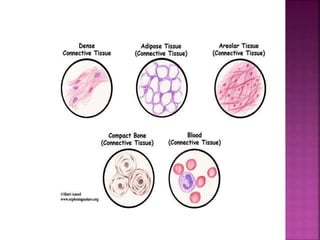
There are four primary tissue types in the body: epithelium, connective tissue, nervous tissue, and muscle tissue. Epithelium forms protective barriers and lines surfaces throughout the body. Connective tissue supports and connects organs, stores fat, and is made up of ground substance, fibers, and cells. Nervous tissue is composed of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves to conduct signals throughout the body. Muscle tissue includes three types - smooth, skeletal, and cardiac - which work to move organs, bones, and blood.