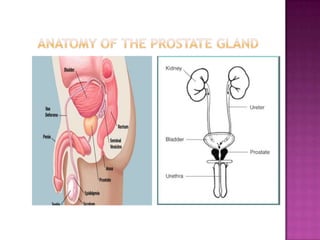
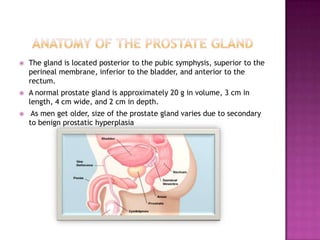
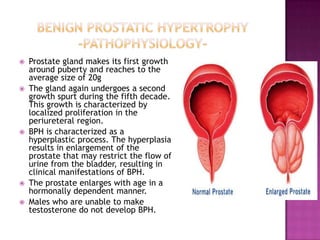
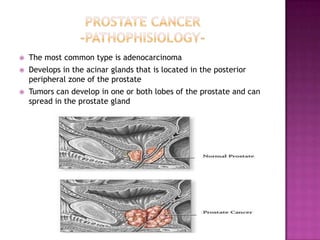
The document summarizes information about the prostate gland and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It discusses the anatomy and function of the prostate gland. It describes how the size of the prostate increases with age due to BPH in many men. Common symptoms of BPH include frequent urination and weak urine stream. Treatment options for BPH include watchful waiting, medications, and surgery. The risk of prostate cancer also increases with age and it is a major health concern for older men.