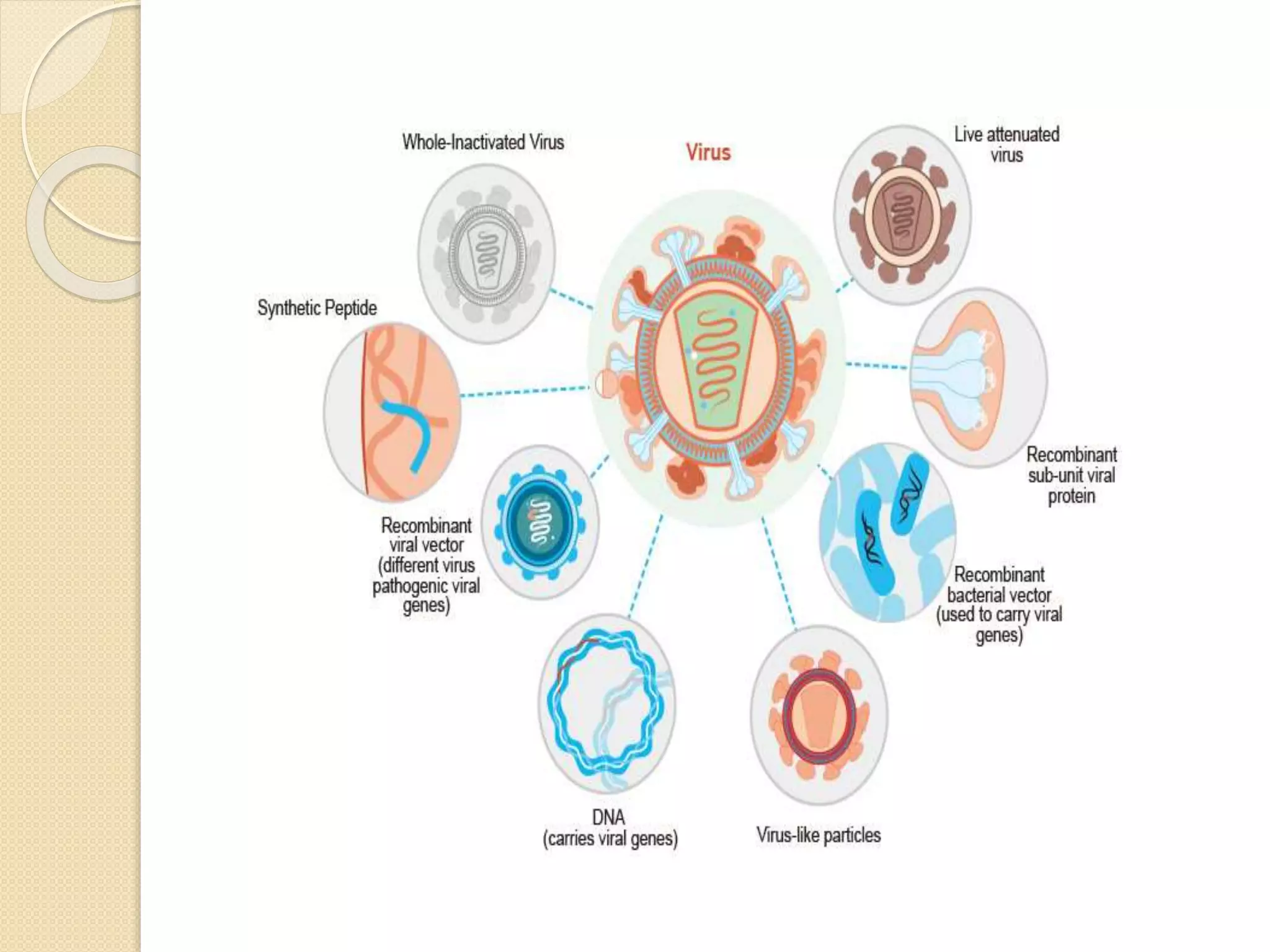
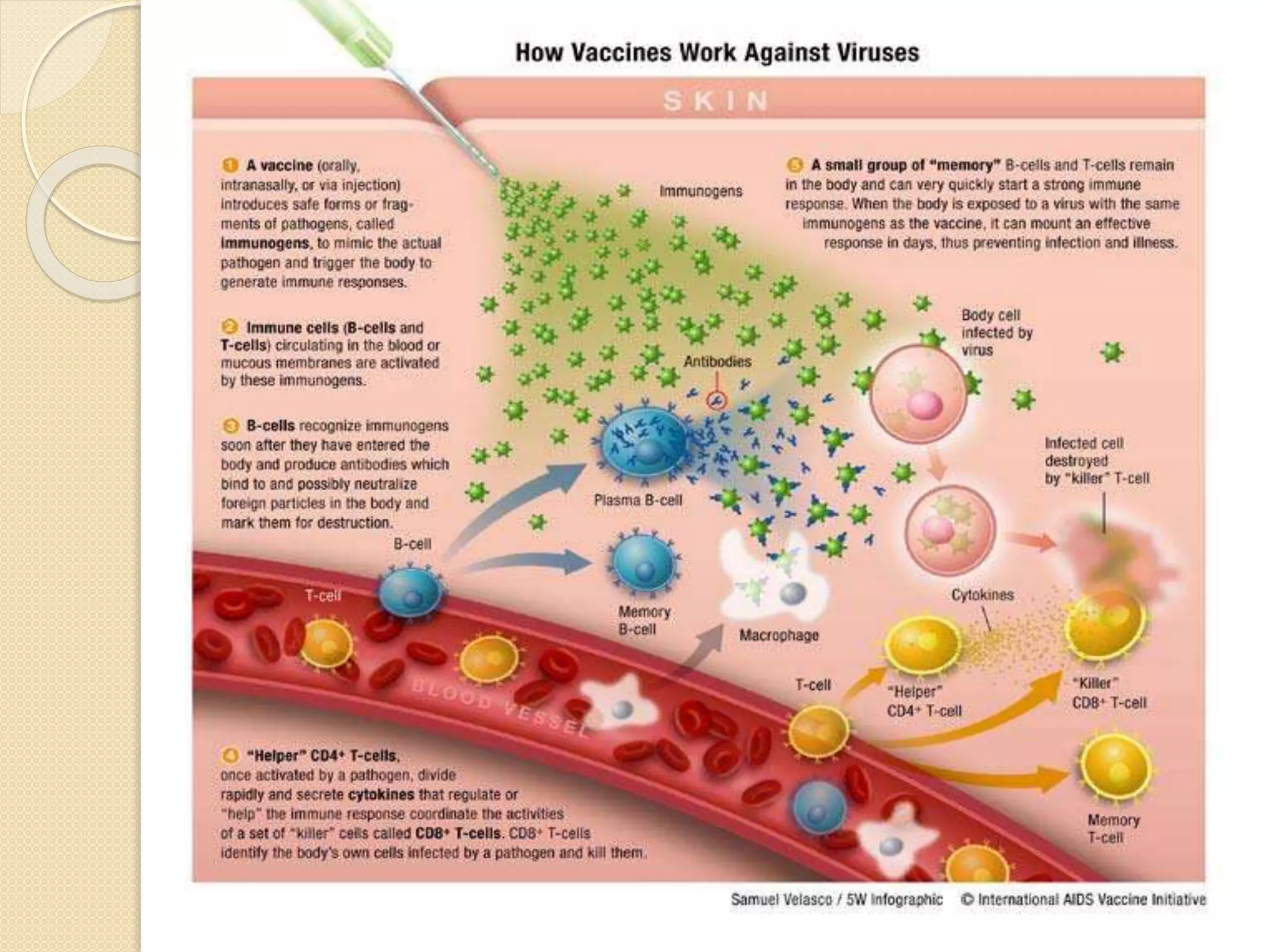
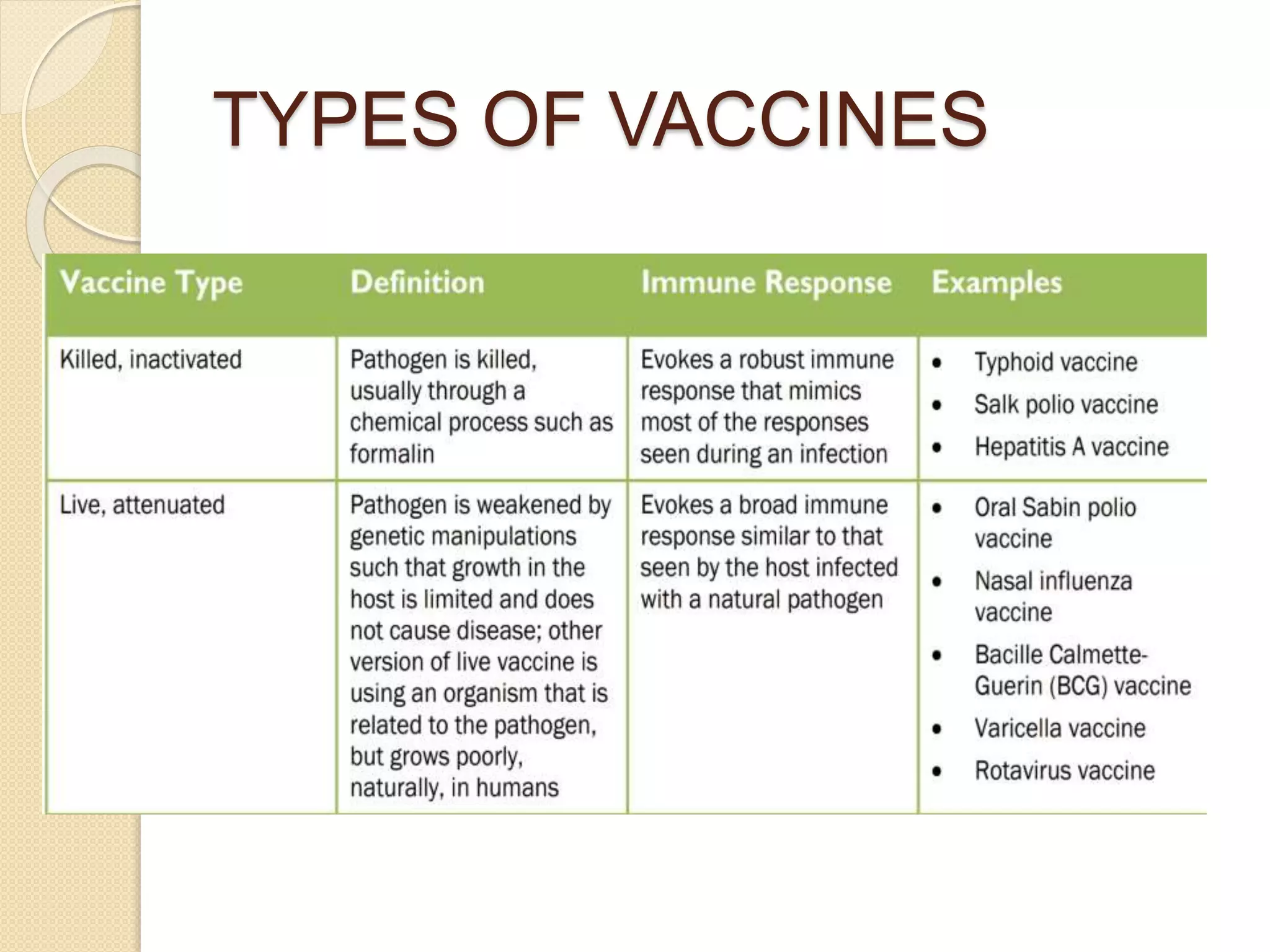
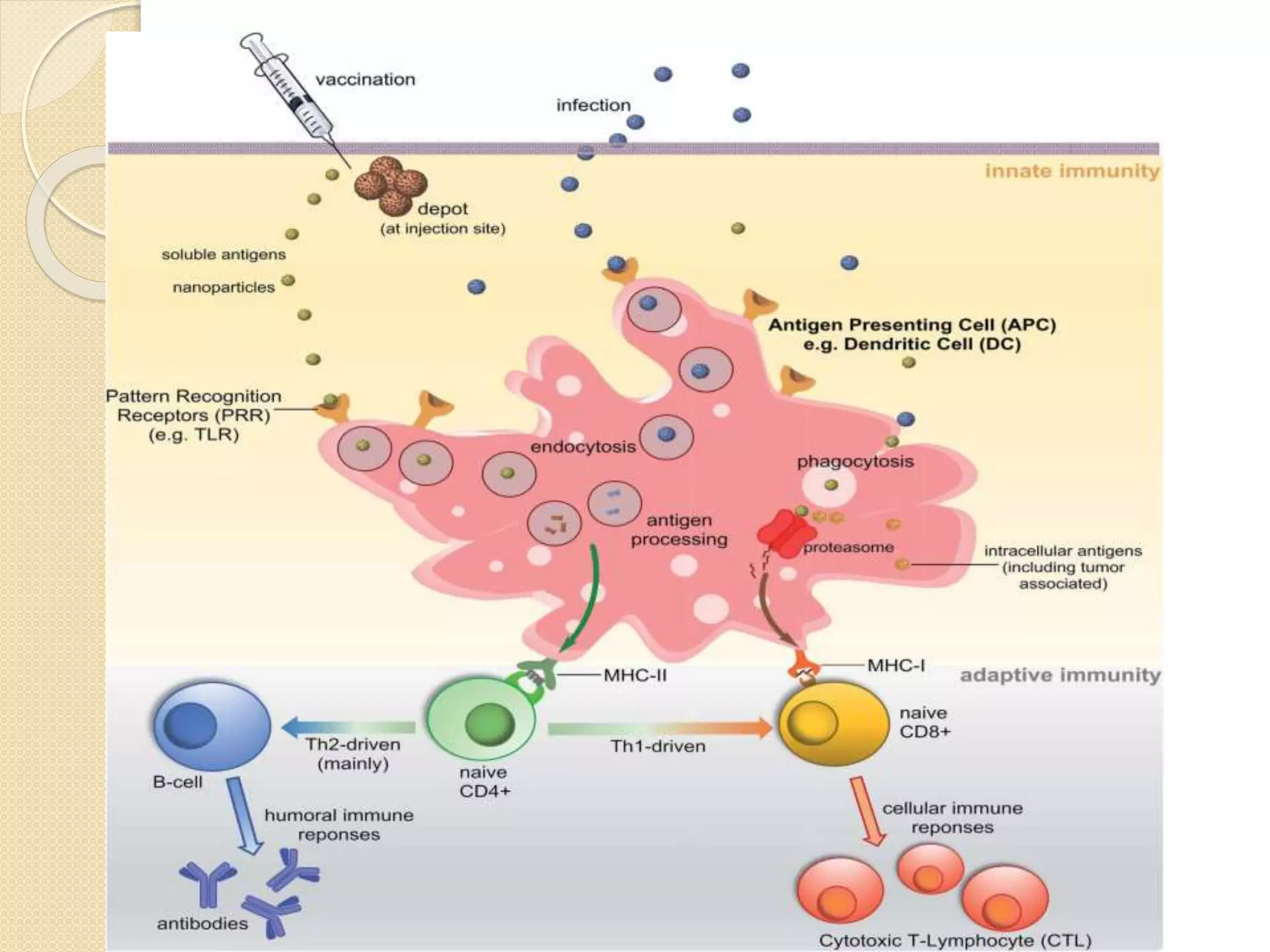
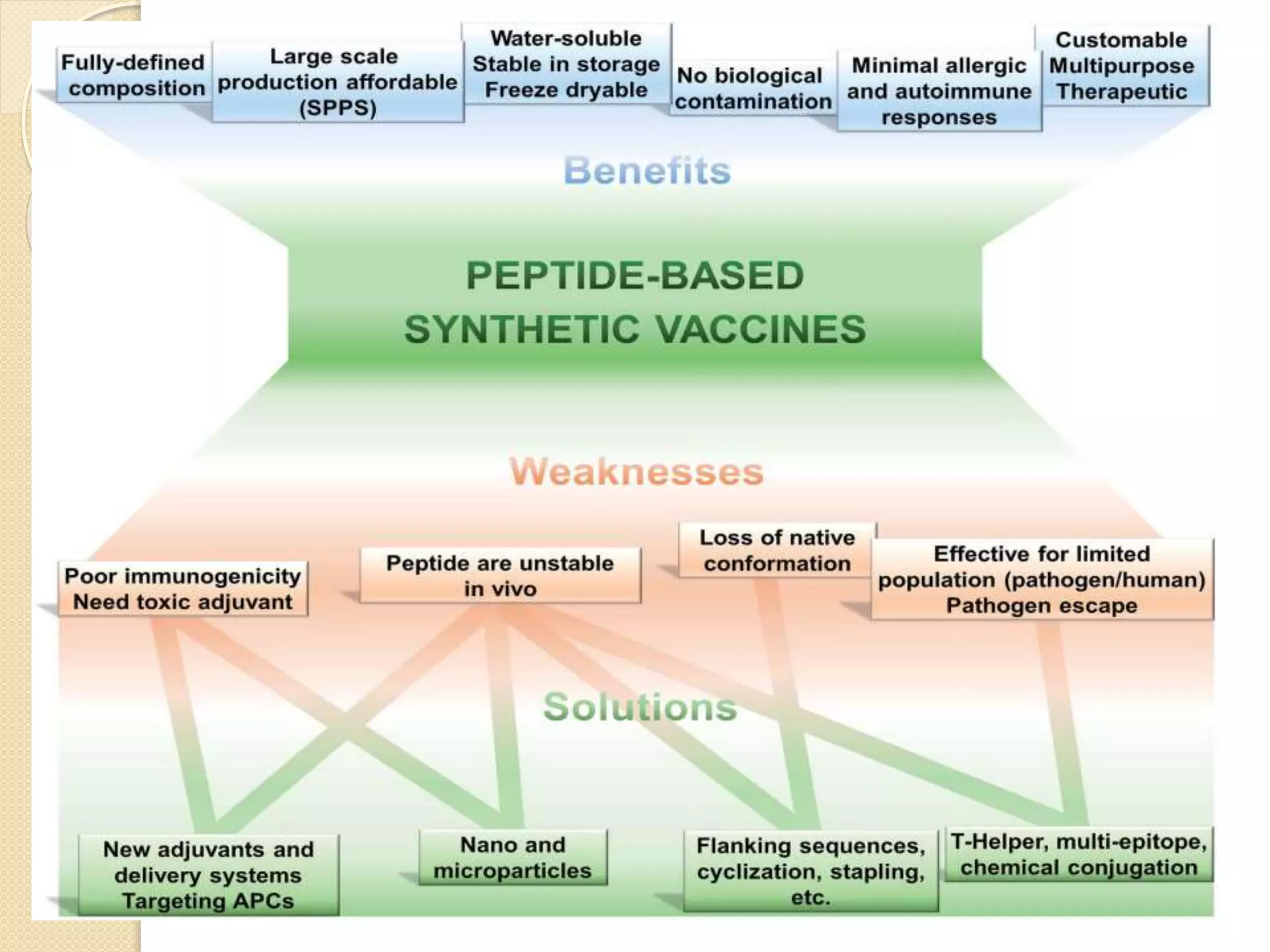
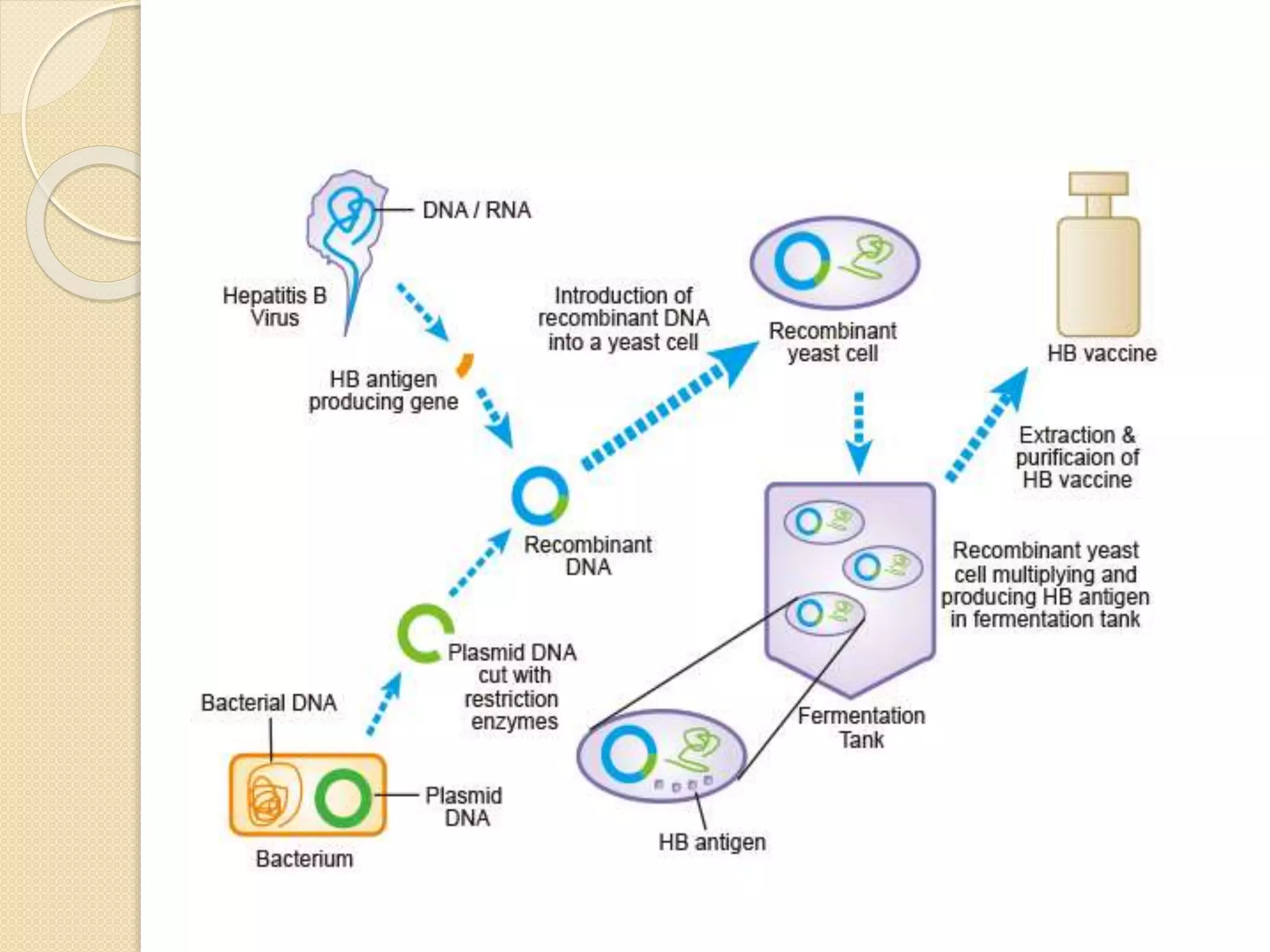
This document discusses synthetic peptide vaccines and recombinant antigen vaccines. It begins with definitions of vaccines and how they work to induce an immune response. It then describes two types of modern vaccines: synthetic peptide vaccines and recombinant antigen vaccines. Synthetic peptide vaccines use short fragments of viral or bacterial proteins that contain epitopes to induce an immune response, while recombinant antigen vaccines produce antigens through DNA technology by inserting viral or bacterial DNA into cells that then express the antigen protein. Both types of modern vaccines offer advantages over traditional vaccines like easier production and stability without refrigeration.