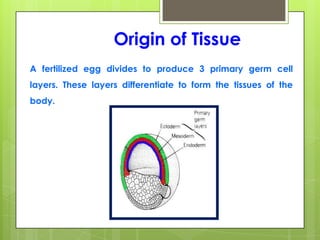
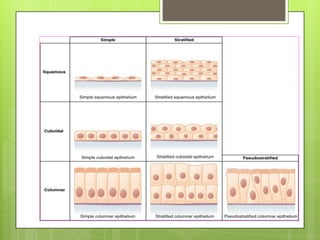
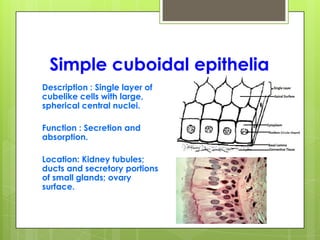
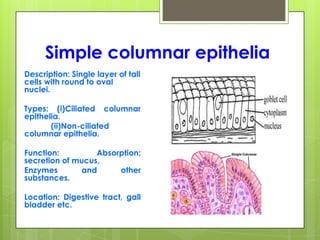
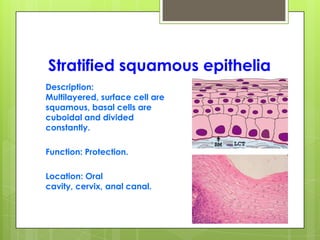
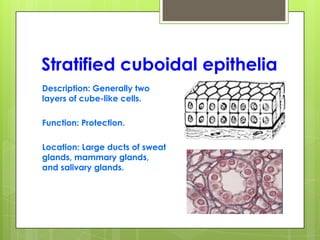
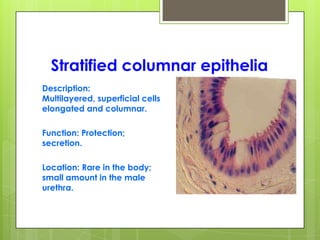
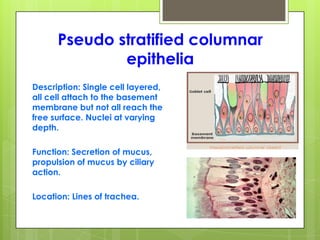
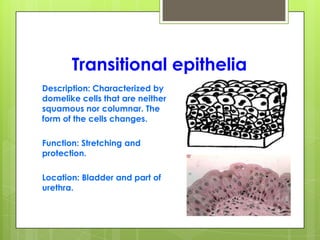
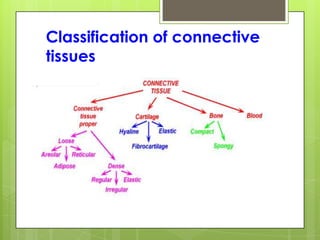
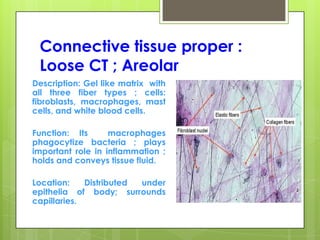
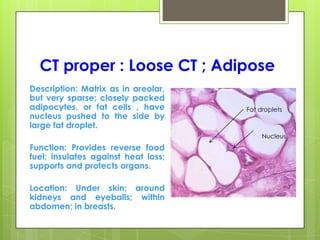
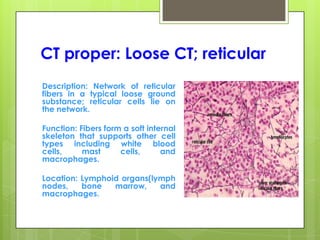
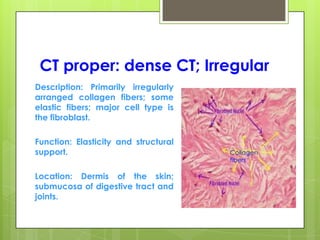
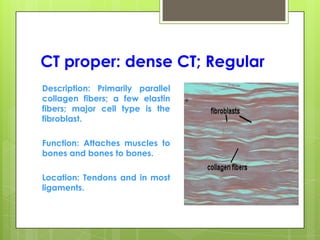
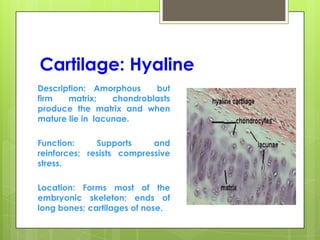
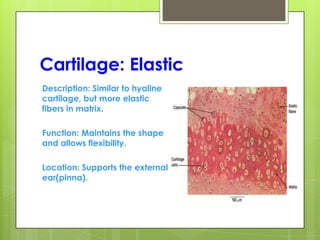
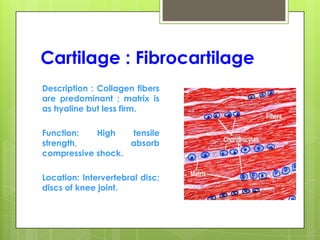
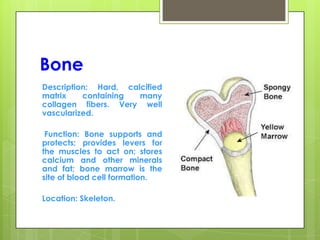
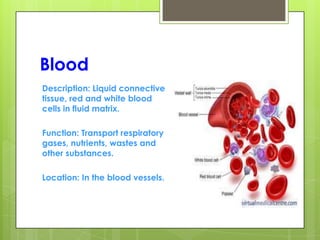
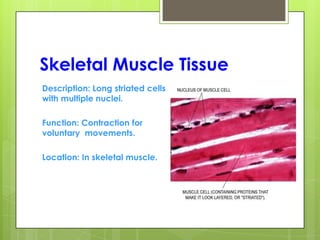
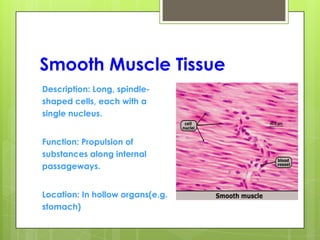
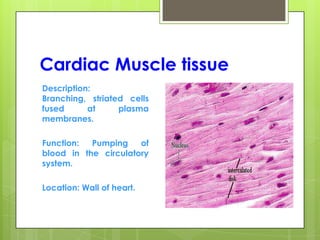
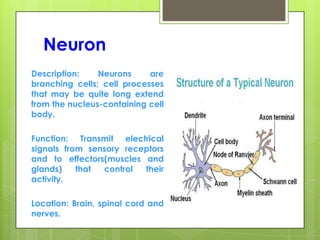
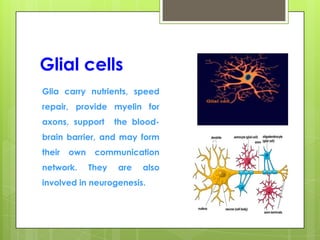
This document provides an overview of the four basic types of tissues in the human body: epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissue. It describes their general characteristics, classifications, and locations. Epithelial tissue covers and lines body surfaces and organs. It is classified based on cell layers and shapes. Connective tissue connects and supports other tissues. Its classifications include connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone, and blood. Muscular tissue is excitable and contractile, with three types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Nervous tissue is the most complex and forms the brain, spinal cord, and nerves to regulate body functions.