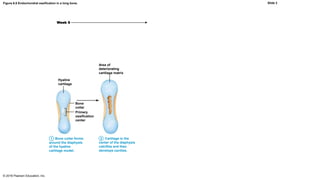
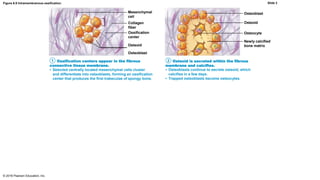
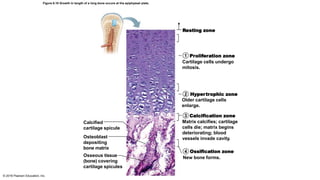
Bone development occurs through two main processes: endochondral ossification and intramembranous ossification. Endochondral ossification forms bones below the skull through replacement of cartilage models with bone tissue in a multi-step process beginning in the second month of development. Intramembranous ossification forms some flat bones of the skull through the direct development of bone within fibrous membranes in mesenchymal tissue. Postnatal bone growth continues through adolescence via growth at the epiphyseal plates of long bones.