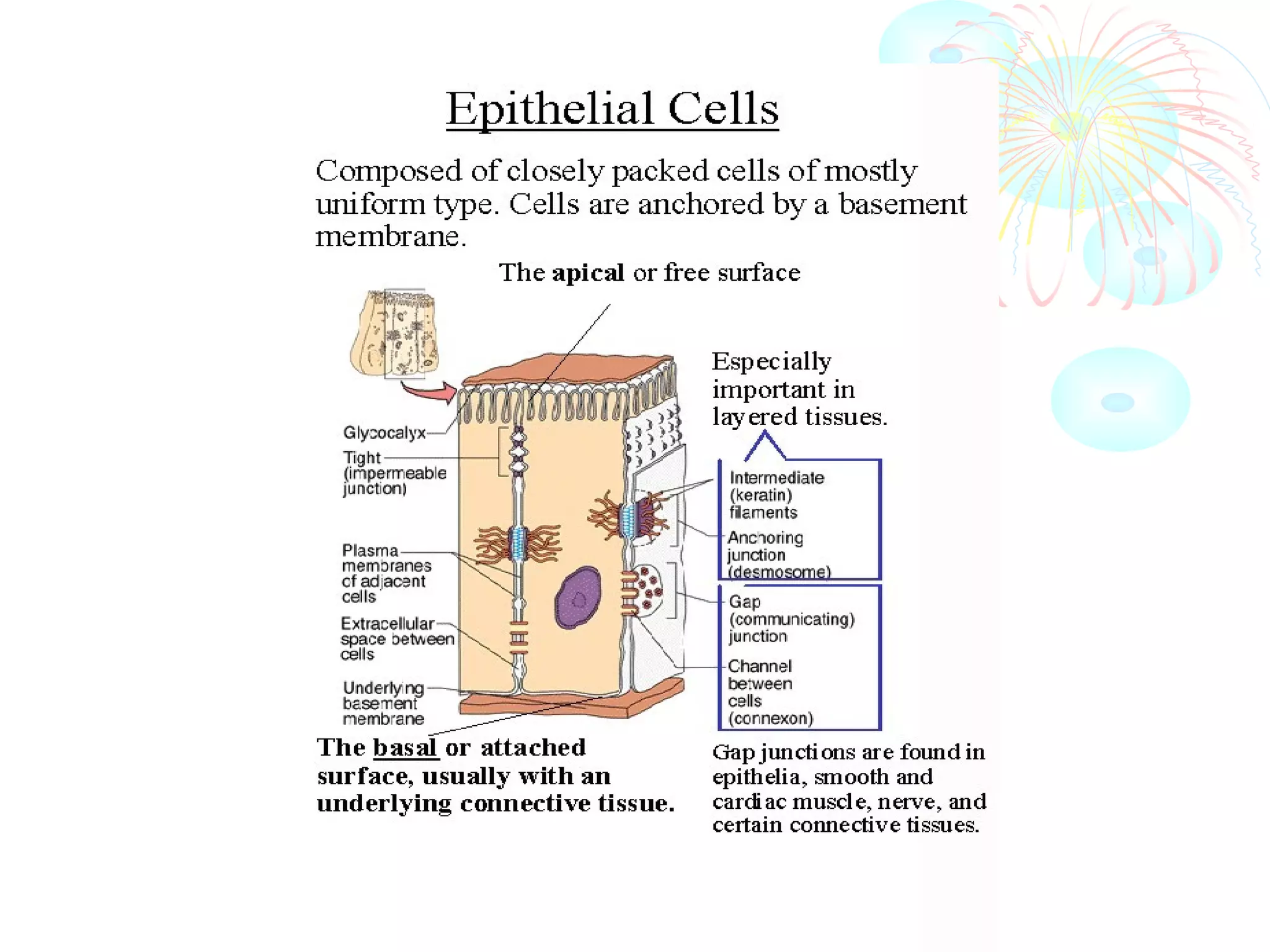
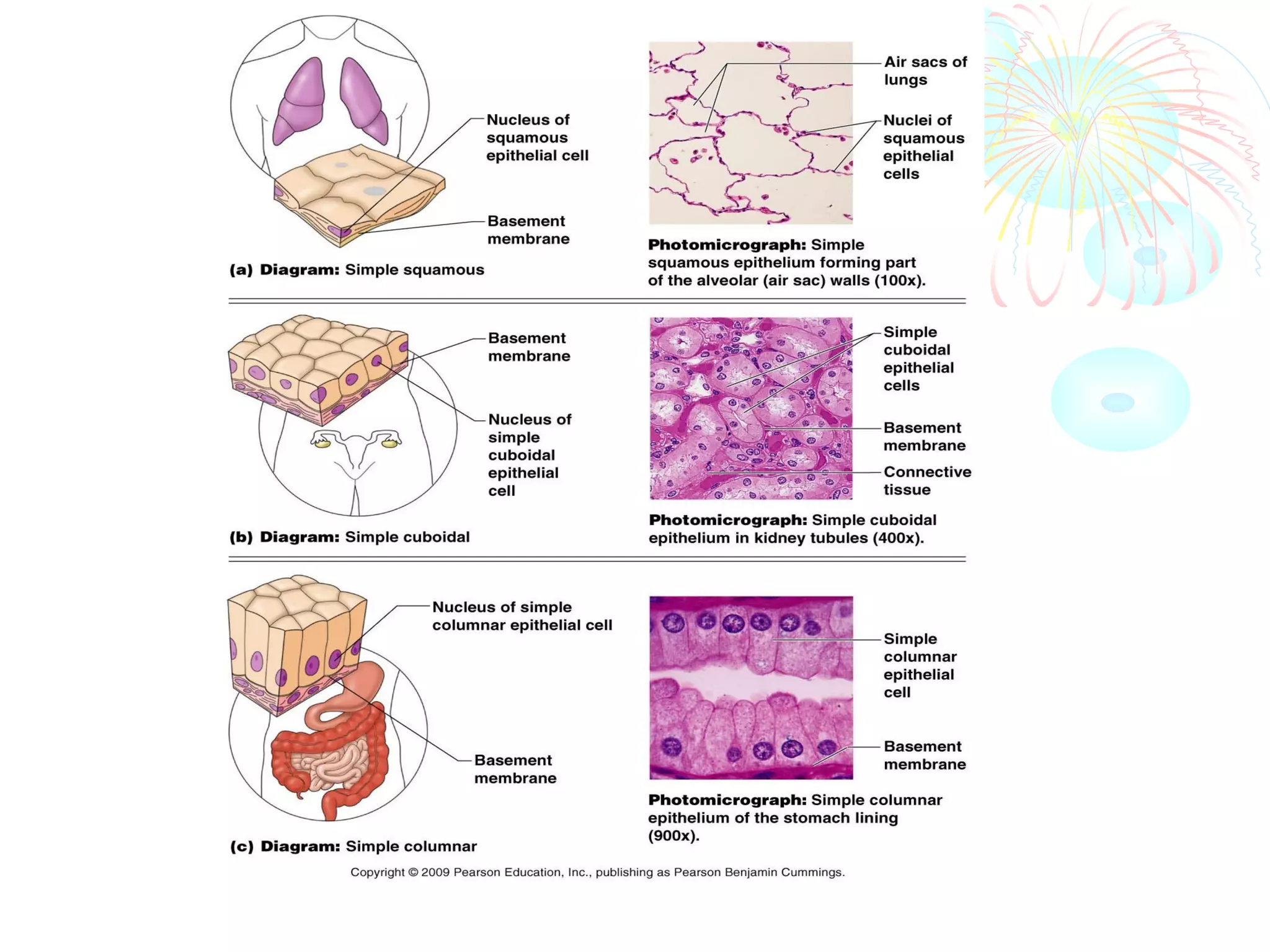
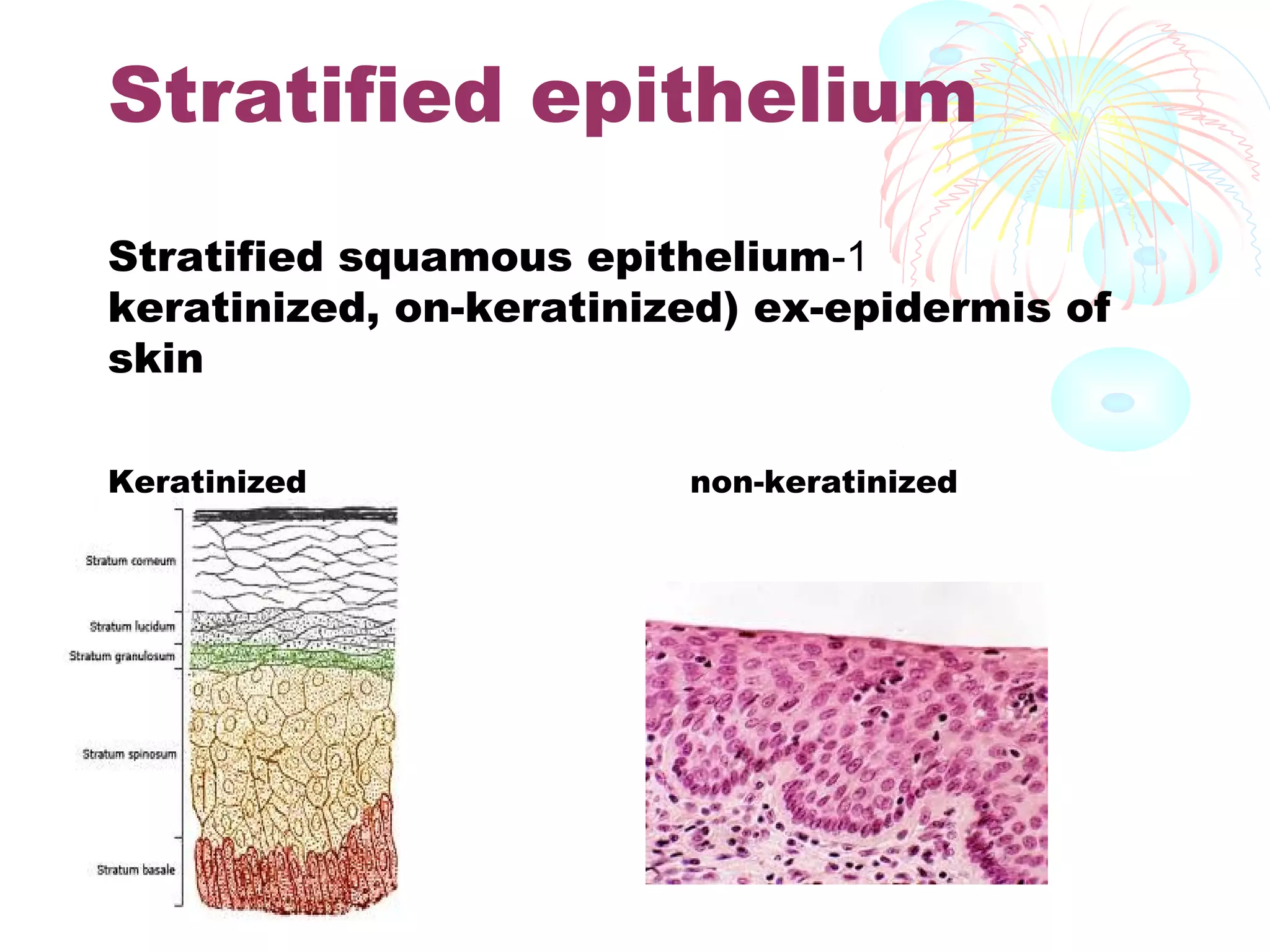
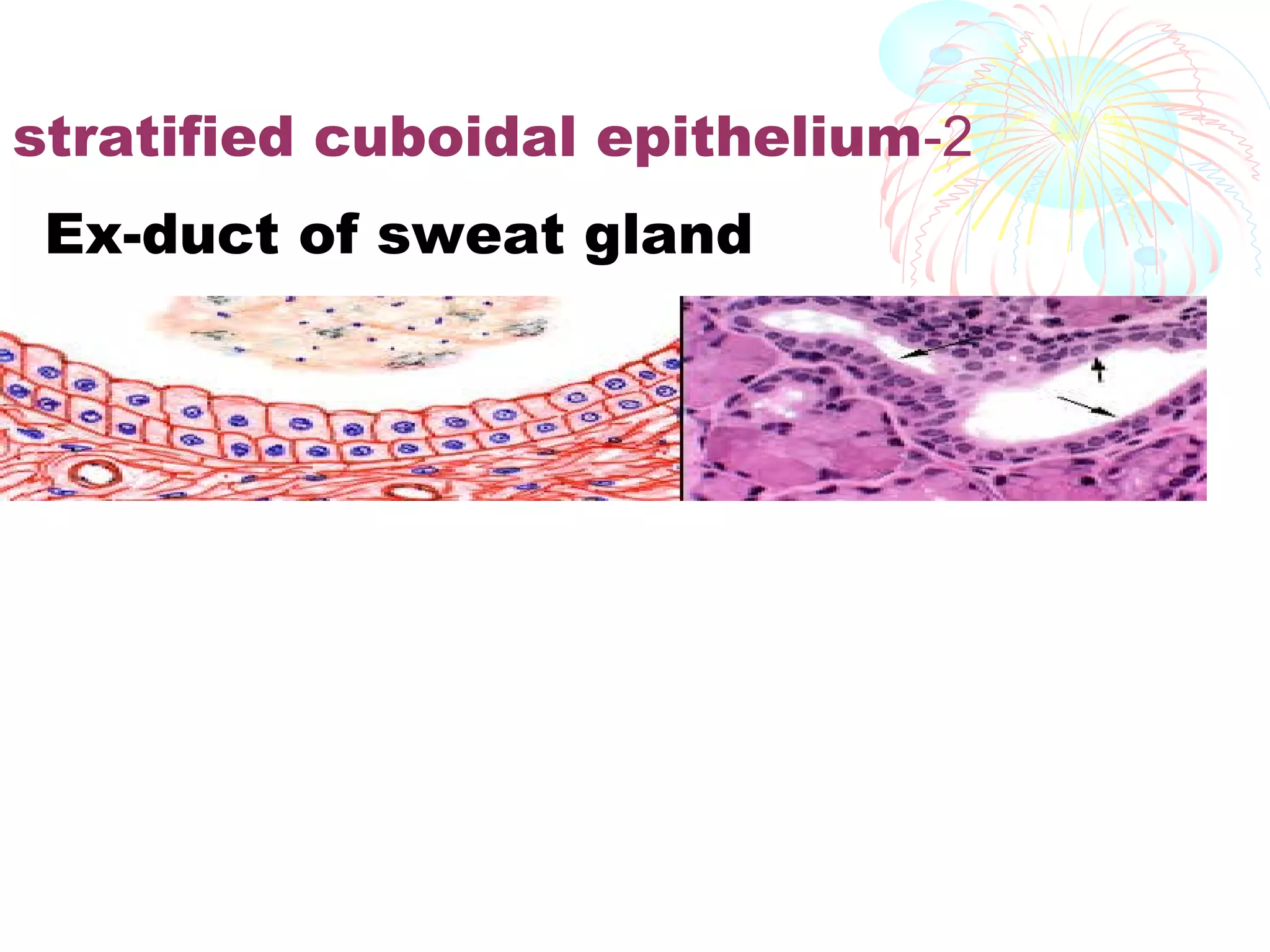
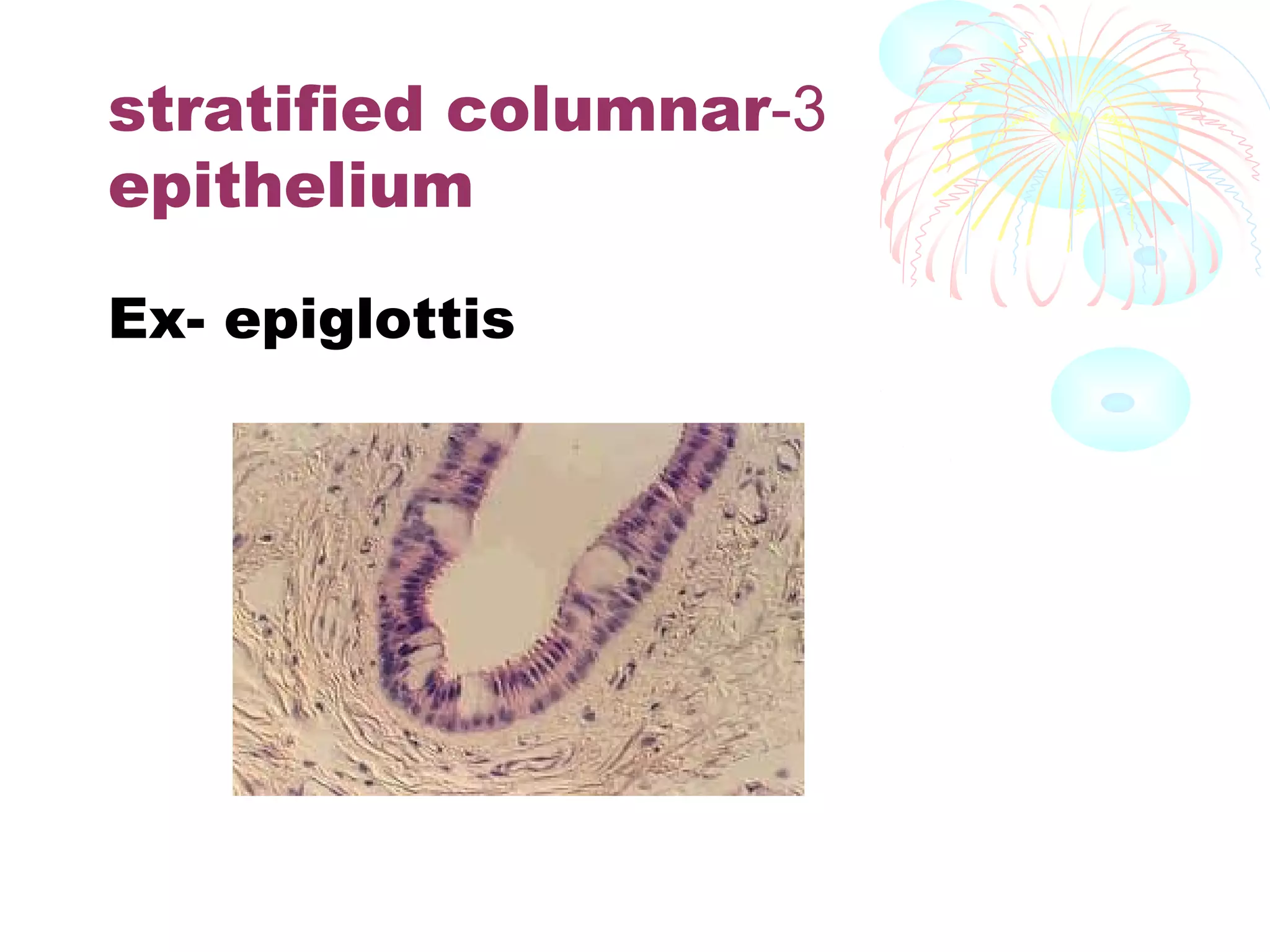
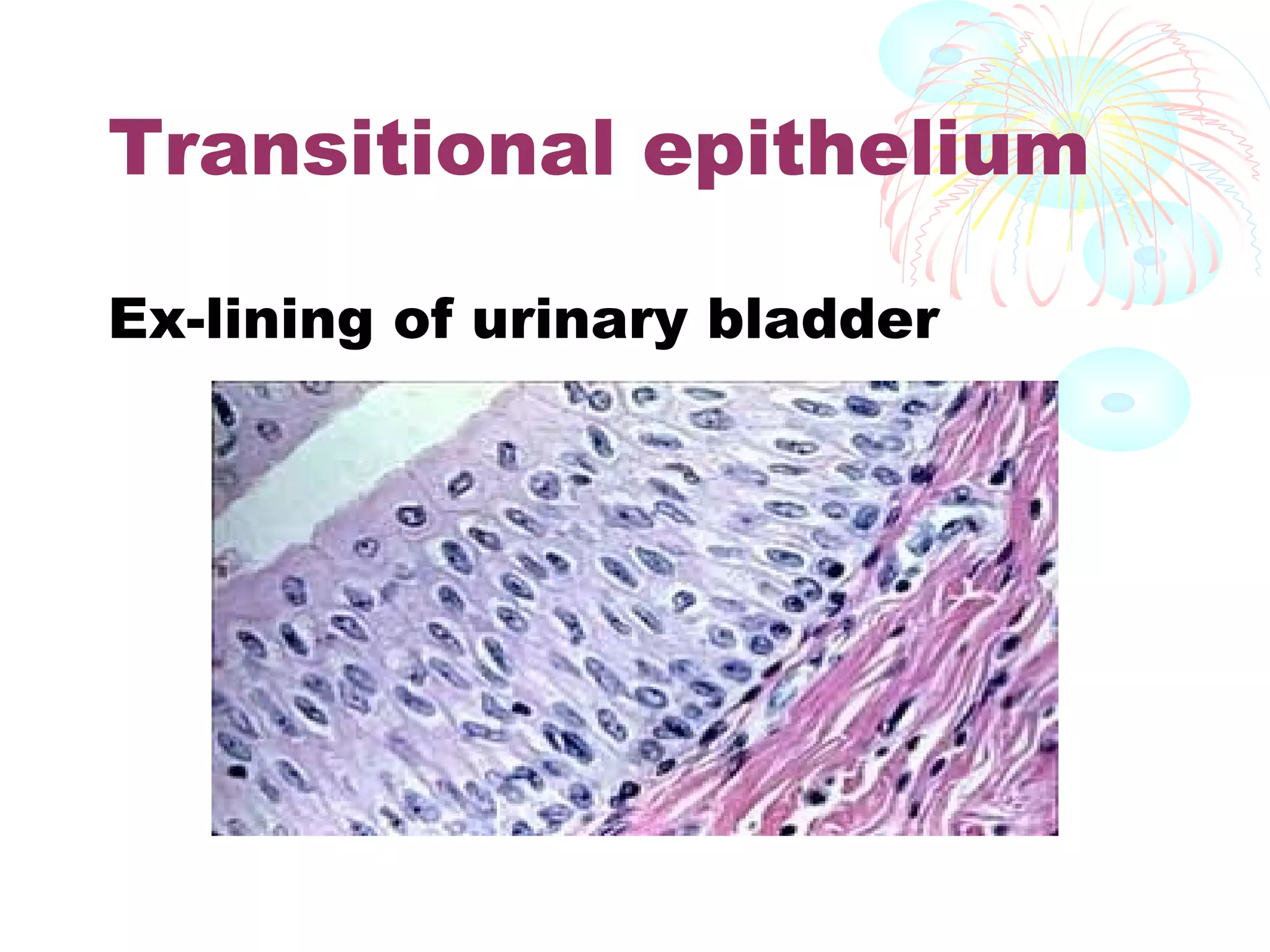
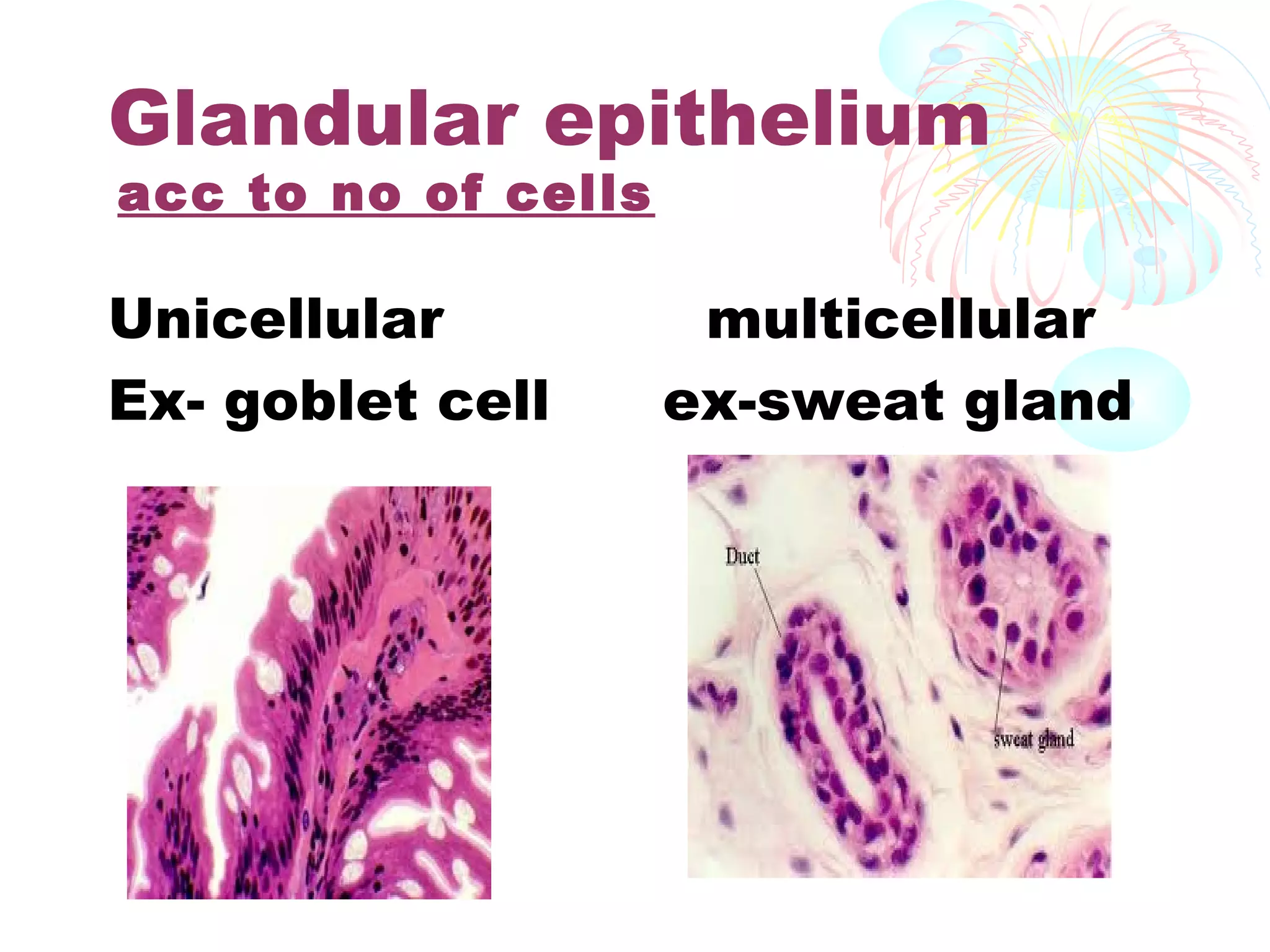
This document provides an overview of general histology. It defines histology as the study of tissues and how they are arranged to form organs. There are four main types of tissues: epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous. Epithelial tissue lines surfaces and forms glands. It is classified based on cell layers and shapes. Glandular epithelium is classified by cell number, presence of ducts, secretion method, and duct system. Special types include neuroepithelium, germinal epithelium, and myoepithelium. Histology is important for medical diagnosis as many diseases are identifiable at the cellular level using histological techniques.