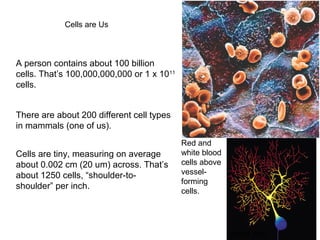
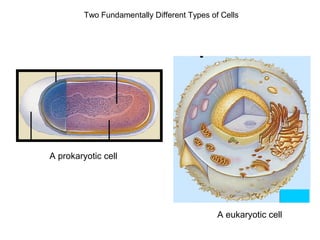
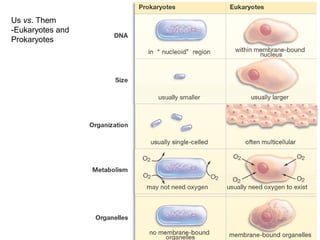
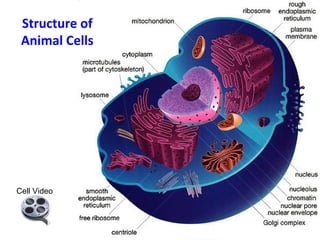
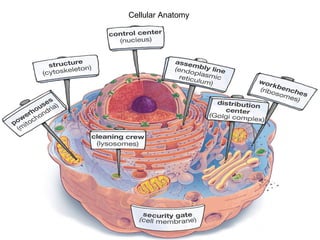
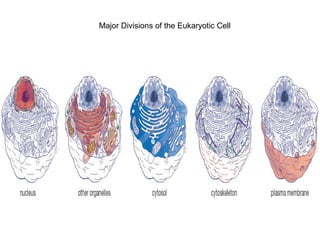
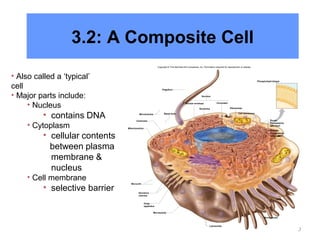
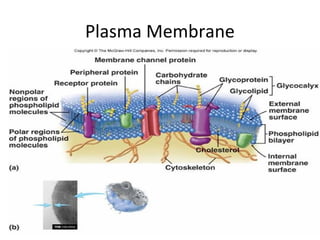
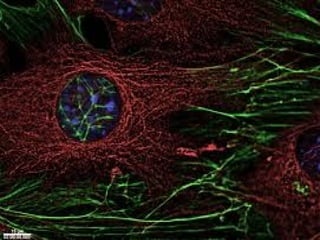
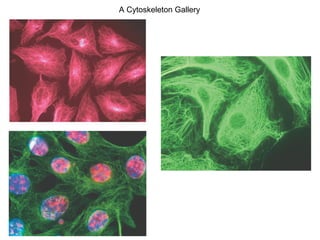
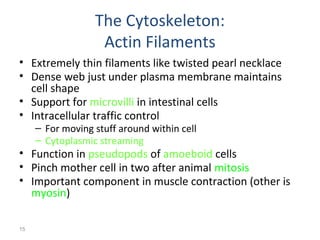
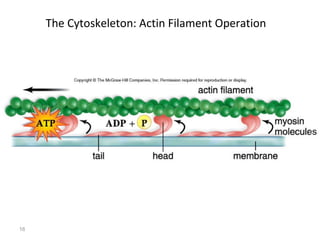
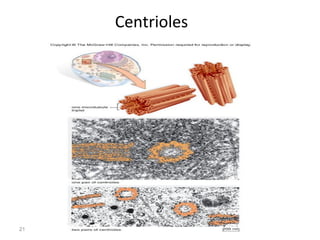
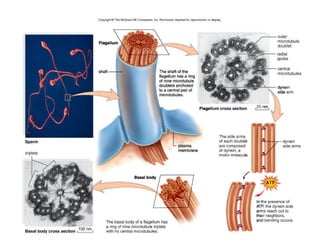
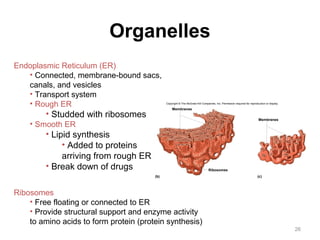
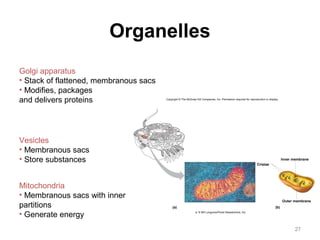
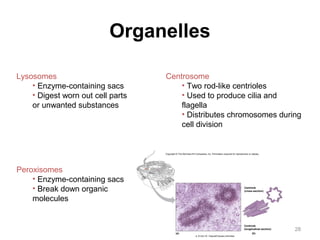
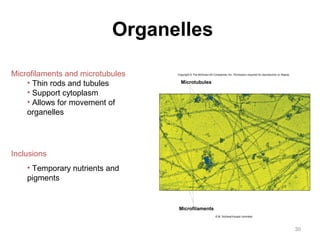
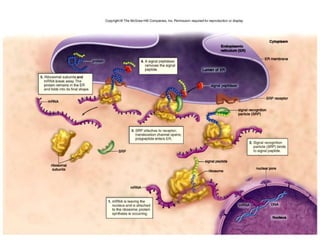
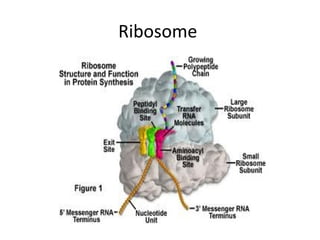
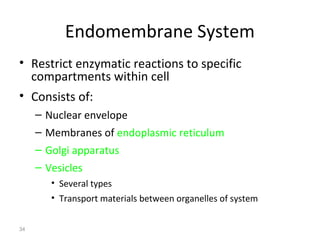
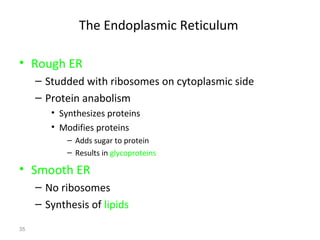
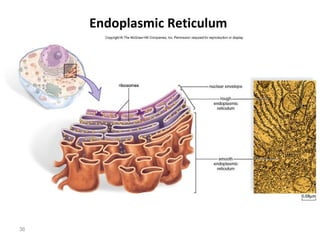
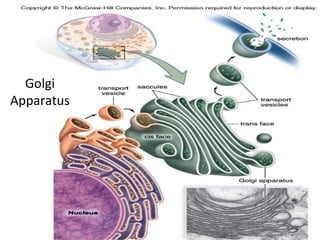
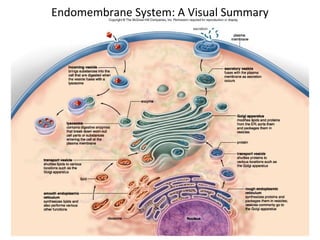
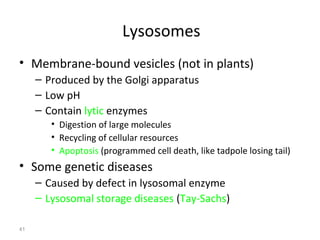
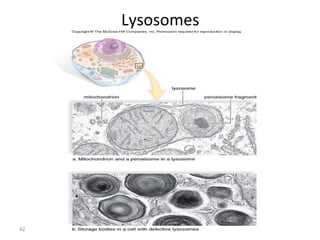
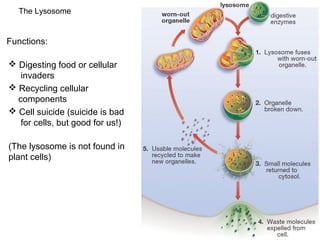
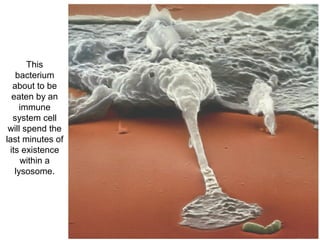
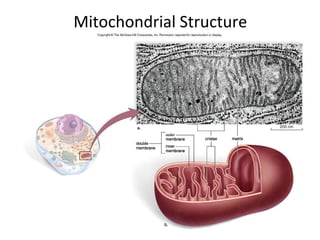
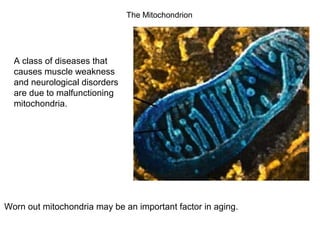
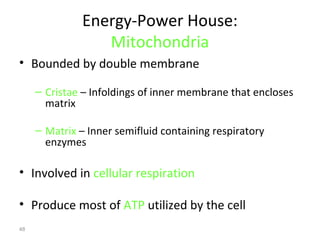
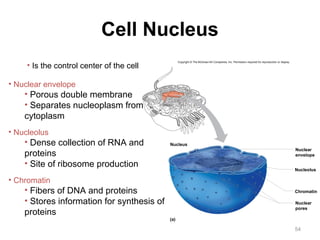
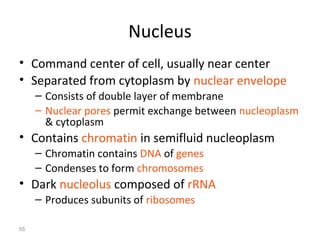
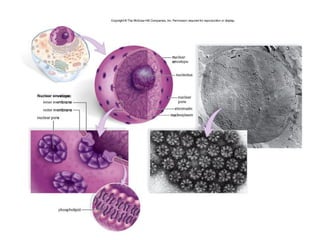
All organisms are composed of one or more cells, which are the basic unit of life. A typical animal cell contains organelles such as a nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and microtubules. The nucleus houses the cell's DNA and directs cell activities, while organelles such as mitochondria generate energy and the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus modify and transport proteins within the cell. Cells arise only through division of preexisting cells, demonstrating the cell theory that cells are the fundamental unit of life.