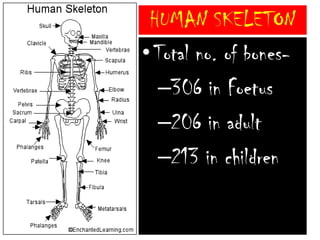
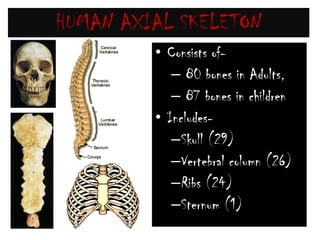
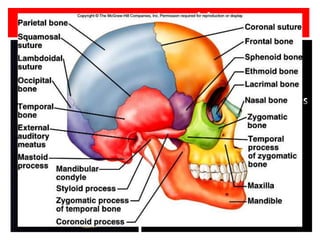
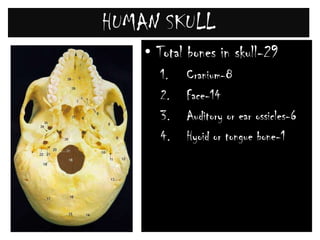
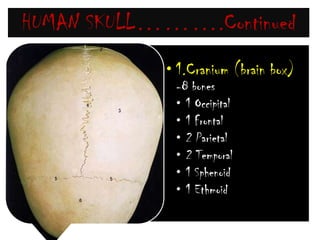
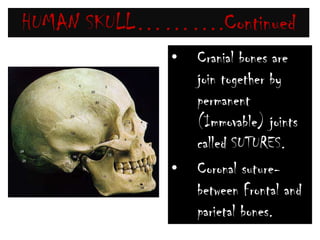
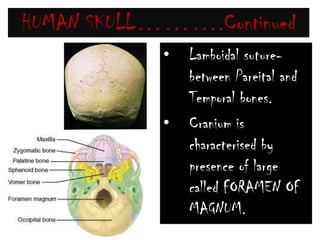
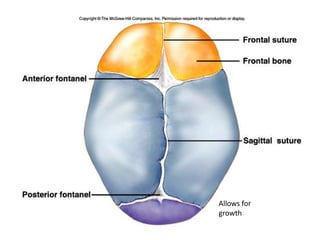
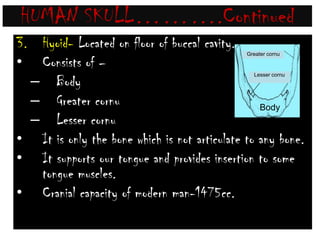
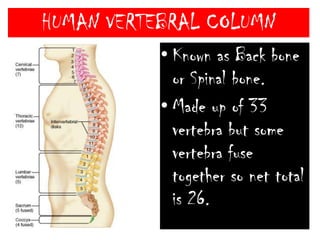
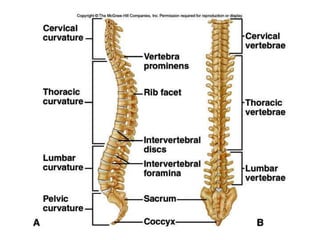
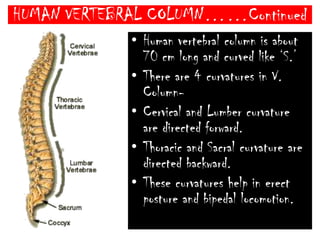
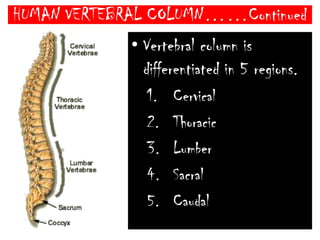
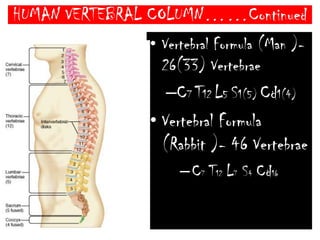
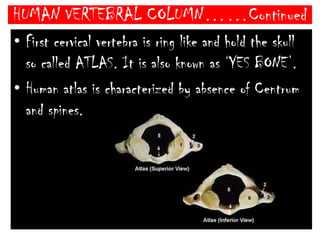
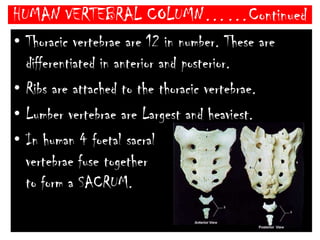
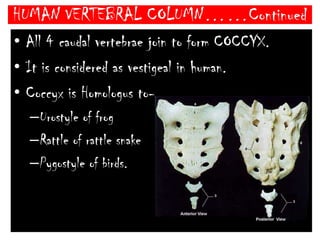
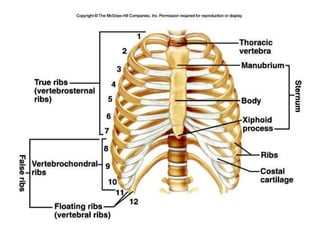
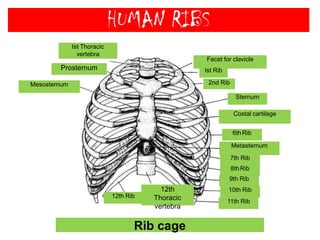
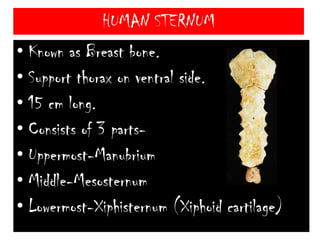
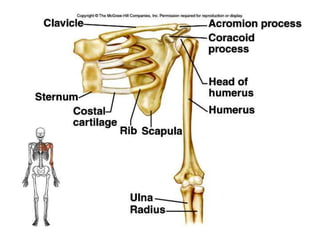
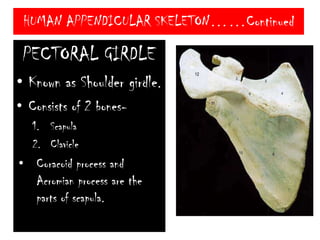
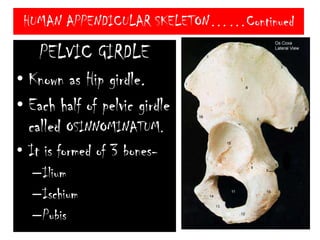
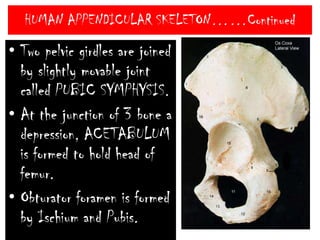
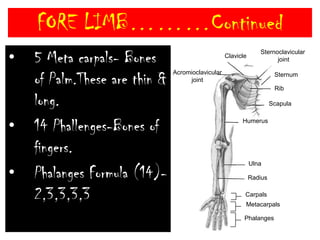
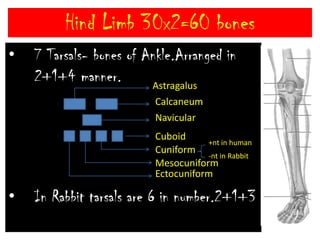
The skeletal system consists of the axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton includes the skull, vertebral column, and ribs. The appendicular skeleton includes the pectoral and pelvic girdles and limb bones. The adult human skeleton has 206 bones, including 80 bones in the axial skeleton and 126 bones in the appendicular skeleton. Key bones of the axial skeleton are the skull, vertebral column consisting of 26 vertebrae, and 12 pairs of ribs. The skull has 29 bones that form the cranium and face. The appendicular skeleton includes the shoulder and pelvic girdles, with the limb bones of the upper and lower limbs making up the remaining bones.