1. The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) helps the immune system recognize foreign substances. It is expressed on nearly all cells and plays a crucial role in organ transplant compatibility.
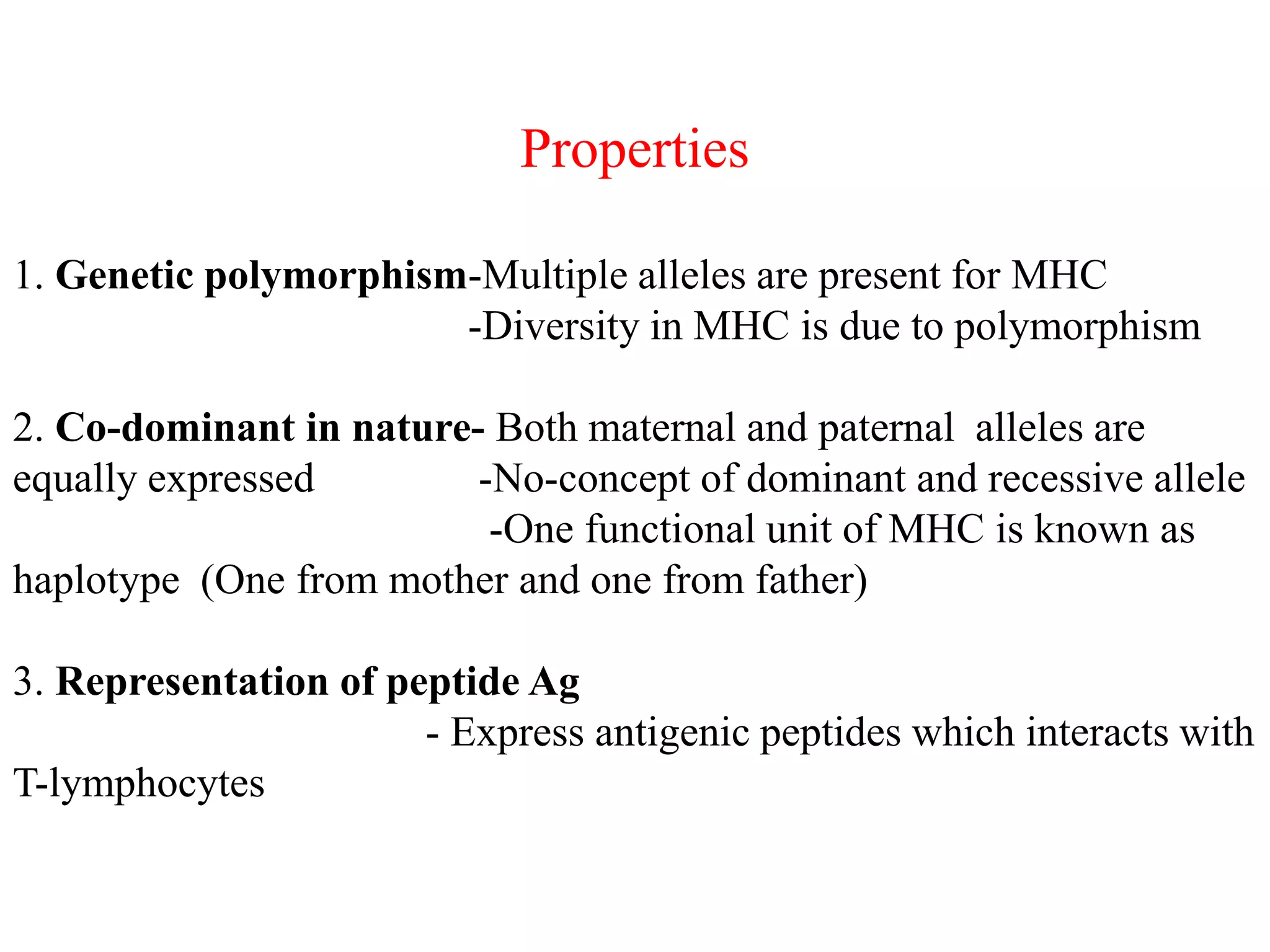
2. MHC molecules are classified into three types - MHC class I presents antigens to T cells within cells, MHC class II presents antigens to T cells between cells, and MHC class III encodes proteins unrelated to antigen presentation.
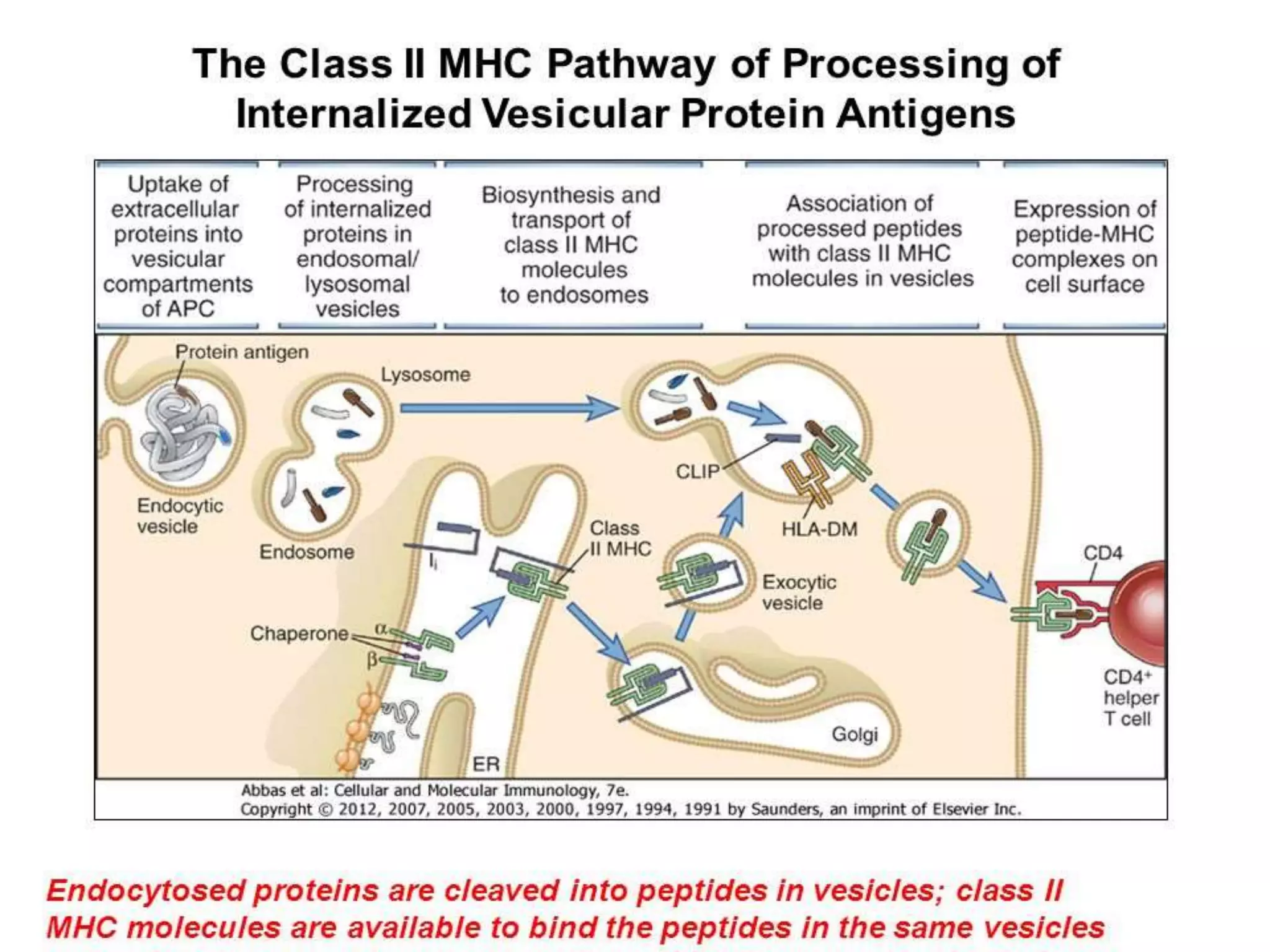
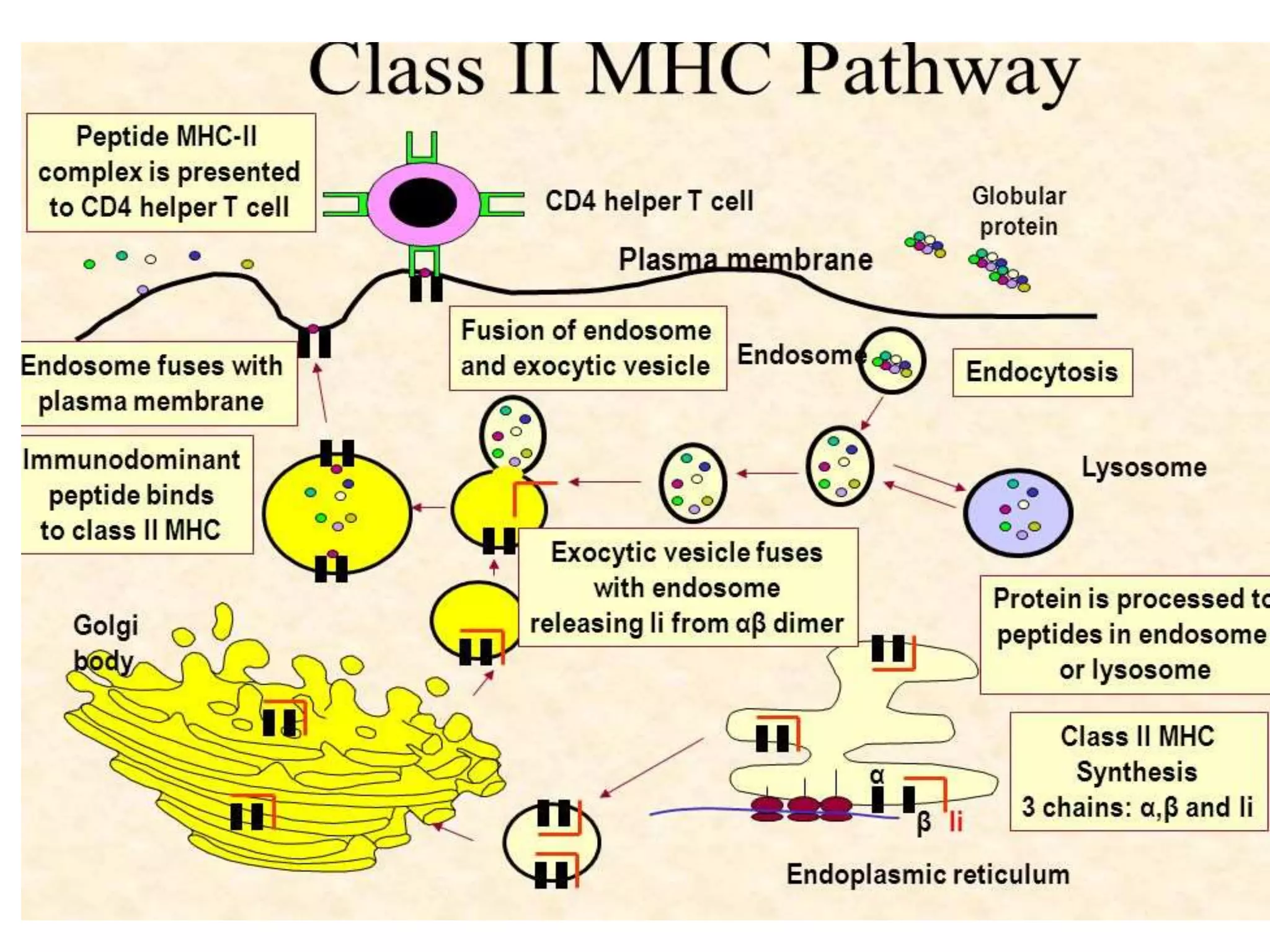
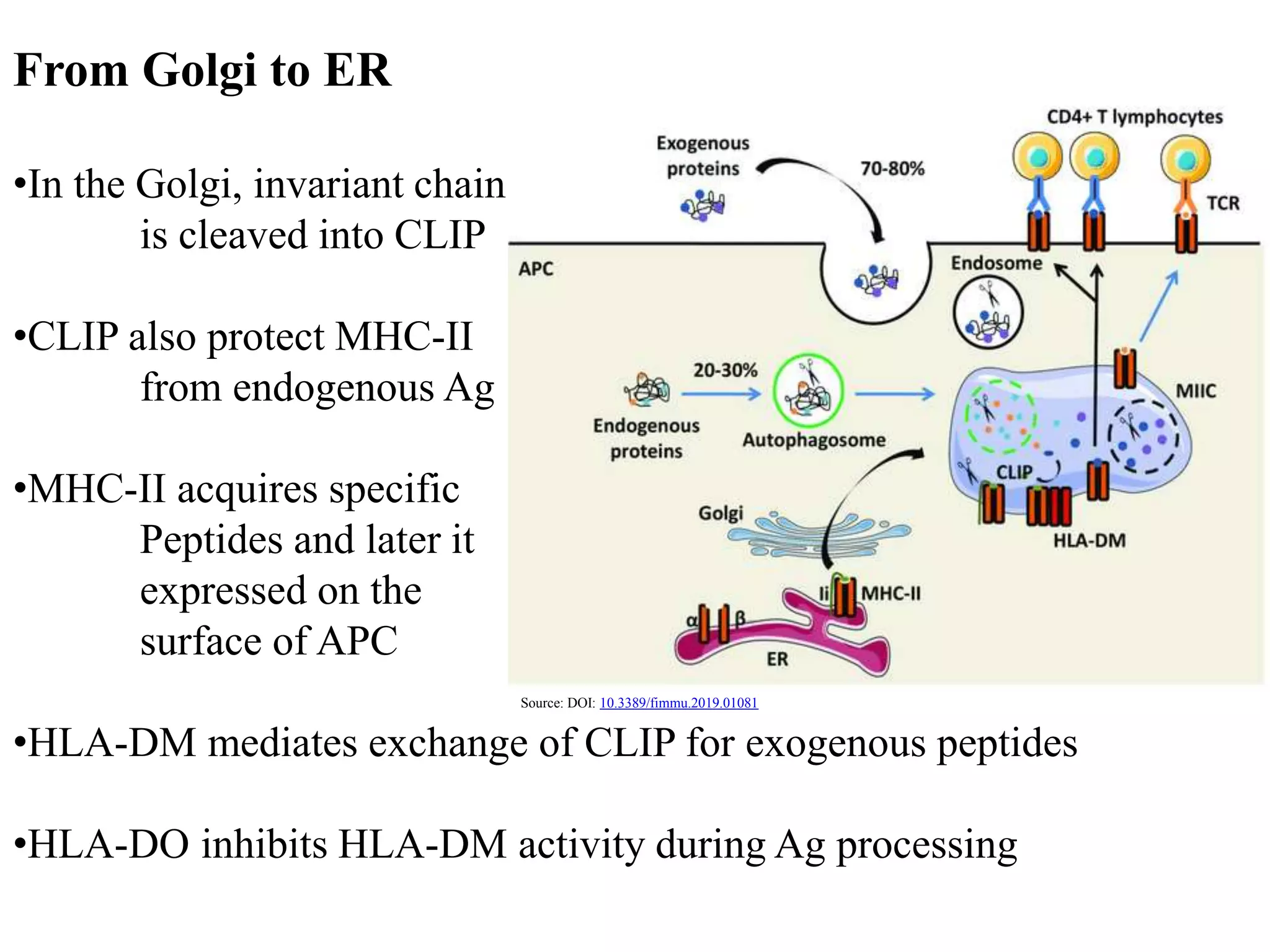
3. Antigens are processed through two pathways - the cytosolic pathway for endogenous antigens and the endocytic pathway for exogenous antigens - and bound to MHC molecules for presentation to T cells, which triggers an immune response against foreign or transplanted tissues that do not match the recipient's MHC.







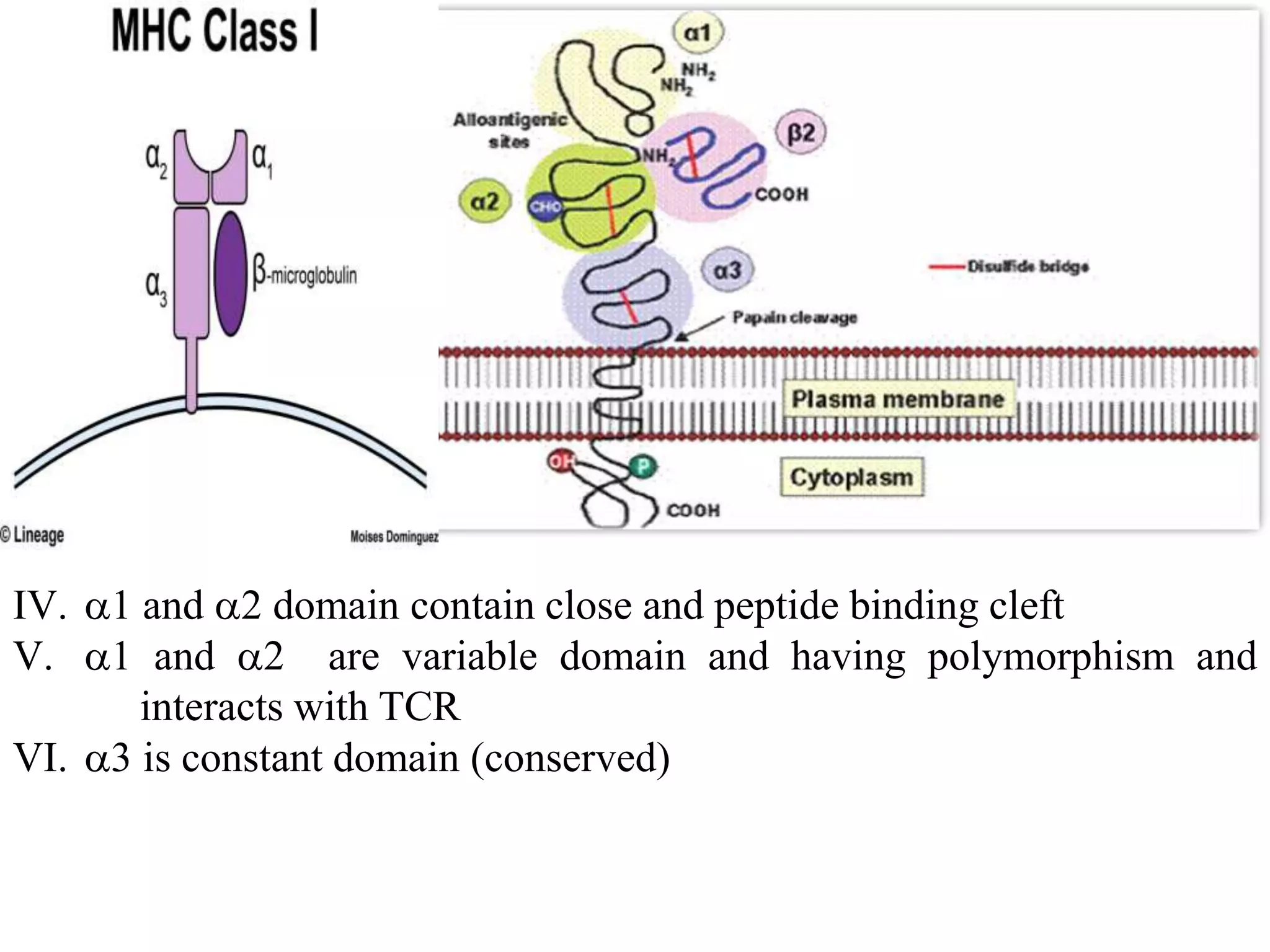

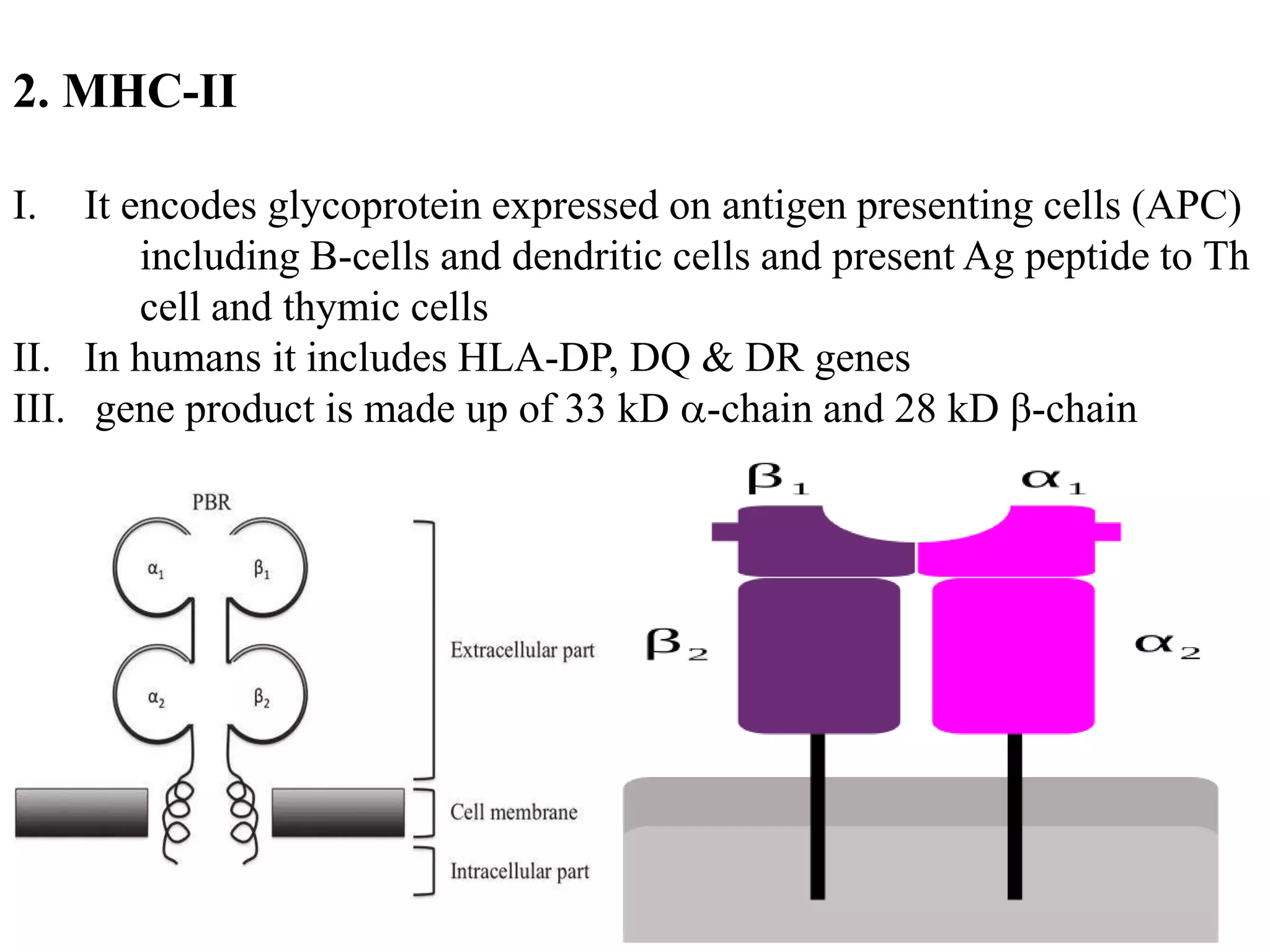
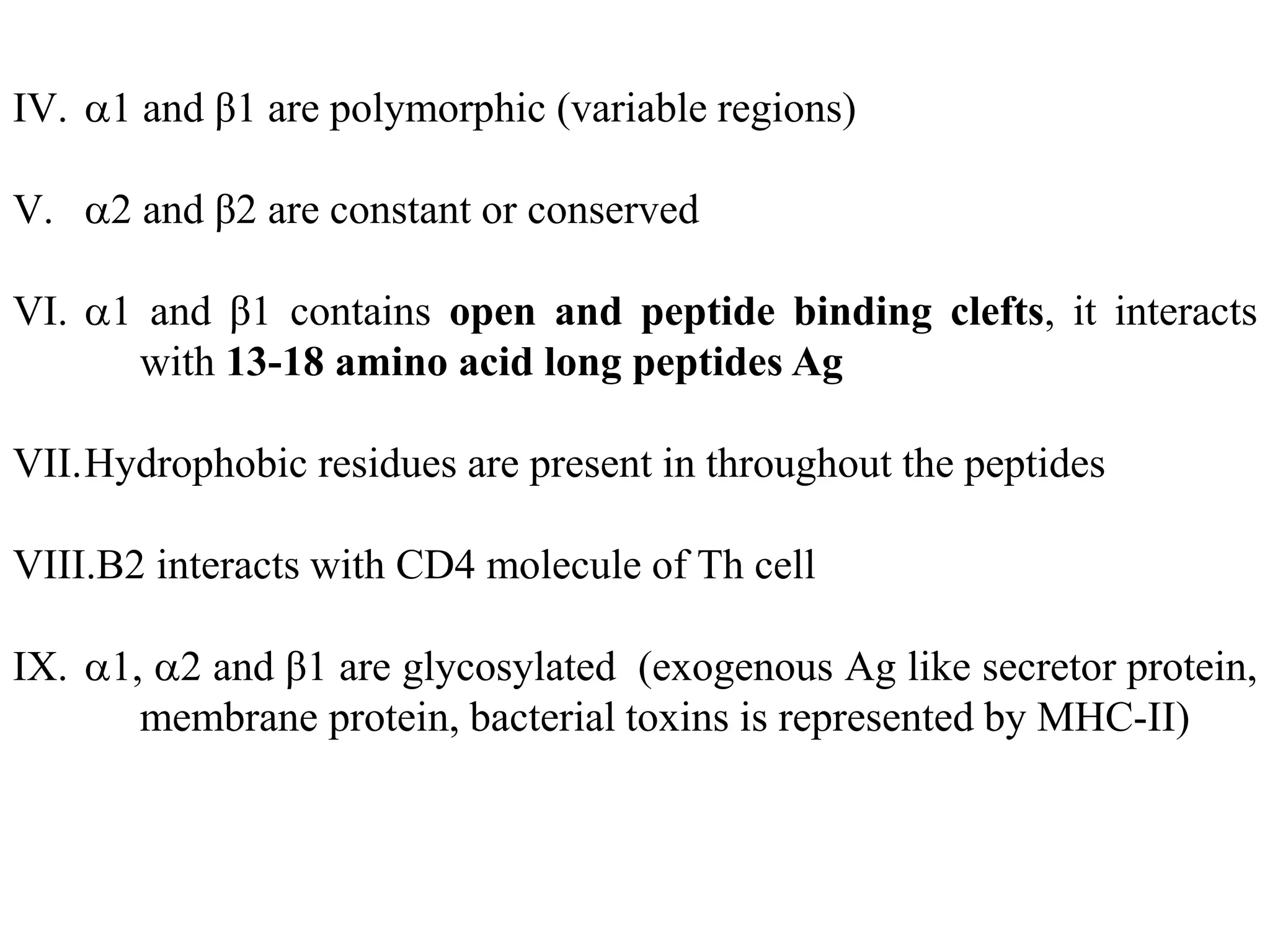

![[Bellanti, JA (Ed). Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease. I Care Press, Bethesda, MD, 2012]
Interaction of MHC with peptide Ag](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mhc-200410173038/75/MHC-STRUCTURE-AND-FUNCTION-14-2048.jpg)