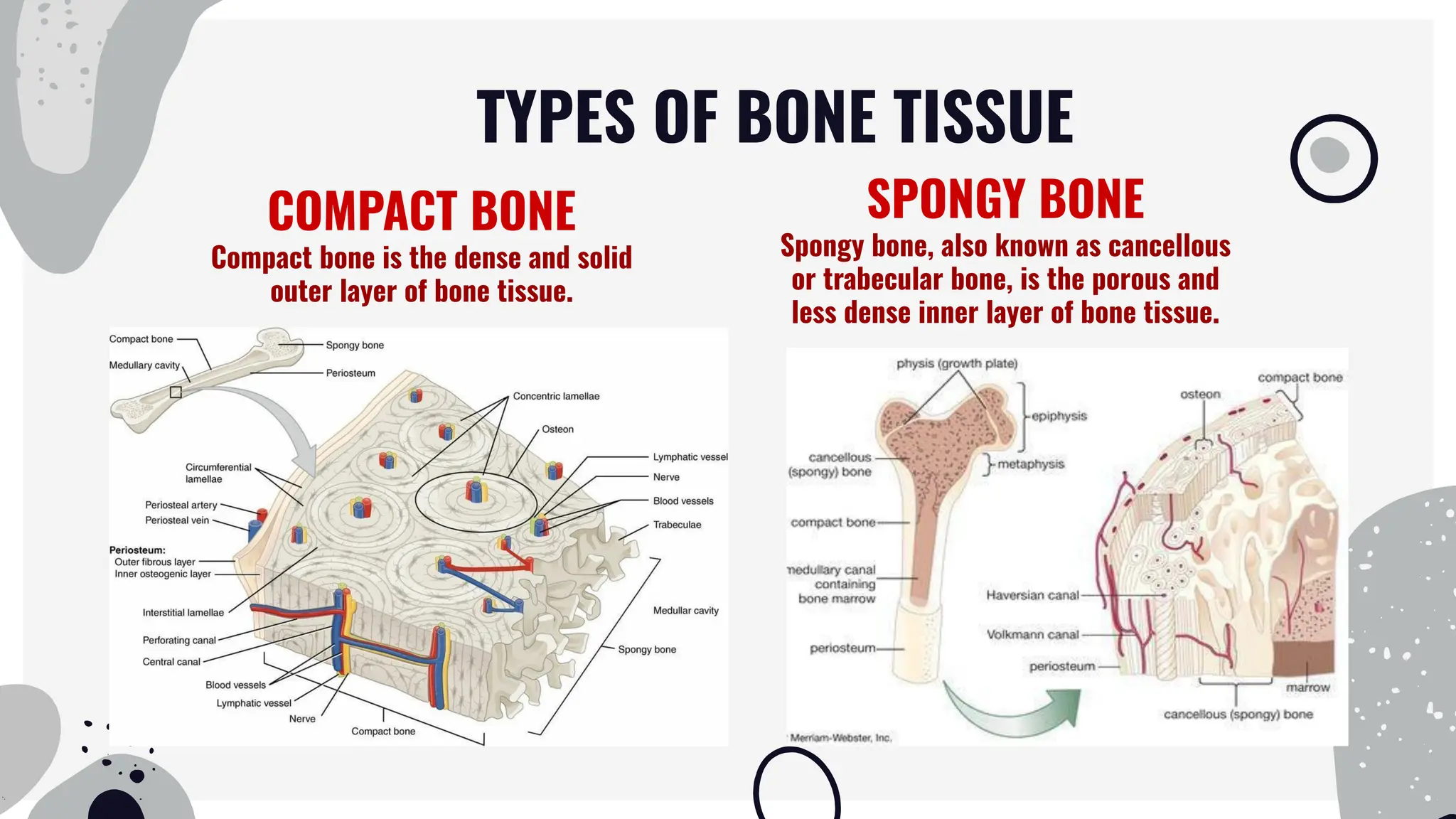
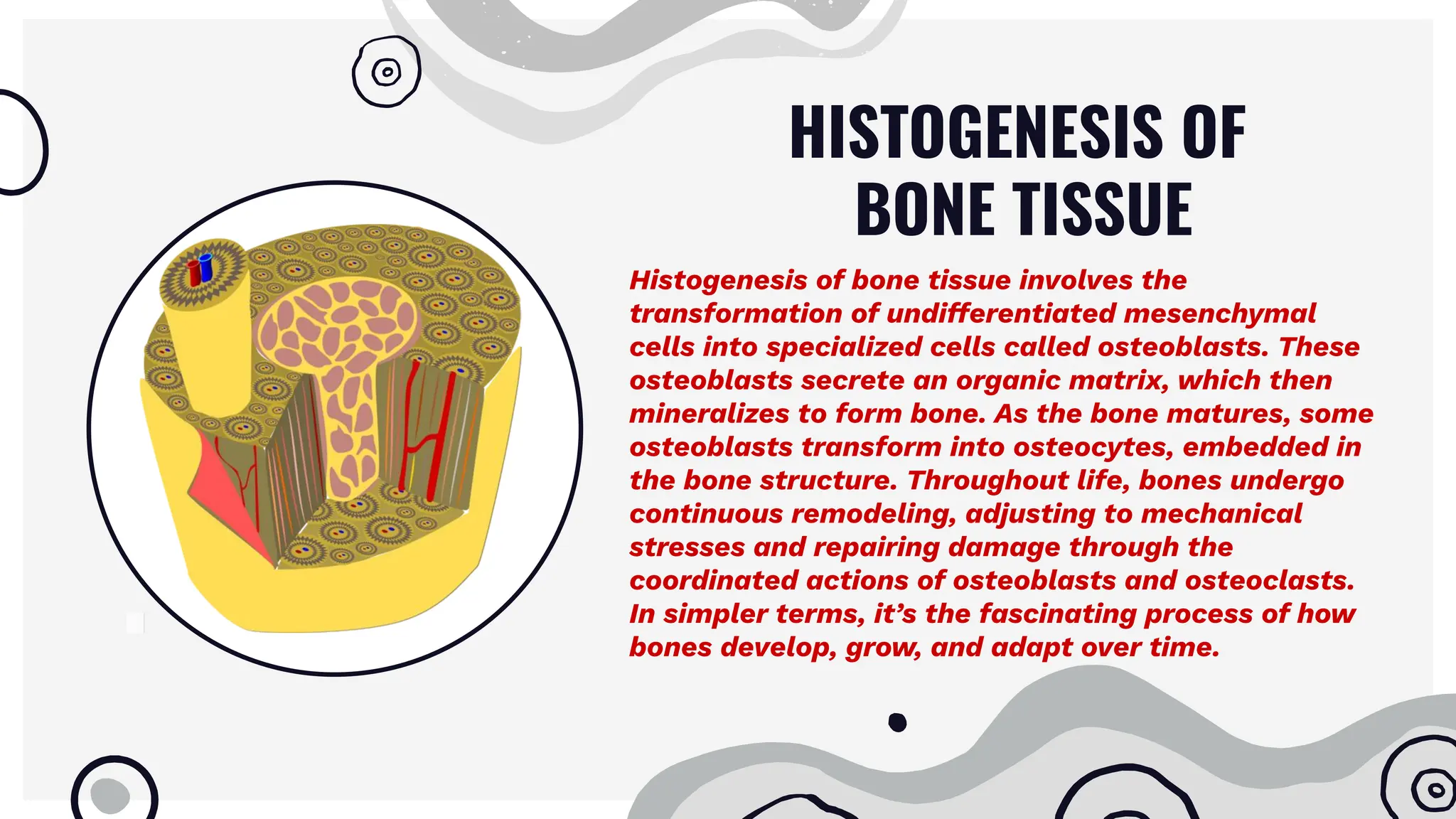
Bone tissue is a specialized connective tissue that forms the skeleton. It consists of cells like osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts embedded in an organic and inorganic matrix. Bone tissue exists in two forms - compact bone, which forms the dense outer layers, and spongy bone, which makes up the interior. Bone undergoes continuous remodeling through the actions of osteoblasts and osteoclasts. It provides structure, protects organs, allows movement, stores minerals, and enables blood cell formation. Understanding bone's structure, development, regeneration, and age-related changes provides insights into maintaining skeletal health.