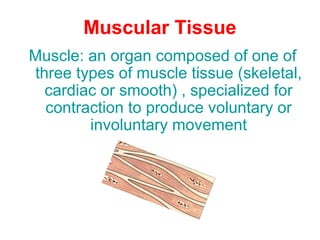
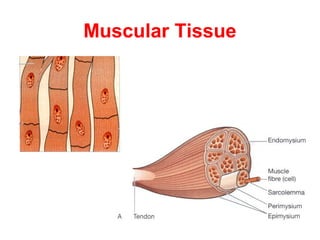
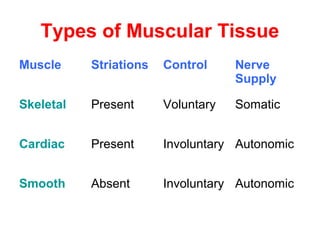
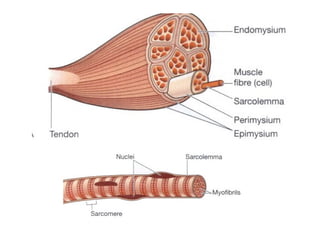
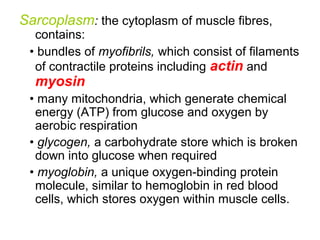
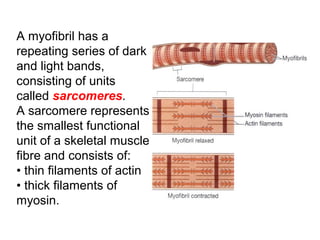
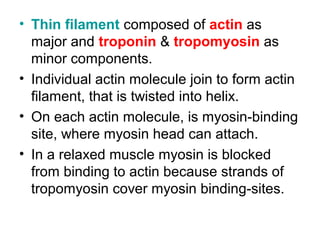
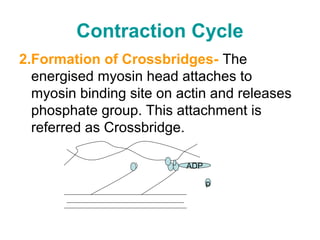
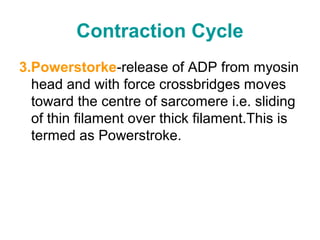
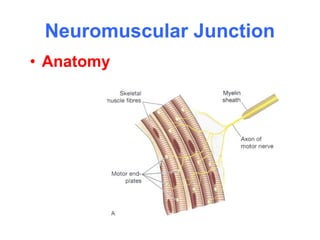
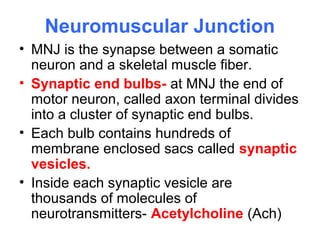
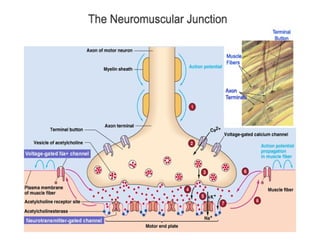
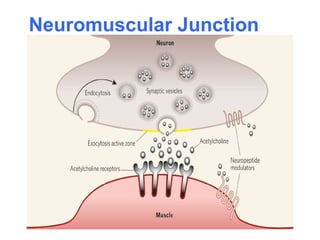
Muscular tissue is composed of muscle fibers that contract in response to electrical signals. There are three types of muscle tissue - skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle is striated, voluntary, and attached to bones. It contracts through a sliding filament mechanism where actin and myosin interact powered by ATP hydrolysis. At the neuromuscular junction, a nerve impulse triggers the release of acetylcholine which binds receptors and generates a muscle action potential, causing contraction.