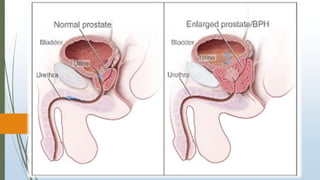
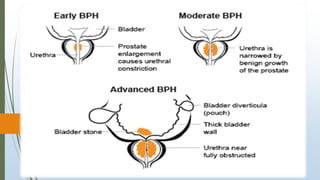
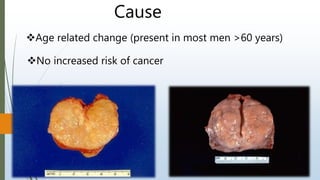
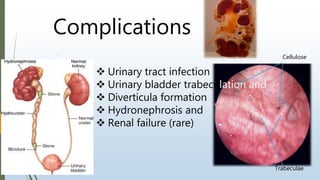
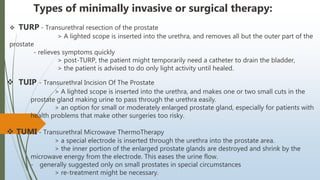
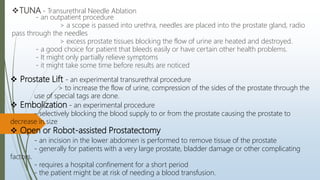
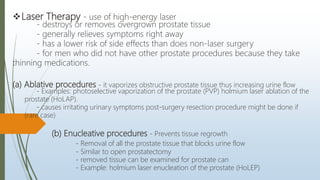
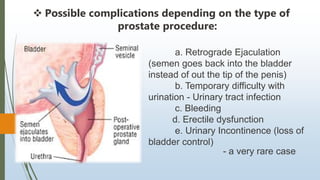
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a noncancerous enlargement of the prostate gland that is common in aging men. BPH occurs when the prostate gland grows larger and squeezes the urethra, causing problems with urination. Symptoms include difficulty starting or stopping urination and frequent urination, especially at night. Treatment options depend on symptom severity and include medications to shrink the prostate or relieve symptoms, minimally invasive procedures such as transurethral resection of the prostate, and surgery for severe cases. Potential complications of treatment include retrograde ejaculation and temporary difficulty urinating.