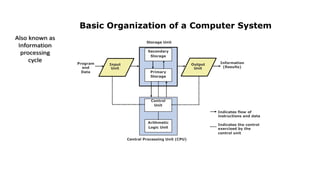
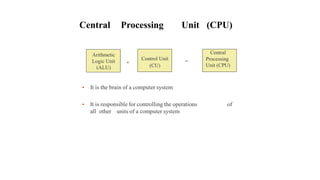
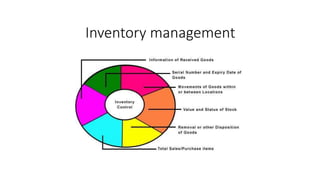
The document outlines the basic organization of a computer system, detailing the roles of various components including the input unit, output unit, storage unit, arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and control unit (CU). It also highlights the applications of computer technology in business processes such as communication, inventory management, and customer relationship management. The central processing unit (CPU) is described as the 'brain' of the computer, coordinating the operations of all other units.