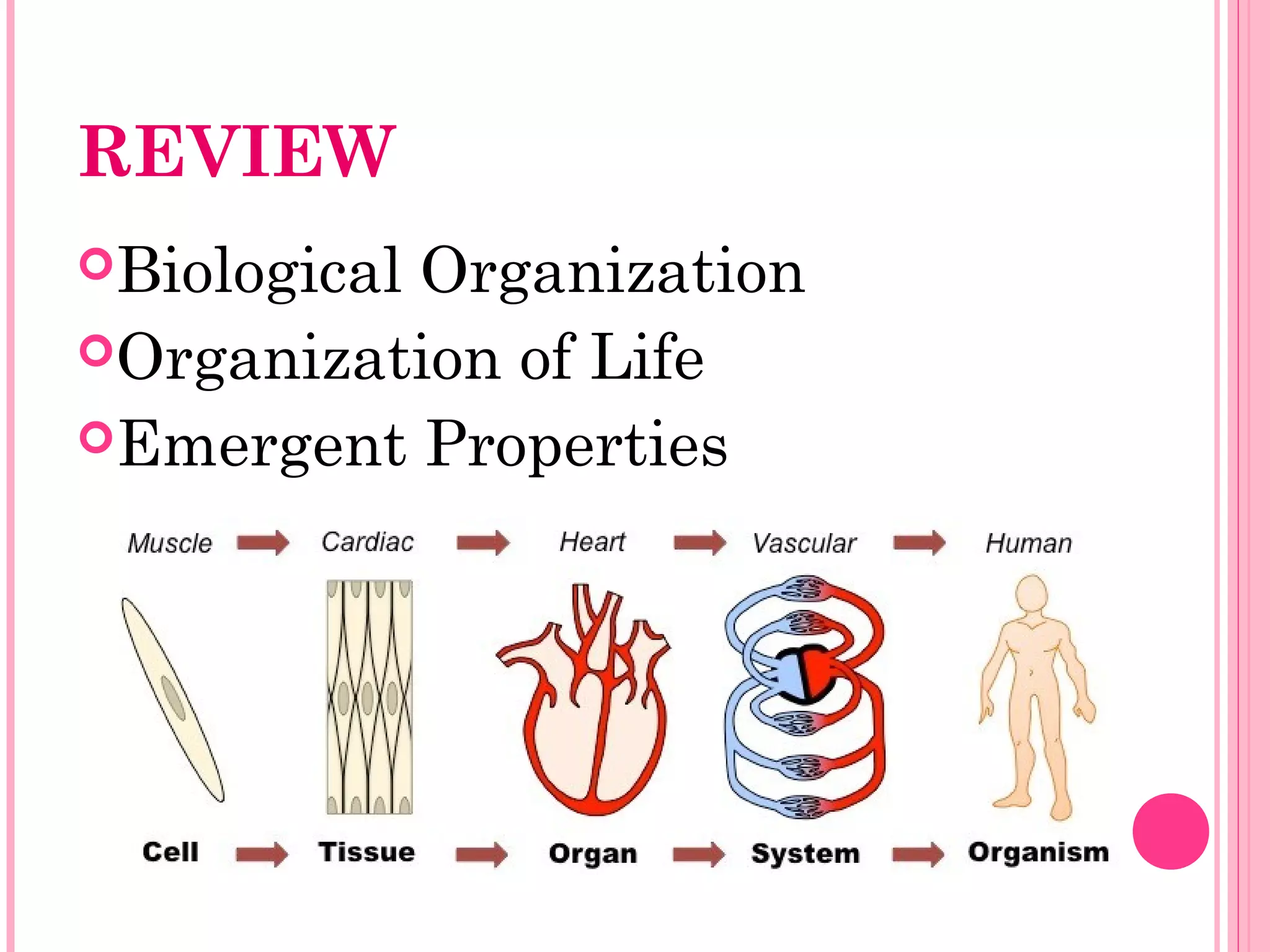
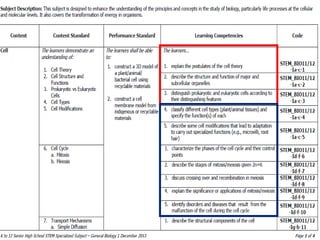
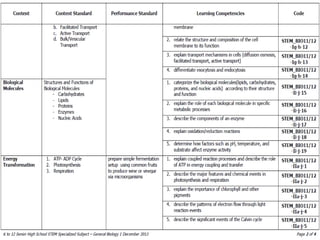
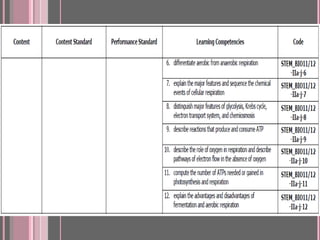
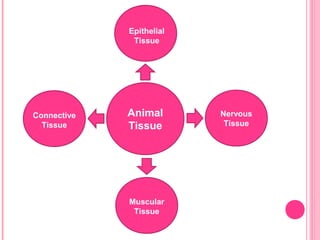
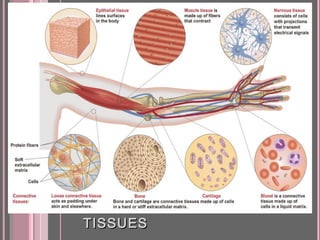
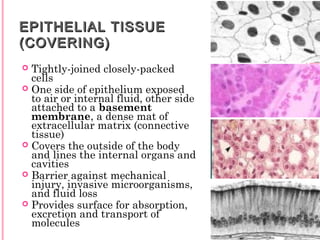
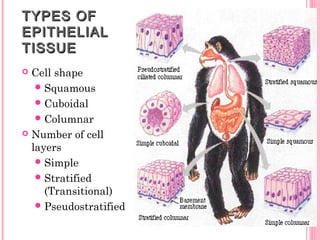
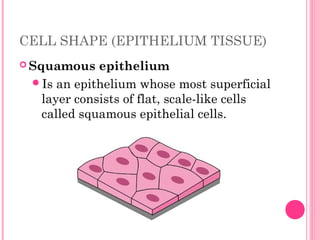
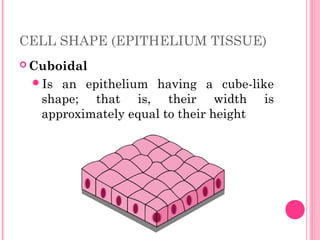
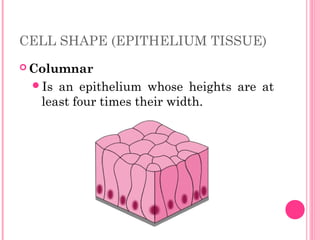
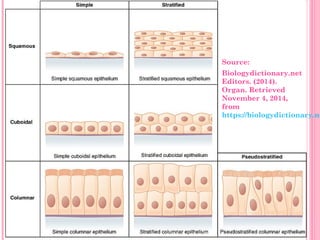
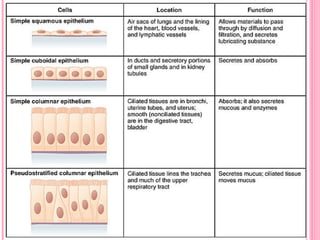
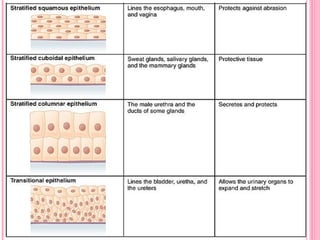
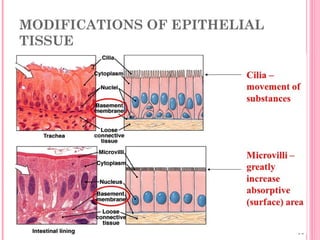
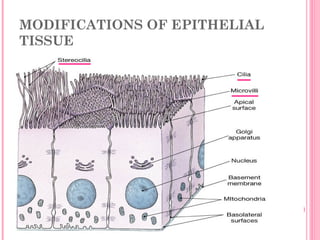
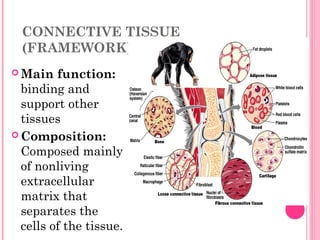
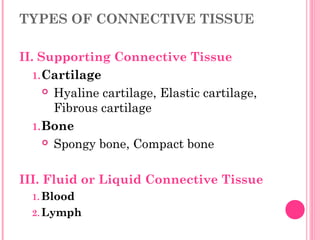
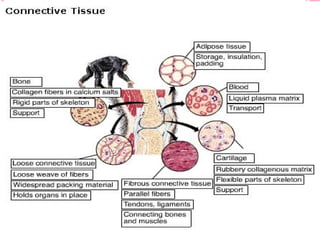
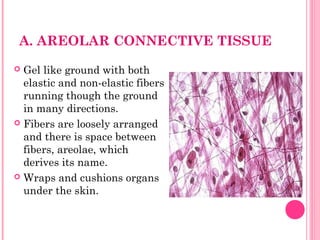
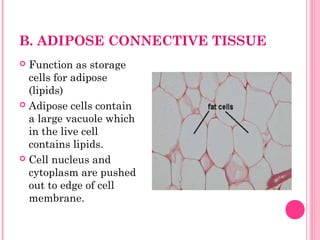
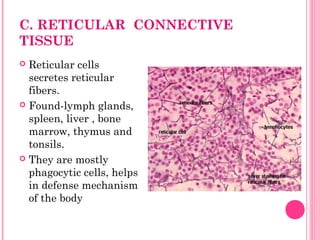
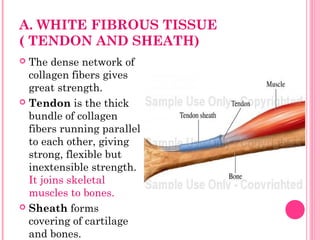
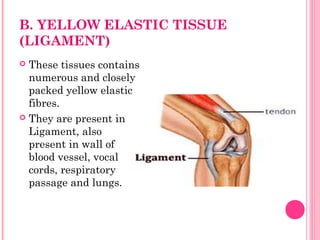
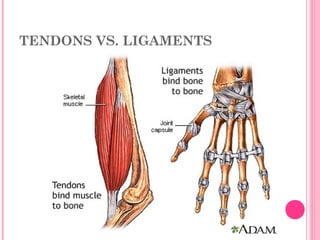
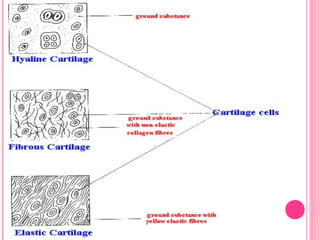
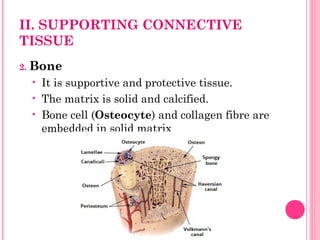
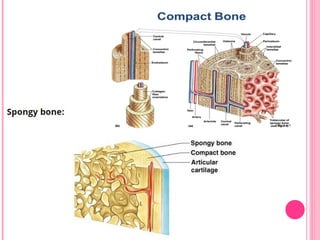
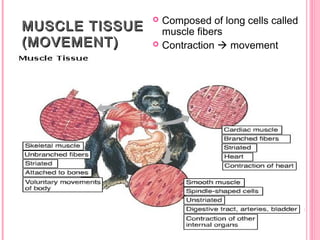
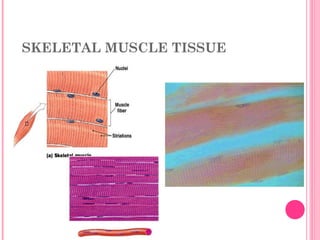
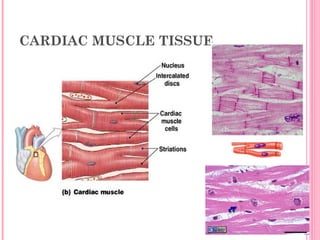
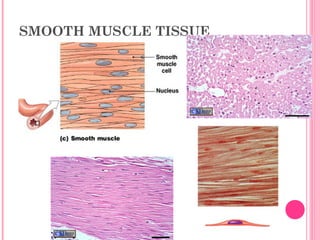
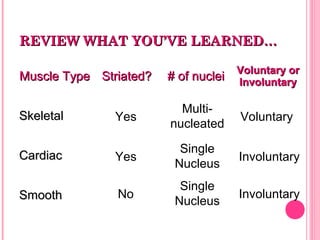
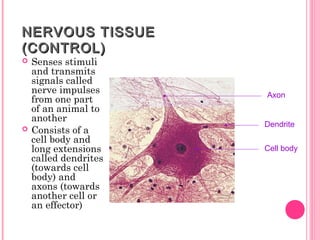
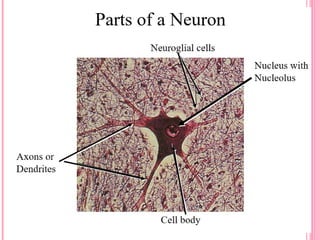
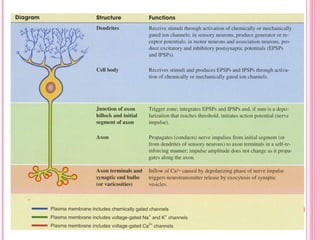
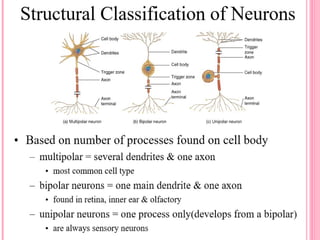
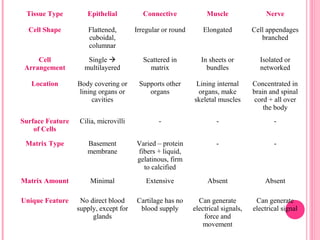
This document discusses the four main types of tissues in animals: epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous tissue. It provides details on the structure and function of each tissue type, including the different cells and materials that make up the tissues. For epithelial tissue, it describes the three main cell shapes - squamous, cuboidal and columnar - and explains how epithelia can be classified based on cell layers. For connective tissue, it outlines the different categories and functions, such as areolar tissue binding organs together and bone providing structure. The document also compares the key characteristics of skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscle cells.