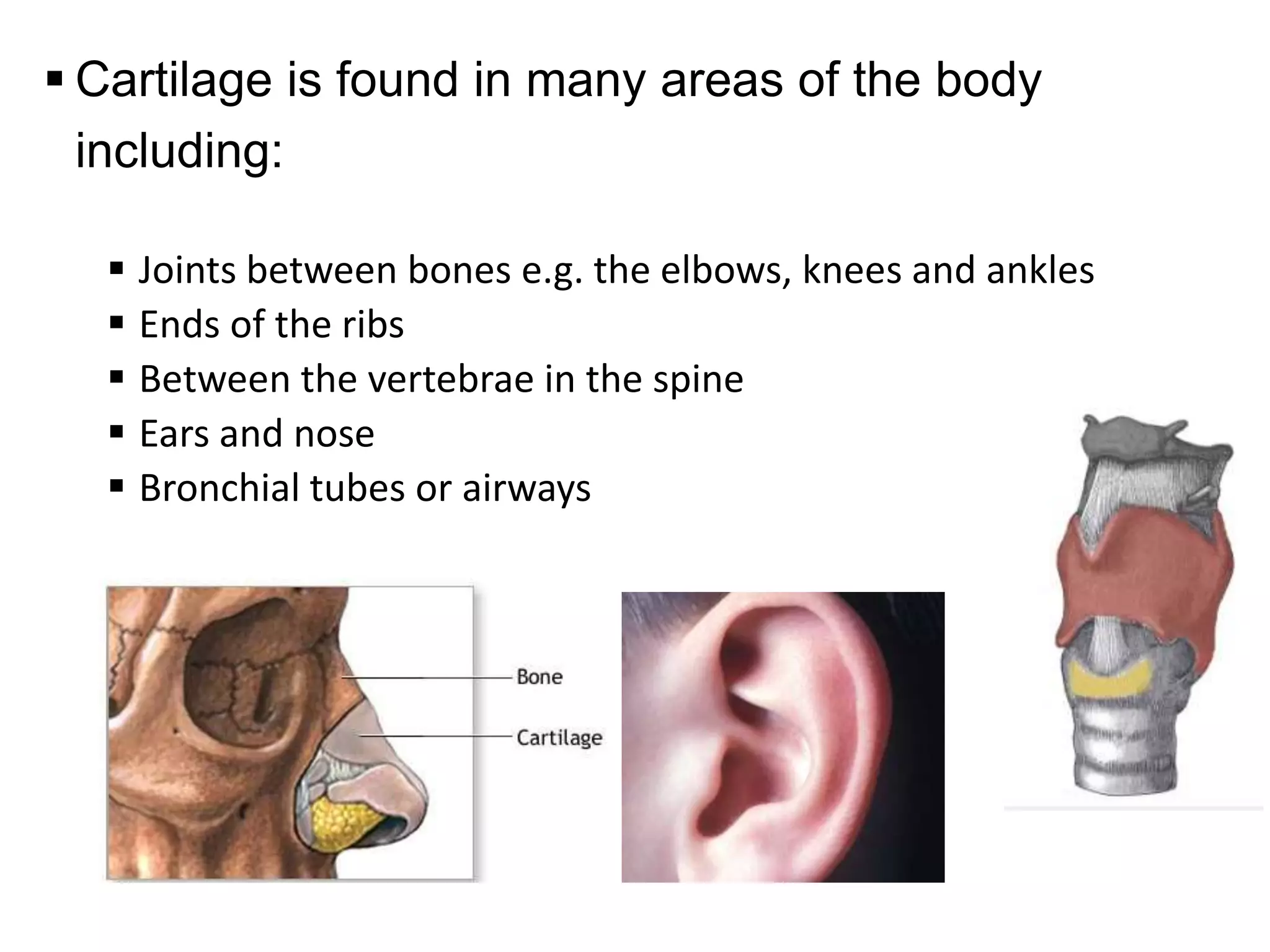
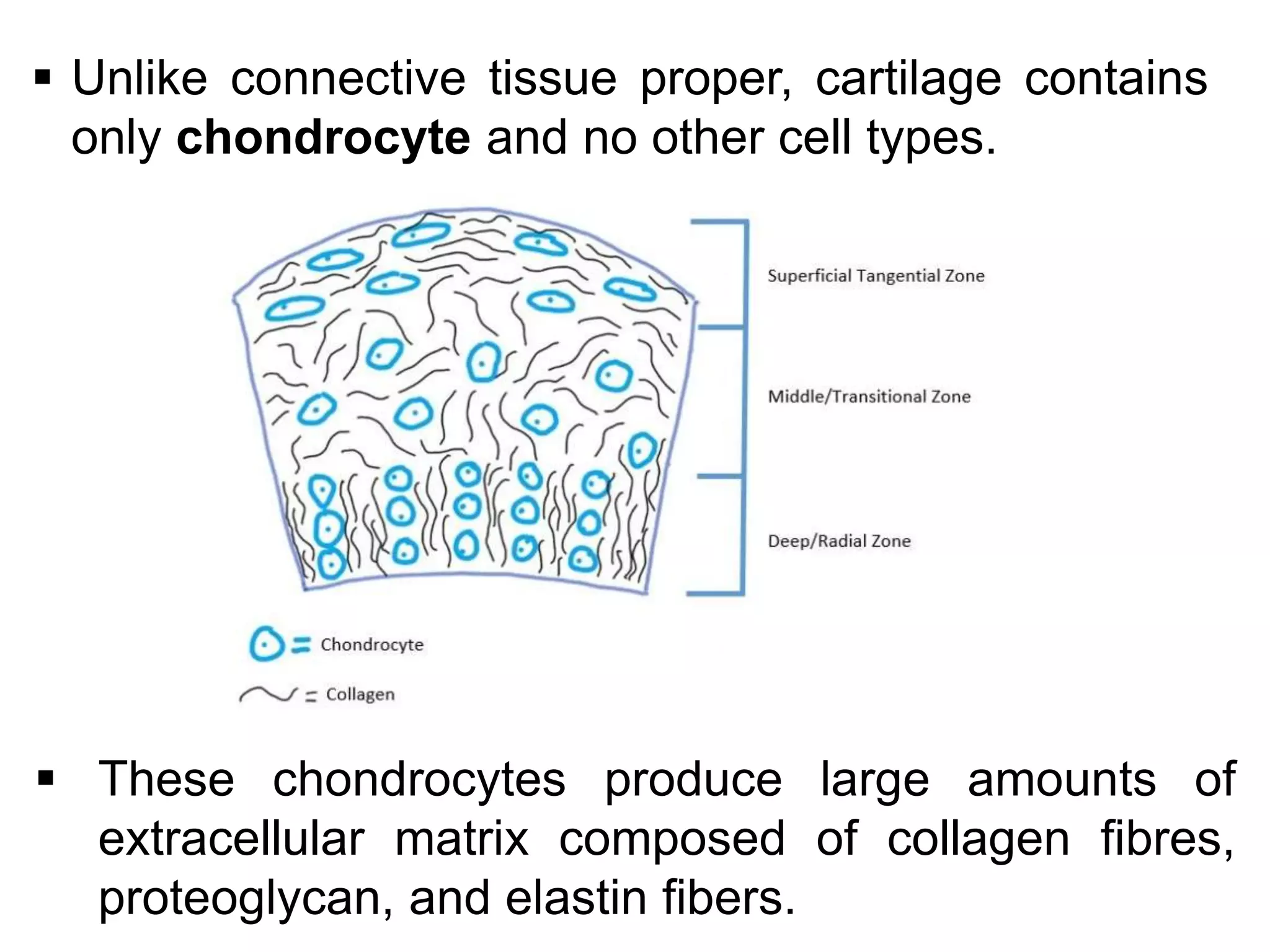
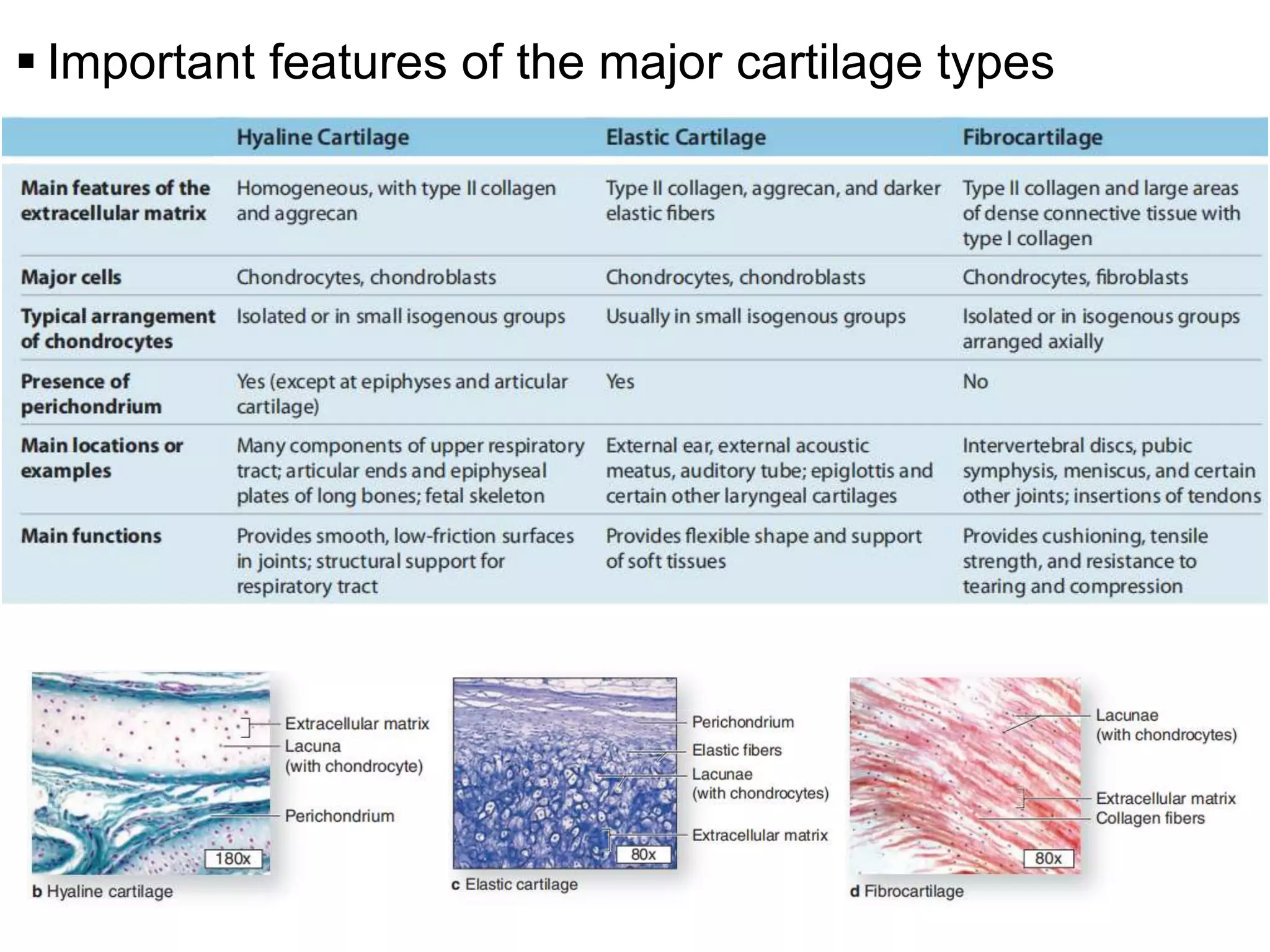
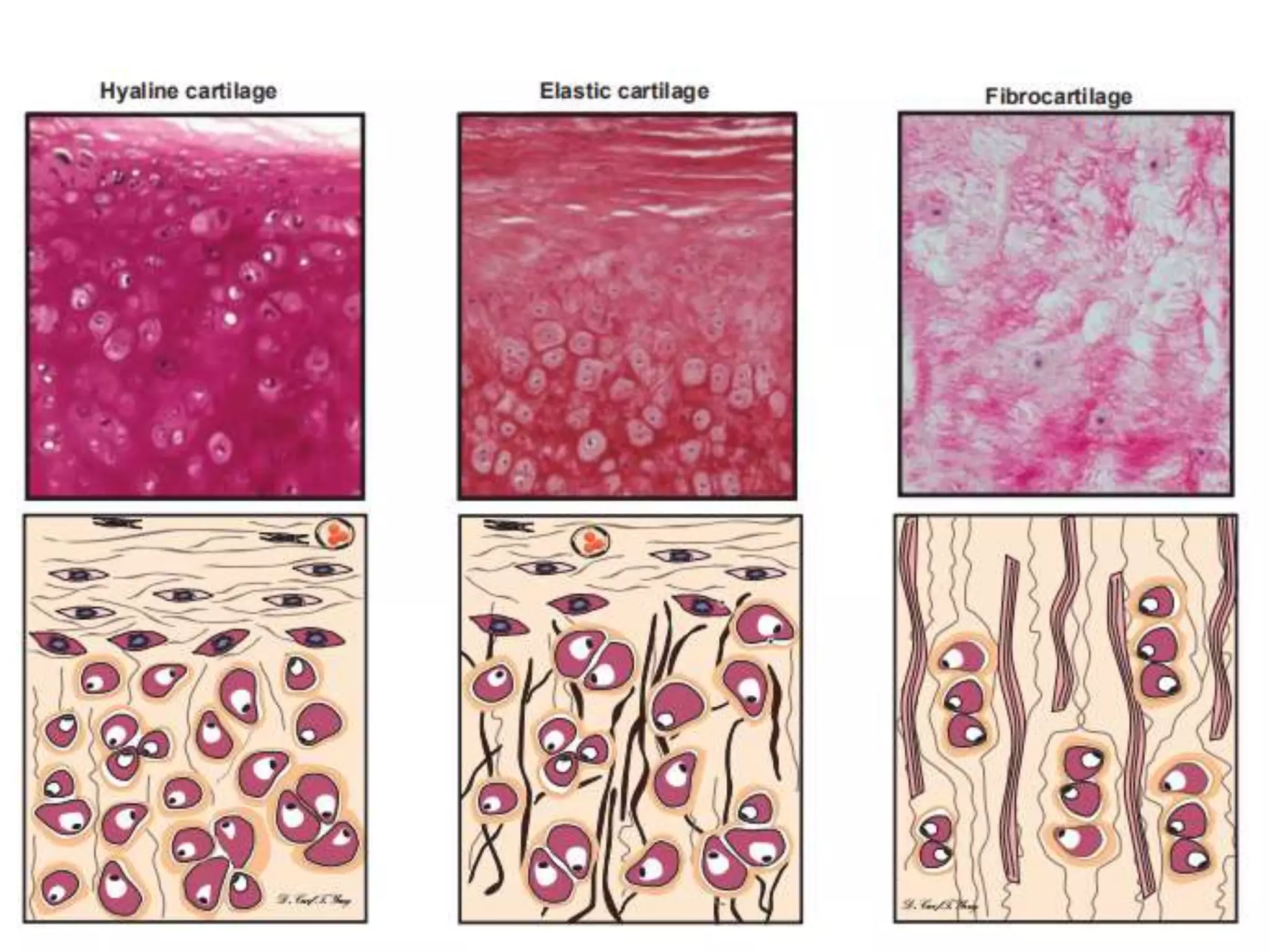
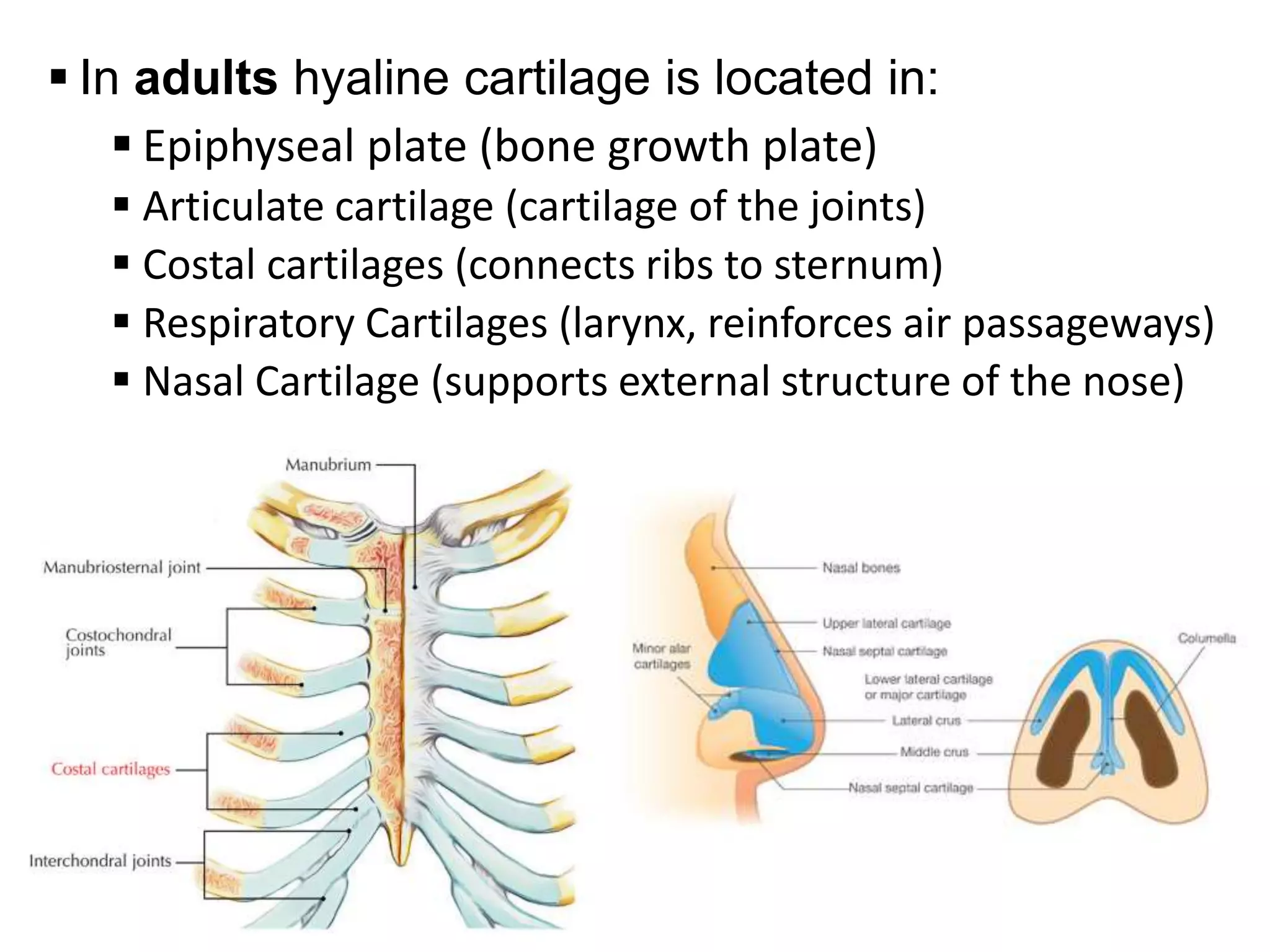
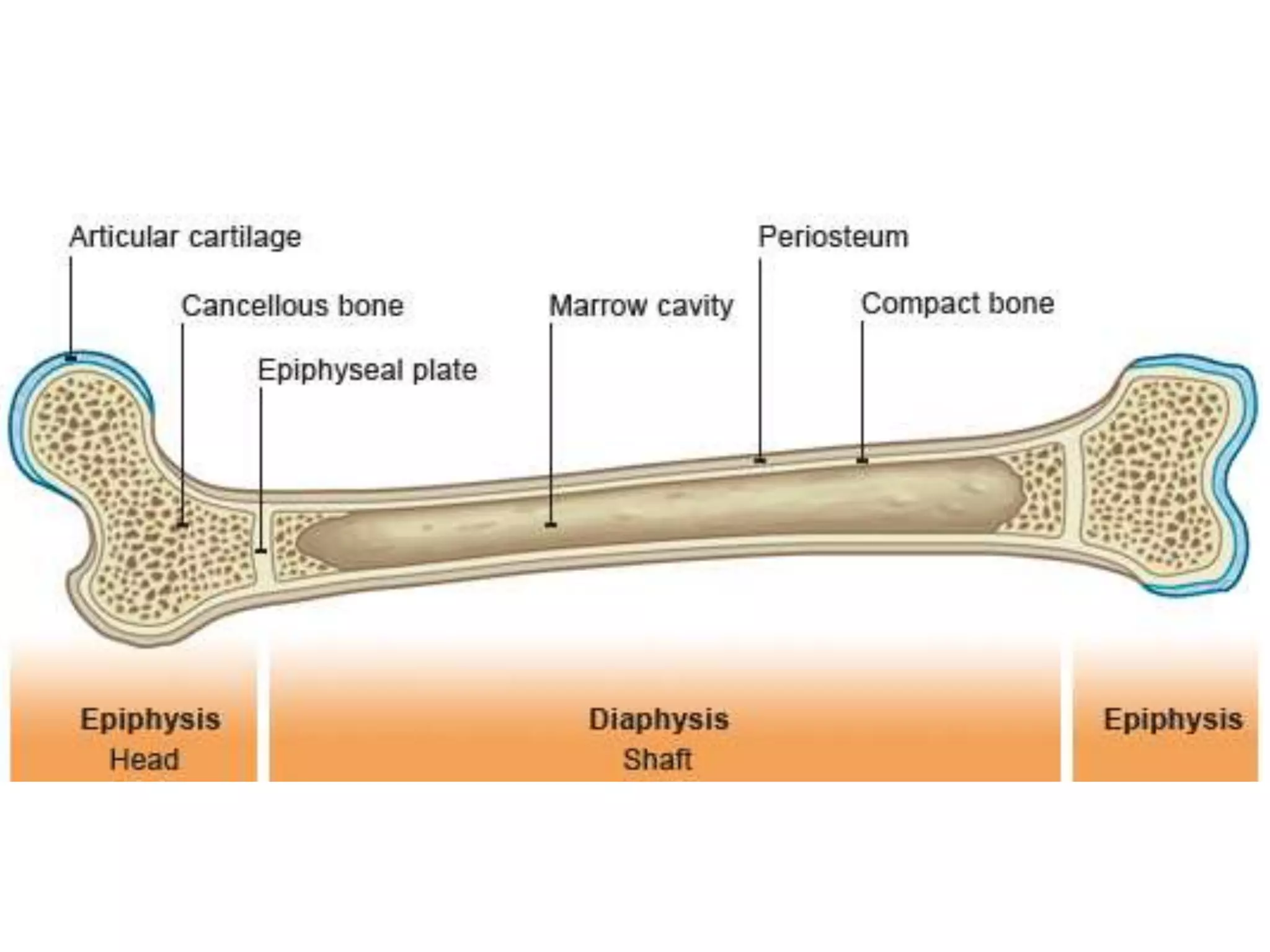
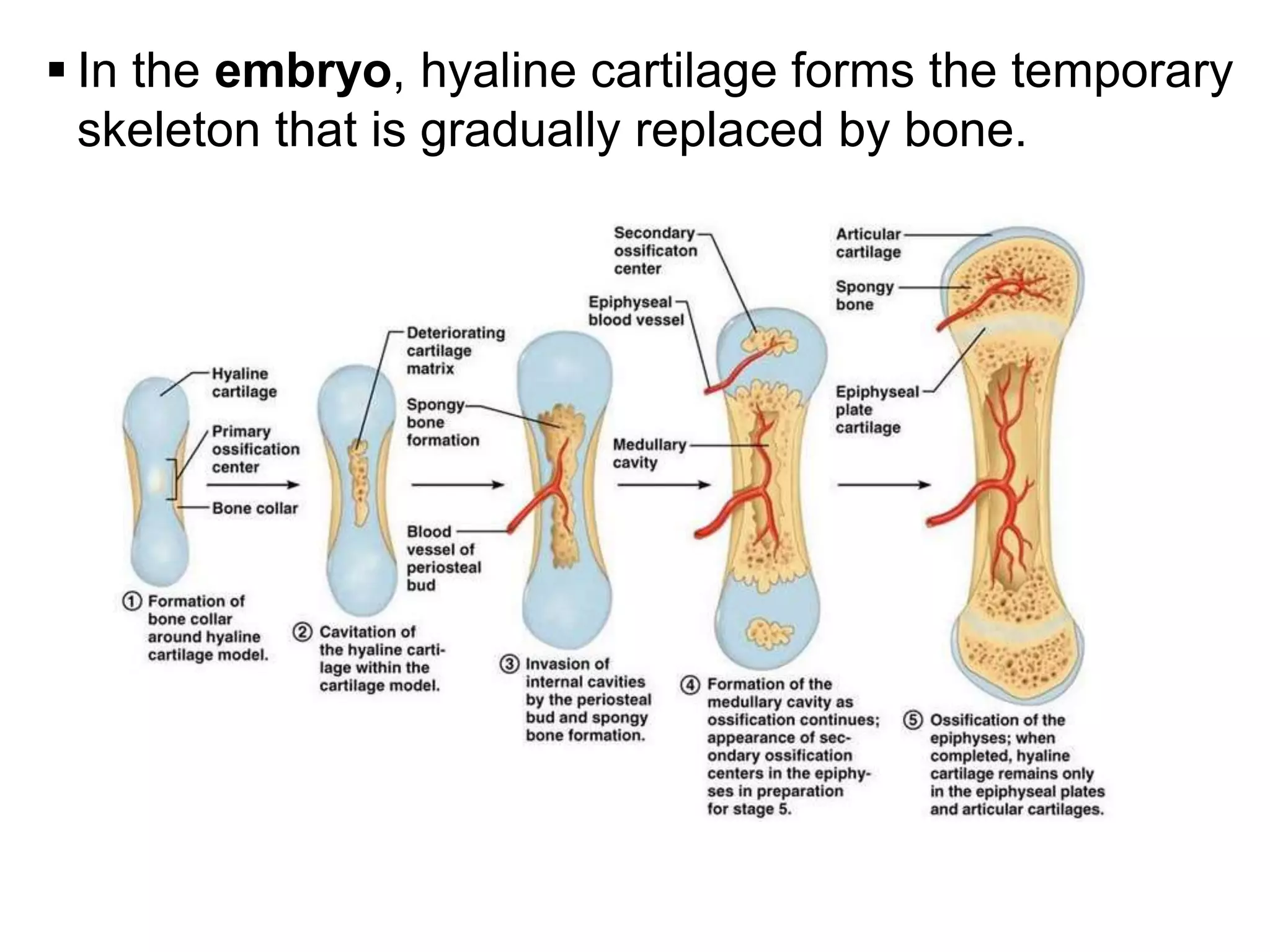
The document provides an extensive overview of cartilage, detailing its types—hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage—and their structural characteristics. It describes the composition of cartilage, the role of chondrocytes, and the significance of the extracellular matrix in providing mechanical support and protection. Additionally, it outlines the processes of cartilage formation, growth, and repair, emphasizing the slow recovery rate due to its avascular nature.