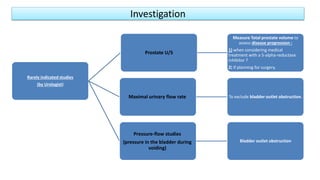
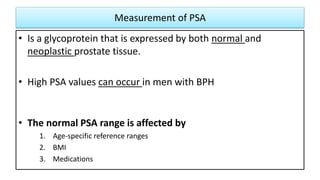
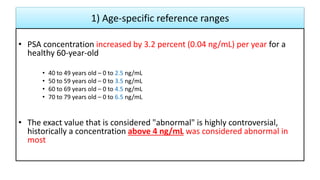
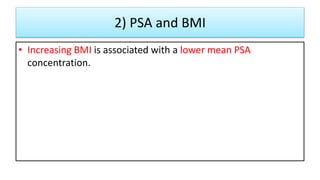
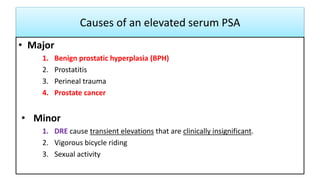
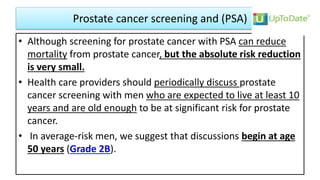
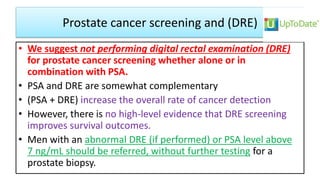
This document provides an overview of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), including its definition, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, complications, differential diagnosis, evaluation, and management. BPH involves noncancerous enlargement of the prostate and commonly causes lower urinary tract symptoms. It predominantly affects older men. Evaluation involves assessment of symptoms, physical exam including digital rectal exam, and tests like prostate-specific antigen. Management includes watchful waiting, lifestyle changes, medications like alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors, and potentially surgery for severe or treatment-resistant cases. Screening for prostate cancer with PSA is not universally recommended.
















![1) Watchful waiting
Recommended for (AUA Standard) :
• Mild symptoms of (LUTS) secondary to BPH (American
Urological Association Symptom Index [AUASI] score < 8)
• Moderate or severe symptoms (AUASI score ≥ 8) who are not
bothered by their LUTS symptoms](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bph-bydr-181205161952/85/benign-prostatic-hyperplasia-by-dr-bagasi-37-320.jpg)











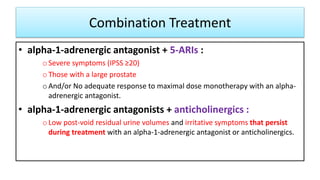

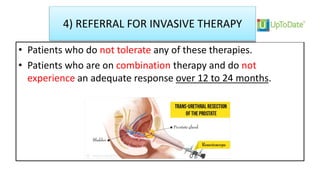
![Prevention
1. Zinc supplementation decreased risk of development of
BPH (level 2 [mid-level] evidence)
2. More physically active lower frequency of LUTS (level 2 [mid-
level] evidence)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bph-bydr-181205161952/85/benign-prostatic-hyperplasia-by-dr-bagasi-56-320.jpg)

