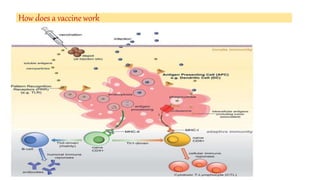
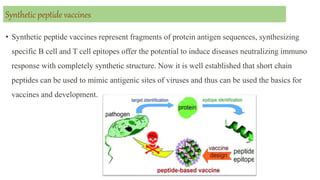
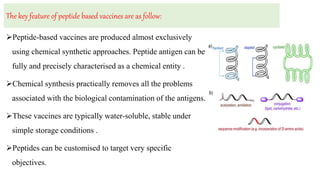
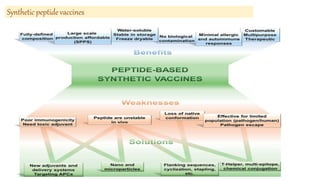
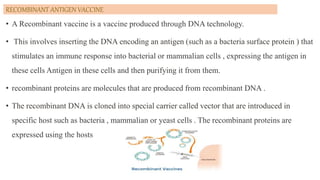
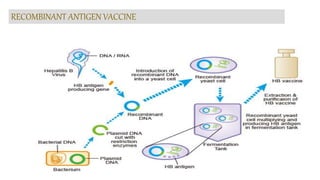
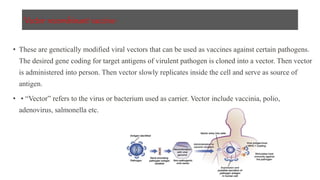
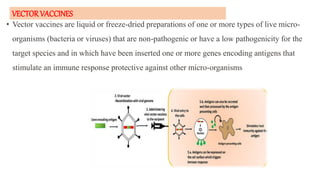
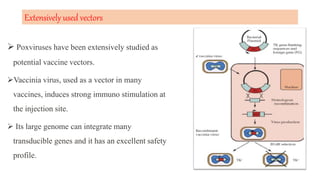
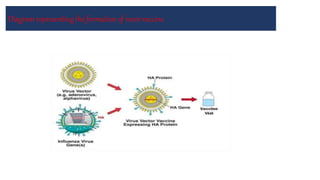
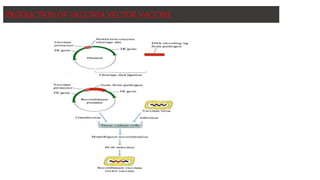
This document discusses different types of vaccines including synthetic peptide vaccines, recombinant antigen vaccines, and vector vaccines. Synthetic peptide vaccines use short peptide fragments to induce an immune response. Recombinant antigen vaccines produce antigens using DNA technology by inserting genes into host cells. Vector vaccines use non-pathogenic viruses or bacteria as vectors to deliver genes encoding antigens to stimulate immunity. Examples of extensively used viral vectors include vaccinia virus and adenovirus. Two vector vaccines are being developed against coronaviruses by using different viral vectors to deliver spike and nucleocapsid proteins.
![Presentation
on
Presented by:
Anshul Vishwakarma
M.PharmI Sem
Y21254007
SYNTHETIC PEPTIDE VACCINES , RECOMBINANT ANTIGEN
VACCINE, VECTOR VACCINES
[A central university]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syntheticpeptidevaccines-220808160923-c40f7a4d/75/Synthetic-peptide-vaccines-pptx-1-2048.jpg)