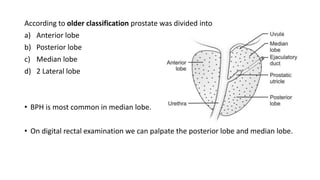
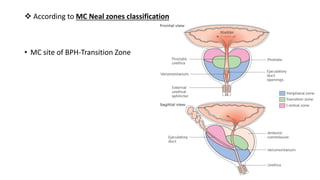
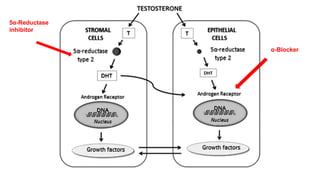
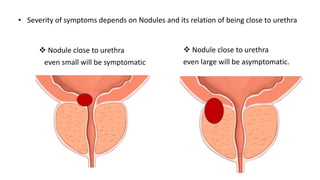
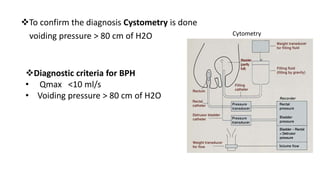
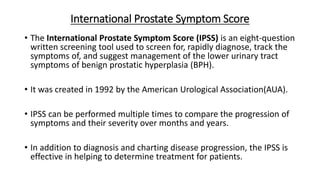
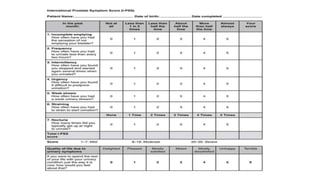
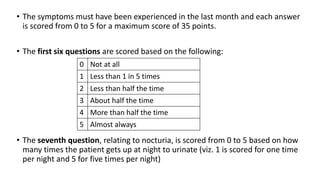
BPH is characterized by increased epithelial and stromal cells in the prostate transition zone. Symptoms include poor urinary flow, frequency, and urgency. Diagnosis involves history, DRE, urinalysis, uroflowmetry and cystometry. Treatment options include watchful waiting for mild symptoms, medical therapy with alpha-blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, and surgery for severe symptoms. Combination drug therapy provides the greatest reduction in long-term complications like urinary retention.