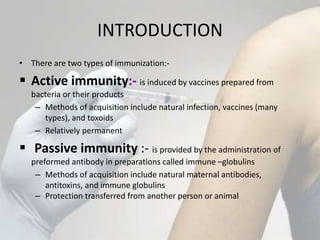
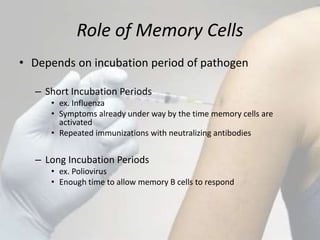
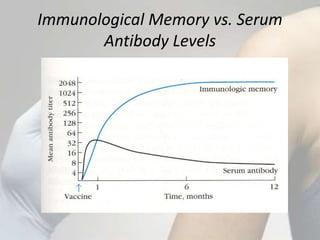
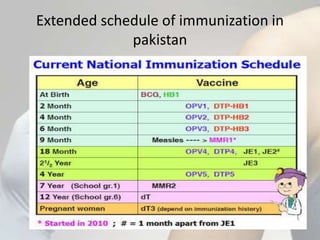
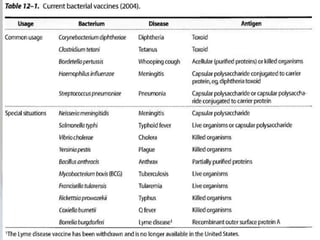
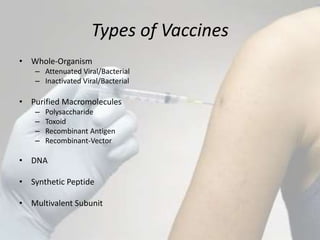
The document discusses different types of bacterial vaccines. It begins by introducing active and passive immunity. Active immunity is induced by vaccines made from bacteria or their products, while passive immunity provides preformed antibodies from another source. The main types of bacterial vaccines discussed are whole-organism attenuated or killed vaccines, purified macromolecule vaccines like polysaccharides or toxoids, and subunit vaccines. Specific examples provided include vaccines for cholera, plague, typhus, pertussis, tetanus, diphtheria, hepatitis B, and human papillomavirus. Memory cells and immunological memory play an important role depending on the incubation period of the pathogen.