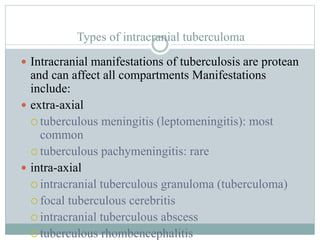
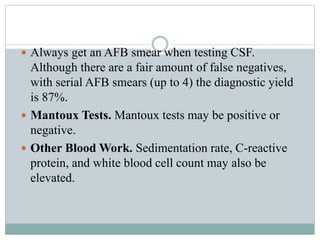
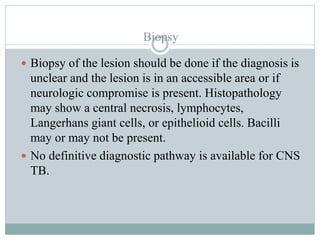
Tuberculoma is a benign, non-cancerous mass caused by a localized tuberculosis infection that most commonly appears in the lungs or brain. It results from infection by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria. Symptoms vary depending on the location of the tuberculoma but often include headaches, fever, and neurological deficits. Diagnosis involves imaging tests like CT or MRI scans showing characteristic lesions, as well as spinal fluid and tissue analysis. Treatment primarily consists of a prolonged course of multiple antibiotic medications over 9-12 months.




![Risk factors
Many factors predispose a person to TB. 95% of their
patients had low social, economic, and nutritional
conditions. CNS tuberculomas are seen in 0.55% to
15% of systemic TB cases, Intracranial tuberculomas
are seen in about 1% of all patients with TB,[6]
whereas intradural spinal tuberculomas are reported
to be 2% to 5% of CNS tuberculomas.[1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tuberculoma-190315175019/85/Tuberculoma-6-320.jpg)