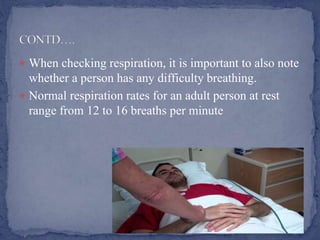
Vital signs are measurements of basic body functions including body temperature, pulse rate, respiration rate, and blood pressure. Body temperature is normally between 97.8-99°F and can be taken orally, by ear, on the skin, under the arm, or rectally. Pulse is the heart rate measured in beats per minute, normally 60-100 bpm. Respiration is breaths per minute, normally 12-16. Blood pressure includes systolic (contraction) and diastolic (relaxation) pressures in mmHg, with normal being below 120/80 mmHg.