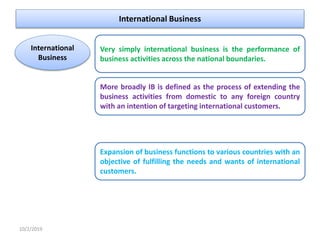
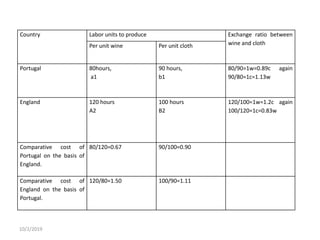
International business involves conducting business activities across national boundaries to meet international customer needs. Key reasons for engaging in international business include surplus production, resource scarcity, competitive pressure, and the pursuit of profit. Common approaches to enter foreign markets include exporting, licensing, joint ventures, and multinational corporations.