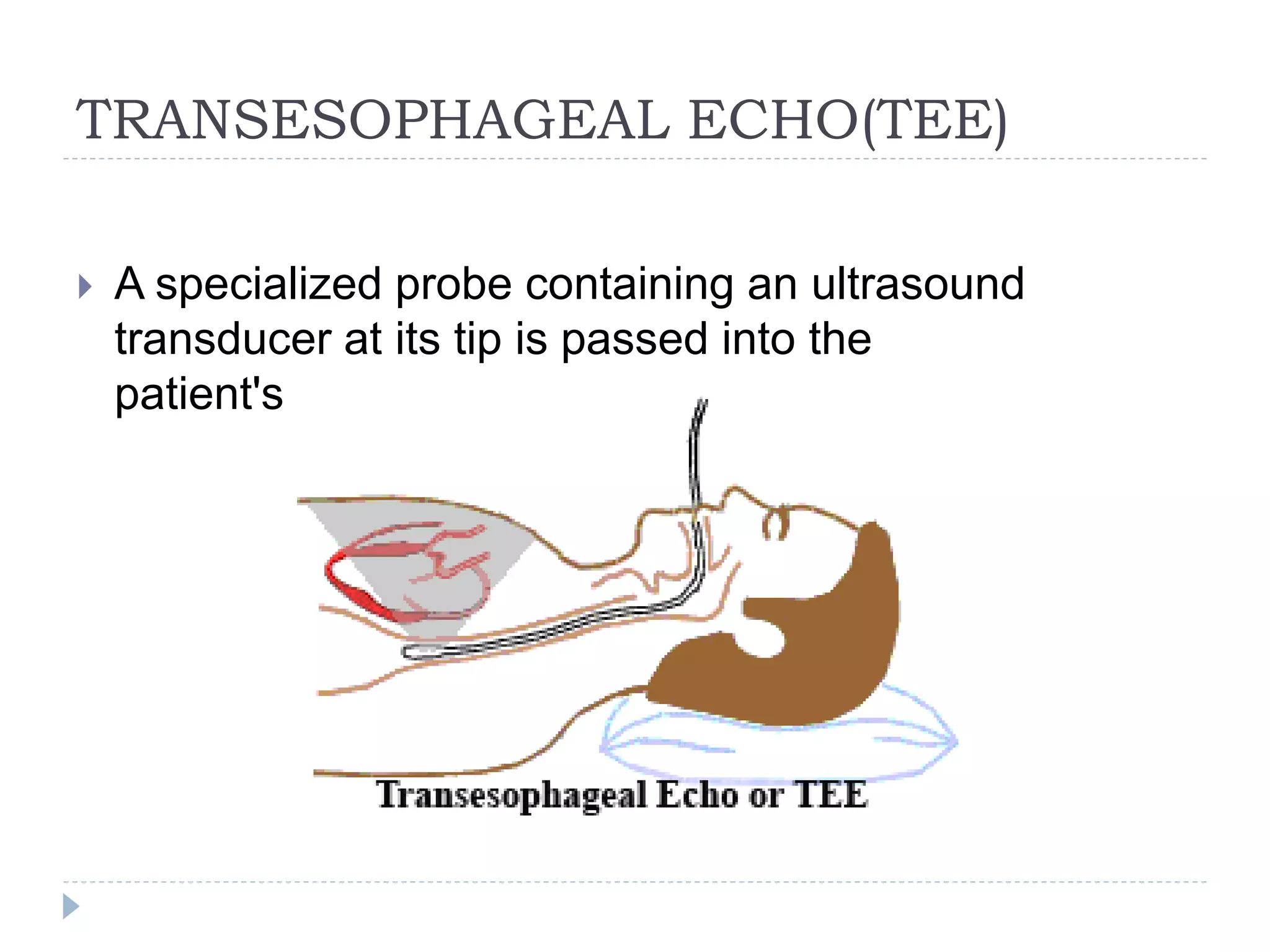
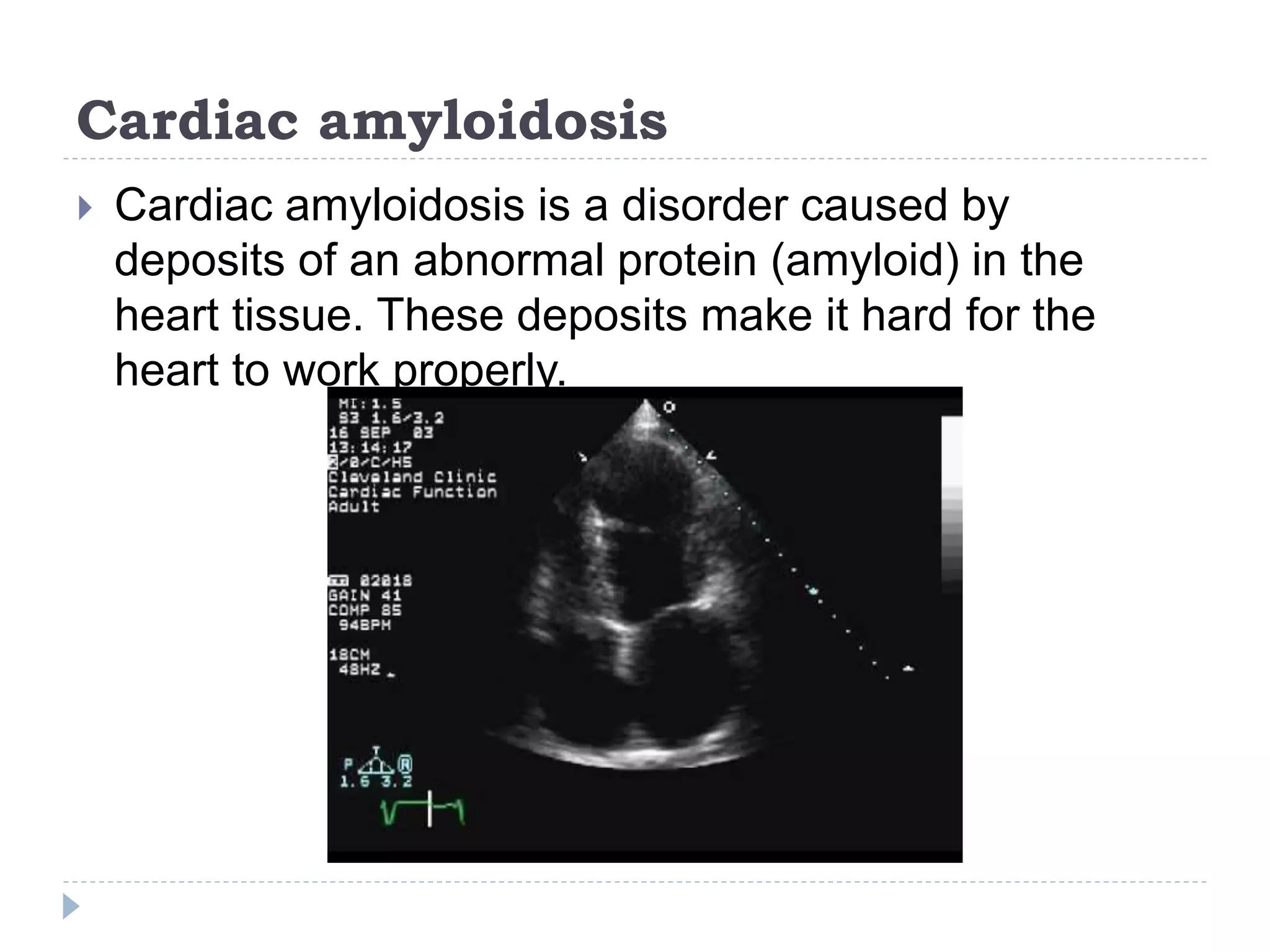
Echocardiography uses ultrasound to create images of the heart. The main types are transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiograms. Transthoracic echocardiograms image the heart non-invasively from the chest, while transesophageal echocardiograms pass an ultrasound probe down the esophagus for clearer images. Doppler echocardiography assesses blood flow velocity and direction. Echocardiography is used to evaluate heart structures and function, detect abnormalities, and help diagnose conditions like heart valve problems, heart muscle diseases, and blood clots.