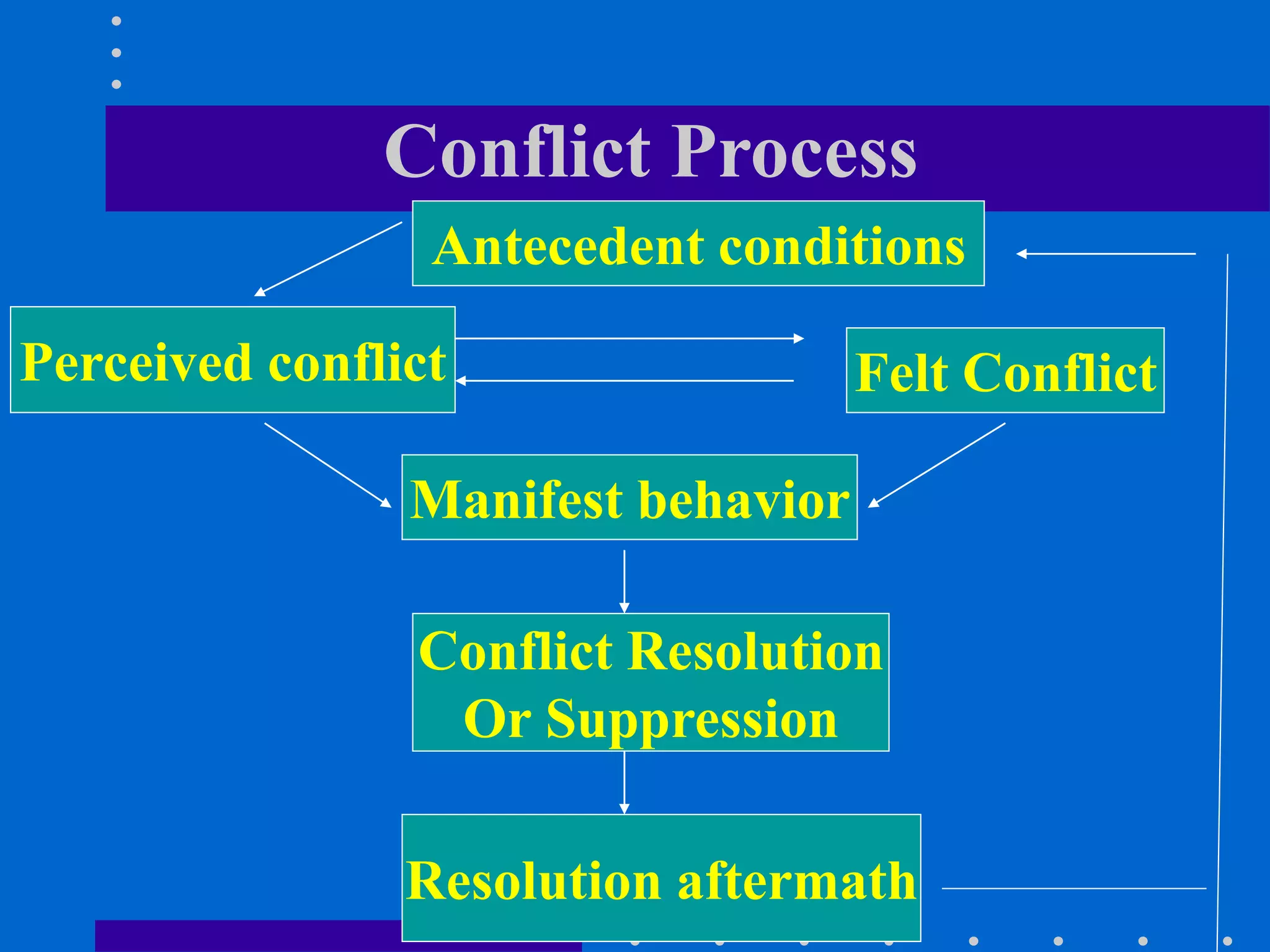
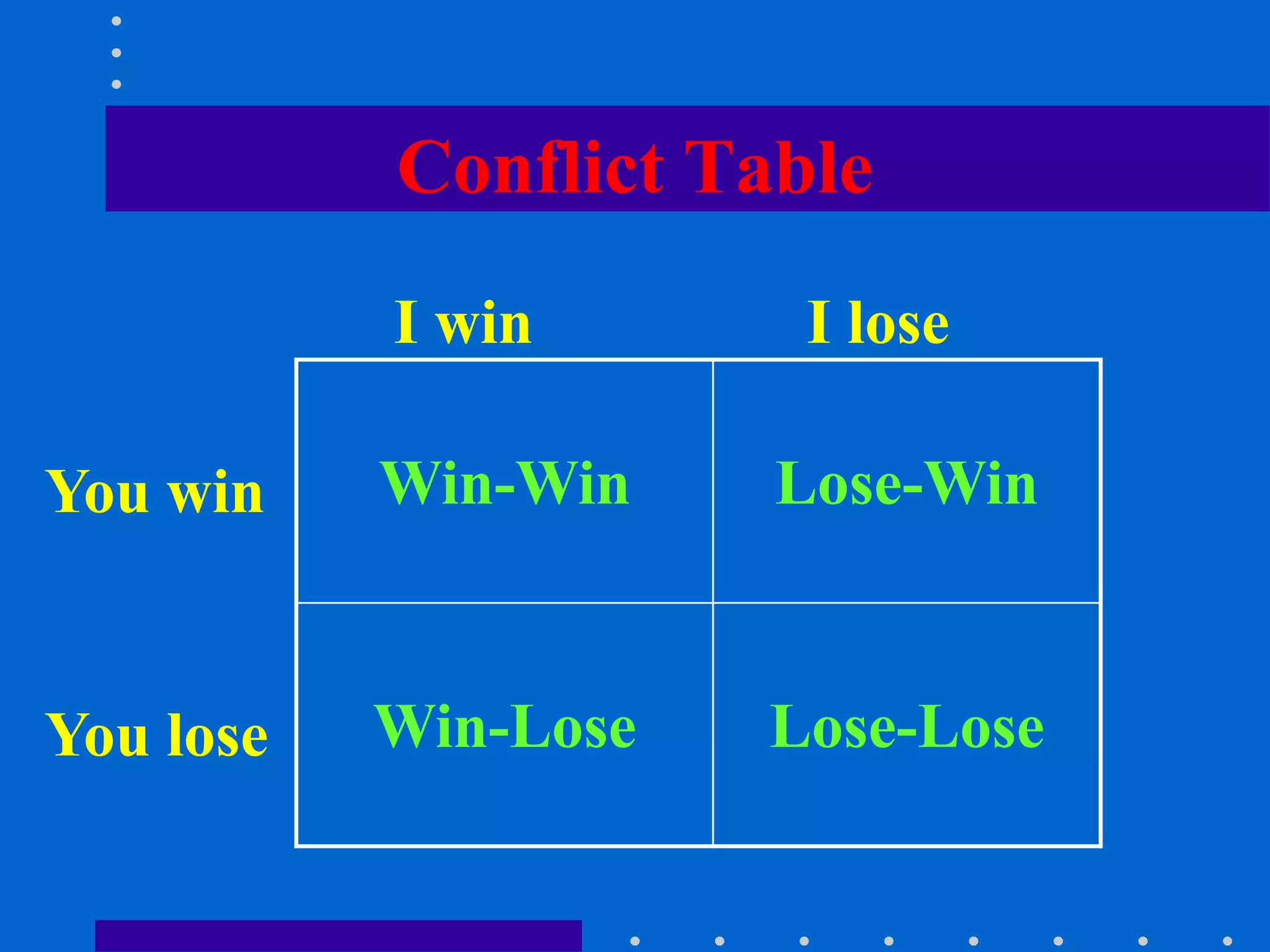
This document discusses conflict management in an organizational context. It begins by defining conflict and outlining learning objectives around understanding conflict, dealing with typical conflicts that arise, and developing skills to resolve conflicts. It then presents a case study about the performance of three typists, Anabia, Sonia and Tania, and asks the reader to evaluate their performance. Additional details provided about each typist may affect the reader's evaluation. The document goes on to discuss causes of conflicts, effects of conflicts in organizations, different approaches to dealing with conflicts, and steps that can be taken to prevent and resolve conflicts. It concludes by noting that while conflict is inevitable and not entirely negative, poorly managed conflicts can have counterproductive results while well-managed