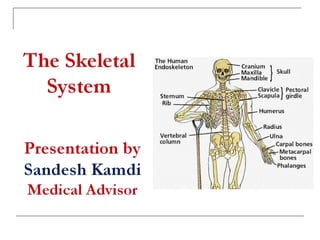
Basics of skeletal system
- 2. The Skeletal System Topics to be covered Functions of Bone and Skeletal System Structure of Bone Histology of Bone Tissue Blood and Nerve Supply of Bone Bone Formation Bone’s Role in Calcium Homeostasis Aging and Bone Tissue
- 4. Functions of Bone and Skeletal System 4. Mineral Homeostasis: Calcium balance: contribute to bone strength; stores 99% of body’s calcium; Phosphorus balance: stored in bones and releases it on demand of the body
- 10. Histology of Bone Tissue Four types of cells are present in bone tissue Osteogenic cell Osteogenic cells Undergo cell division; the resulting cells develop into osteoblasts Osteoblasts Bone-building cells Osteoblast Synthesize extracellular matrix of bone tissue Osteocytes Mature bone cells, maintains bone tissues Exchange nutrients and wastes with the blood Osteoclasts Osteocytes Release enzymes that digest the mineral components of bone matrix (resorption) Regulate blood calcium level Osteoclast
- 12. Bone Formation The process by which bone forms is called ossification or osteogenesis Bone formation occurs in four situations: 1. Formation of bone in an embryo 2. Growth of bones until adulthood 3. Remodeling of bone 4. Repair of fractures
- 13. 1. Formation bone 1. Development of the ossification center. At site where bone develops specific chemical messages cause mesenchymal cells to aggregate and differentiate, first into osteogenic cells then osteoblasts. Blood capillary Ossification center Mesenchymal cell Osteoblast Collagen fiber 1 Development of ossification center
- 14. 1. Formation bone 2. Calcification: Within a few days calcium and other mineral salts are deposited and extracellular matrix becomes calcified. Osteocyte in lacuna Canaliculus Osteoblast Newly calcified bone matrix 2 Calcification
- 15. 1. Formation bone 3. Formation of trabeculae: Extracellular matrix develops into trabeculae that fuse with each other to form spongy bone Blood vessels grow into the spaces Connective tissue associated with blood vessels differentiates into red marrow Mesenchyme condenses Blood vessel Spongy bone trabeculae Osteoblast 3 Formation of trabeculae
- 16. 1. Intramembranous ossification 4. Development of the periosteum: In conjunction with formation of trabeculae, the mesenchyme condenses at the periphery Eventually a thin layer of compact bone replaces the spongy bone, but spongy bone remains in the center Much of the new bone is remodeled as the bone is transformed into adult shape and size Periosteum Spongy bone tissue Compact bone tissue 4 Development of the periosteum
- 17. Bone Growth During Infancy, Childhood and Adolescence Growth in Length The growth in length of long bones involves four major events: 1. Growth of cartilage on the epiphyseal plate 2. Replacement of cartilage by bone tissue in the epiphyseal plate 3. The activity of the epiphyseal plate is the way bone can increase in length 4. At adulthood, the epiphyseal plates close and bone replaces all the cartilage leaving a bony structure called the epiphyseal line
- 18. Bone Growth During Infancy, Childhood and Adolescence Growth in Thickness Bones grow in thickness at the outer surface Remodeling of Bone Bone forms before birth and continually renews itself The ongoing replacement of old bone tissue by new bone tissue Old bone is continually destroyed and new bone is formed in its place throughout an individual’s life
- 20. Factors Affecting Bone Growth and Bone Remodeling Normal bone metabolism depends on several factors Minerals Large amounts of calcium and phosphorus and smaller amounts of magnesium, fluoride, and manganese are required for bone growth and remodeling Vitamins Vitamin D helps build bone by increasing the absorption of calcium from foods in the gastrointestinal tract into the blood Vitamins K are also needed for synthesis of bone proteins
- 21. Bone’s Role in Calcium Homeostasis Bone is the body’s major calcium reservoir Levels of calcium in the blood are maintained by controlling the rates of calcium resorption from bone into blood and of calcium deposition from blood into bone Both nerve and muscle cells depend on calcium ions (Ca2+) to function properly Blood clotting also requires Ca2+ Many enzymes require Ca2+ as a cofactor
- 22. Bone’s Role in Calcium Homeostasis Actions that help elevate blood Ca2+ level Parathyroid hormone (PTH) regulates Ca2+ exchange between blood and bone tissue PTH increases the number and activity of osteoclasts PTH acts on the kidneys to decrease loss of Ca2+ in the urine PTH stimulates formation of calcitriol a hormone that promotes absorption of calcium from foods in the gastrointestinal tract
- 24. Bone’s Role in Calcium Homeostasis Actions that work to decrease blood Ca2+ level The thyroid gland secretes calcitonin (CT) which inhibits activity of osteoclasts The result is that CT promotes bone formation and decreases blood Ca2+ level Accelerates uptake of calcium and phosphate into bone matrix
- 25. Exercise and Bone Tissue Bone tissue alters its strength in response to changes in mechanical stress Under stress, bone tissue becomes stronger through deposition of mineral salts and production of collagen fibers by osteoblasts Unstressed bones diminishes because of the loss of bone minerals and decreased numbers of collagen fibers The main mechanical stresses on bone are those that result from the pull of skeletal muscles and the pull of gravity Weight-bearing activities help build and retain bone mass
- 26. Aging and Bone Tissue The level of sex hormones diminishes during middle age, especially in women after menopause A decrease in bone mass occurs Bone resorption by osteoclasts outpaces bone deposition by osteoblasts Female bones generally are smaller and less massive than males Loss of bone mass in old age has a greater adverse effect in females
- 27. Aging and Bone Tissue There are two principal effects of aging on bone tissue: 1) Loss of bone mass Results from the loss of calcium from bone matrix The loss of calcium from bones is one of the symptoms in osteoporosis 2) Brittleness Results from a decreased rate of protein synthesis Collagen fibers gives bone its tensile strength The loss of tensile strength causes the bones to become very brittle and susceptible to fracture
