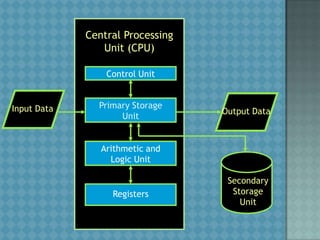
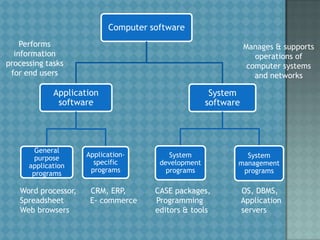
This document provides an overview of computer components and software. It defines a computer as an electronic device that can accept data as input, manipulate it according to programmed rules, produce output from that processing, and store results. The central processing unit (CPU) contains a control unit that interprets instructions and an arithmetic logic unit that performs logical and arithmetic processes. Input and output devices allow entering and presenting data. Primary storage like RAM stores active data and software, while secondary storage like hard disks store inactive data. The document outlines types of computer systems and peripherals, input and output technologies, and categories of system and application software.