrograde ejaculation and erectile dysfunction.